Alcohol And Its Effects
By Tayla Hogno,
Cassandra Barracosa
& Grace Koster
Alcohol Introduction
Psychoactive:

alters brain function,
behaviour,
general mood,
and consciousness
Can also cause disease and injury
Males most at risk of alcohol-related fatalities
Morbidity and Prevelance
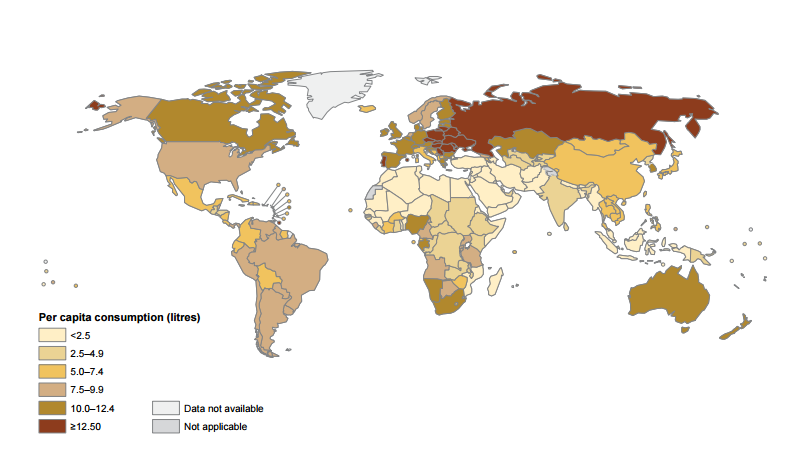
Text
Text
- High Consumption Levels (dark brown)= European and American Regions
- Intermediate Consumption Levels (Light browns)= Western Pacific and African Regions
- Low Consumption Levels (Lightest brown/white)= South East Asian and Eastern Mediterranean Regions
Mortality Rates
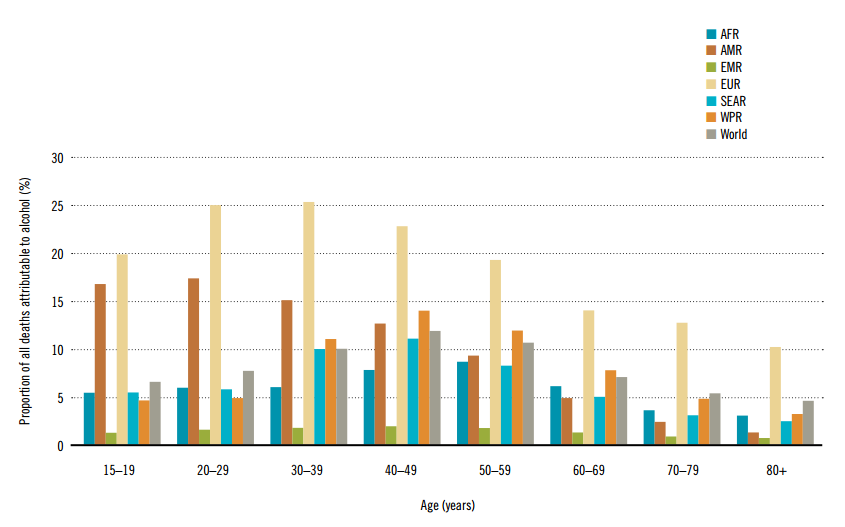
- 5.9% of global deaths are attributed to alcohol.
- Roughly ONE in every TWENTY deaths in the world.
- Highest percentage of deaths related to alcohol is within the 40-49 year old age group.
- European region has highest rate of death for ALL regions
Current Strategies for Health Promotion
- "Alcohol Beverages Advertising Code" (ABAC) scheme is used to prevent inappropriate advertising of alcoholic beverages.
- This is done by referring to the ABAC standards and if they are not met, the advertiser is asked to withdraw or modify the material.
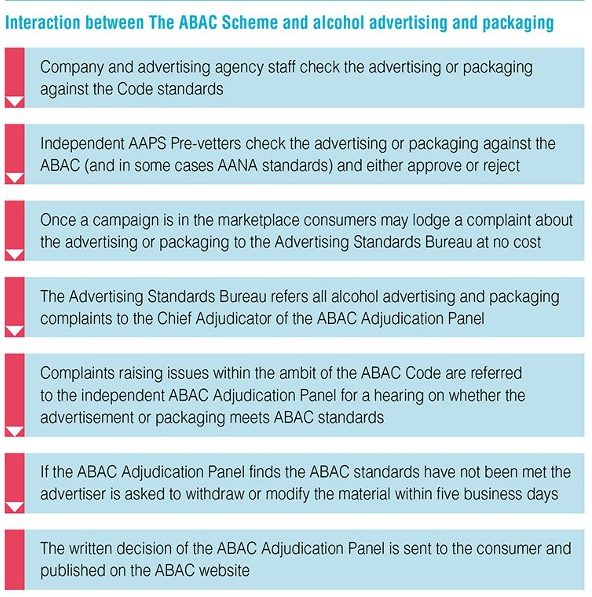
Current Strategies for Health Promotion
2. Drug and Alcohol Treatment Services
- Allocation of $200 MILLION by the government to drug and alcohol services, organisations, research and prevention activities.
- Including services such as alcohol rehabilitation and alcoholic support groups.


Current Strategies for Health Promotion
3. Danny Green's Coward Punch Campaign
- Campaign of increasing awareness of the dangers of drinking including violence and health risks.
- Government supported the campaign by funding $200,000
- Slogan "One punch can ruin lives"

Effectiveness of These Strategies
- Daily drinking declined significantly between 2010 and 2013 from 7.2% to 6.5% which was the lowest level seen since 1991.
- Fewer people aged 12-17 are drinking alcohol
- Proportion of people abstaining from alcohol increased significantly between 2010 and 2013 from 64% to 72%.
- This data suggests that the health promotion strategies put in place have significantly impacted the community in a positive way .
Alcohol Etiology
- Top 5 risk factors for disease, disability and death globally
Causes health problems such as:
- mental and behavioral disorders,
- alcohol dependence,
- liver cirrhosis, some cancers,
- cardiovascular diseases, and
- injuries resulting from violence and road clashes and accidents
- sexually transmitted disease prevalence is also increasing
Mechanisms of Harm
- Intoxication, leading to impairment of physical coordination, consciousness, cognition, perception, affects and personal behaviour.
- Toxic effects on organs and tissues.
- Dependance of an individual on alcohol.
Age Limits
- It is illegal within Australia for minor >18 to purchase or consume alcohol in any circumstances.
- Peer pressure is a major contributing factor to underage alcohol consumption.
- Underage drinking impacts individuals physically as well as mentally
- Alcohol is considered a drug; a depressant, and is often self-medicated as a coping mechanism.
- Excessive alcohol consumption has remained relatively low in public policy priorities.
- The World Health Organisation is attempting to increase the awareness of the risks associated alcohol consumption.
Conclusion
105 Alcohol Group Presentation
By Grace Koster
105 Alcohol Group Presentation
- 238



