Neural Computation Using Temporal Coding on Loihi


Gregor Lenz
Mobile Computing

- limited power capacity
- growing demands of functionality
- need for efficient computing
How does it scale?

- limited power capacity:
~5% battery improvement / year - need for efficient computing: more transistors / area
- growing demands of functionality: cloud computing
==> scales badly!
Can we learn from the brain?
- computes extremely efficiently (20 W)
- completely different mechanisms of computation
- copy it by recreating the basic components
Neural Computation on Neuromorphic Hardware
- General Purpose Computation using neurons only
- ANN-SNN conversion
Loihi
- research chip
- fully digital architecture
- 130k neurons across 128 cores & 130m synapses per chip

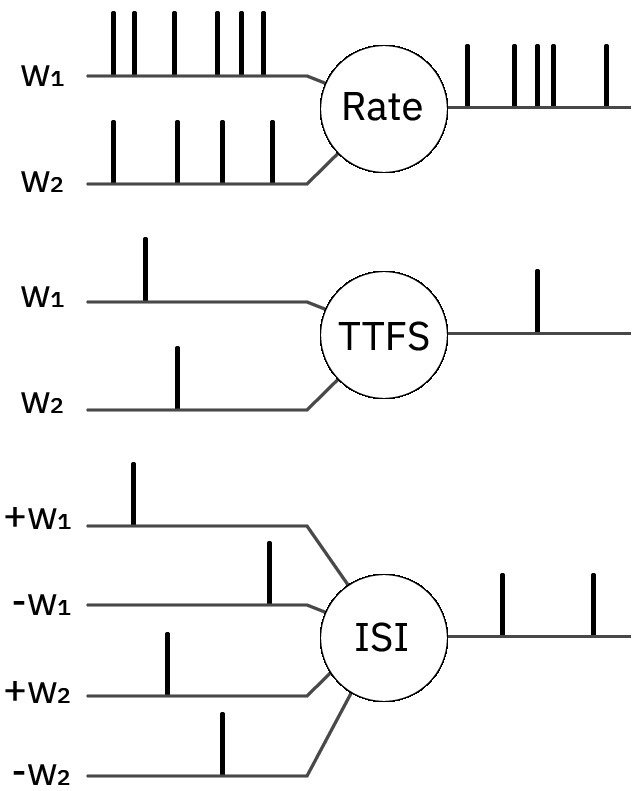
Neural Computation on Loihi
- Almost all spiking neural
networks use rate coding
- Temporal encoding exists:
Time To First Spike (TTFS)
but very inaccurate
- We use alternative
encoding scheme based
on inter spike intervals (ISI)
Spike Time Computation Kernel (STICK)
- Values are encoded in Inter Spike Intervals
- 4 different synapses provide 3 different current accumulation methods
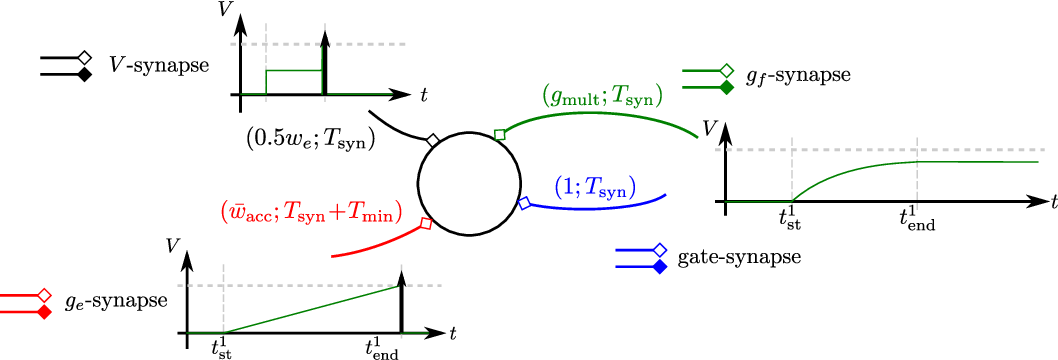
Lagorce & Benosman, 2015
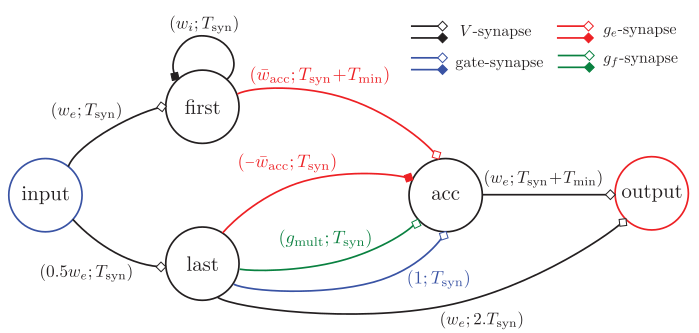
Spike Time Computation Kernel (STICK)
- Mathematical operations are cast into handcrafted spiking neural networks
- Networks for value storage, linear, nonlinear and differential computation
Lagorce & Benosman, 2015
Logarithm network
Spike Time Computation Kernel (STICK)
Lagorce & Benosman, 2015

General Purpose Computation on Loihi
- Composable networks compute arbitrary mathematical systems using artificial neurons more reliably than rate coded nets
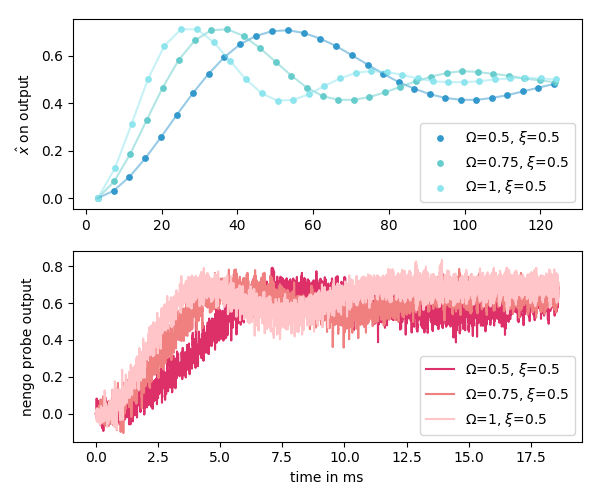

General Purpose Computation on Loihi
- Lower errors for same energy profile in comparison to rate coded network implemented using Nengo on Loihi
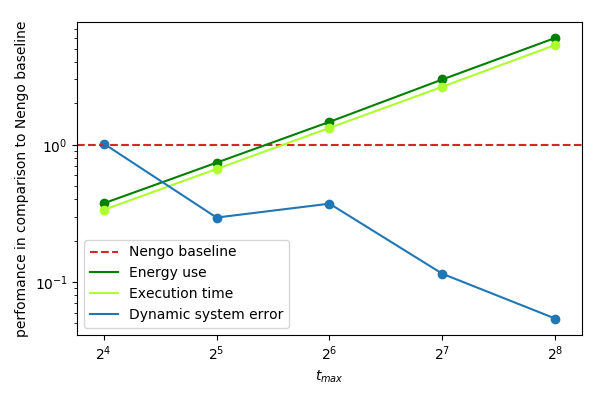
ANN - SNN conversion
- convert ANN units into SNN neurons


ANN - SNN conversion
- Conversion of networks trained on GPUs for efficient inference on Loihi


Conclusions
- New computing principles for low-power devices
- Precise Timing of spike necessary
- Neuromorphic computing can potentially extend the capabilities of current devices
interview
By Gregor Lenz
interview
- 294



