
What is a build system?
A build system is a collection of tasks (a.k.a. 'task runners') that automate repetitive work.
Why a task runner?
- Eliminates repetition of consistent tasks
- Eliminates complexity
- Improves quality
- Delivery of app faster
- Consistent and repeatable processes
Common Tasks
- Concatenation
- Minification
- Compiling pre-processed css
- Firing up a server for live reload
- Deployment builds
- Testing
- Code analysis
Common Build Systems



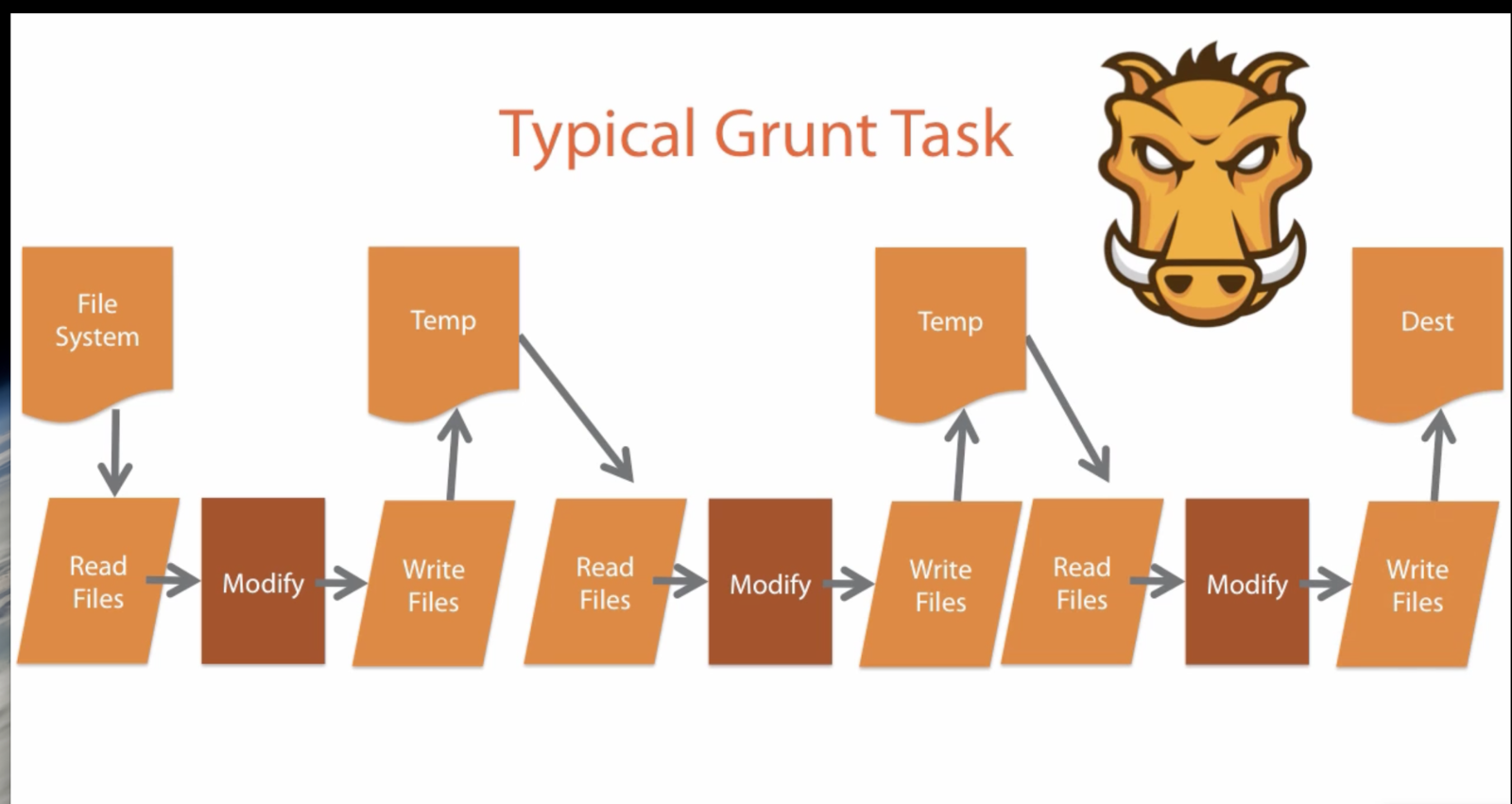
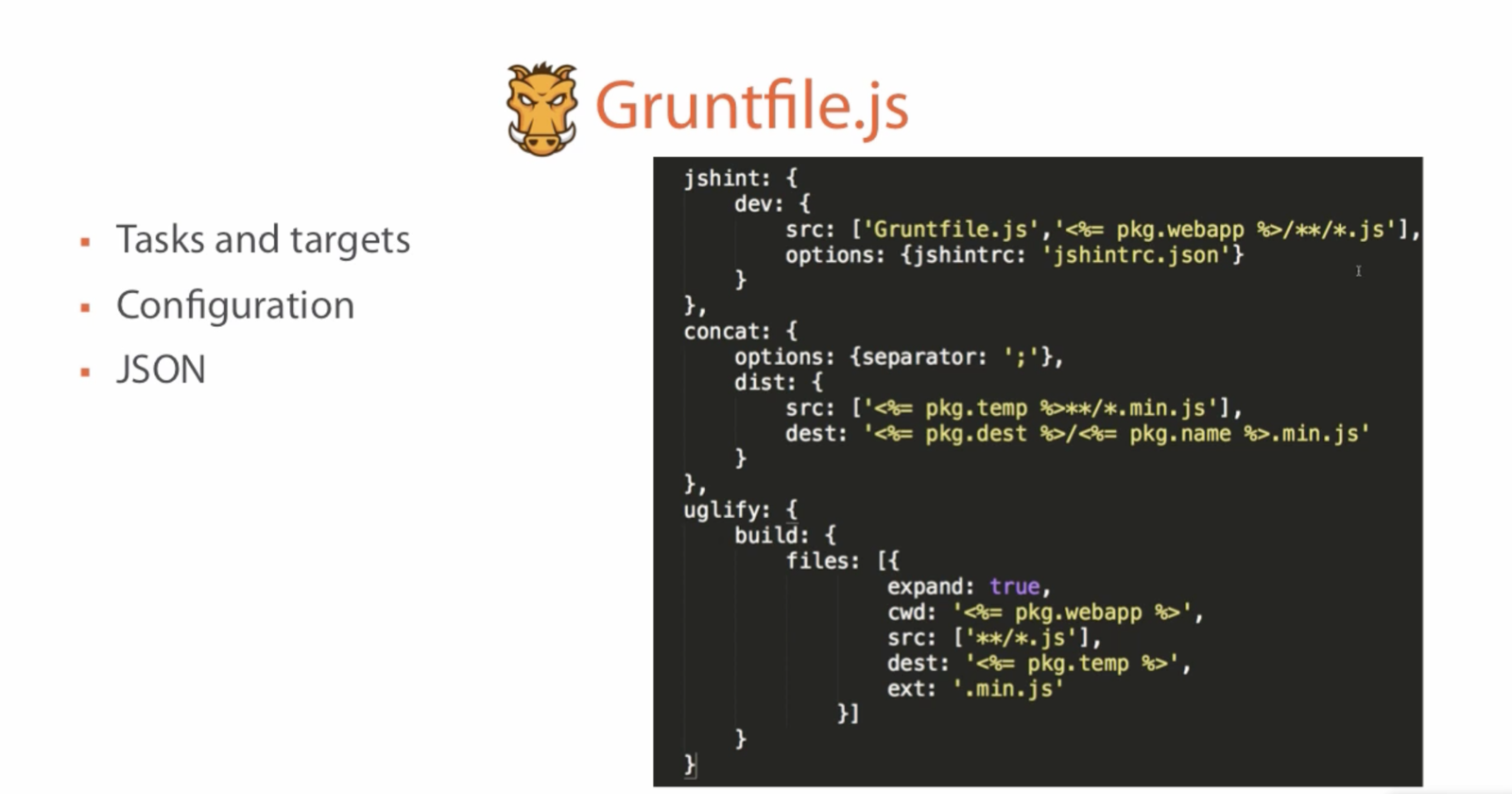
- Configuration over code - you have to write config files in json
- File based - Files are read and written continually
- 3900+ plugins


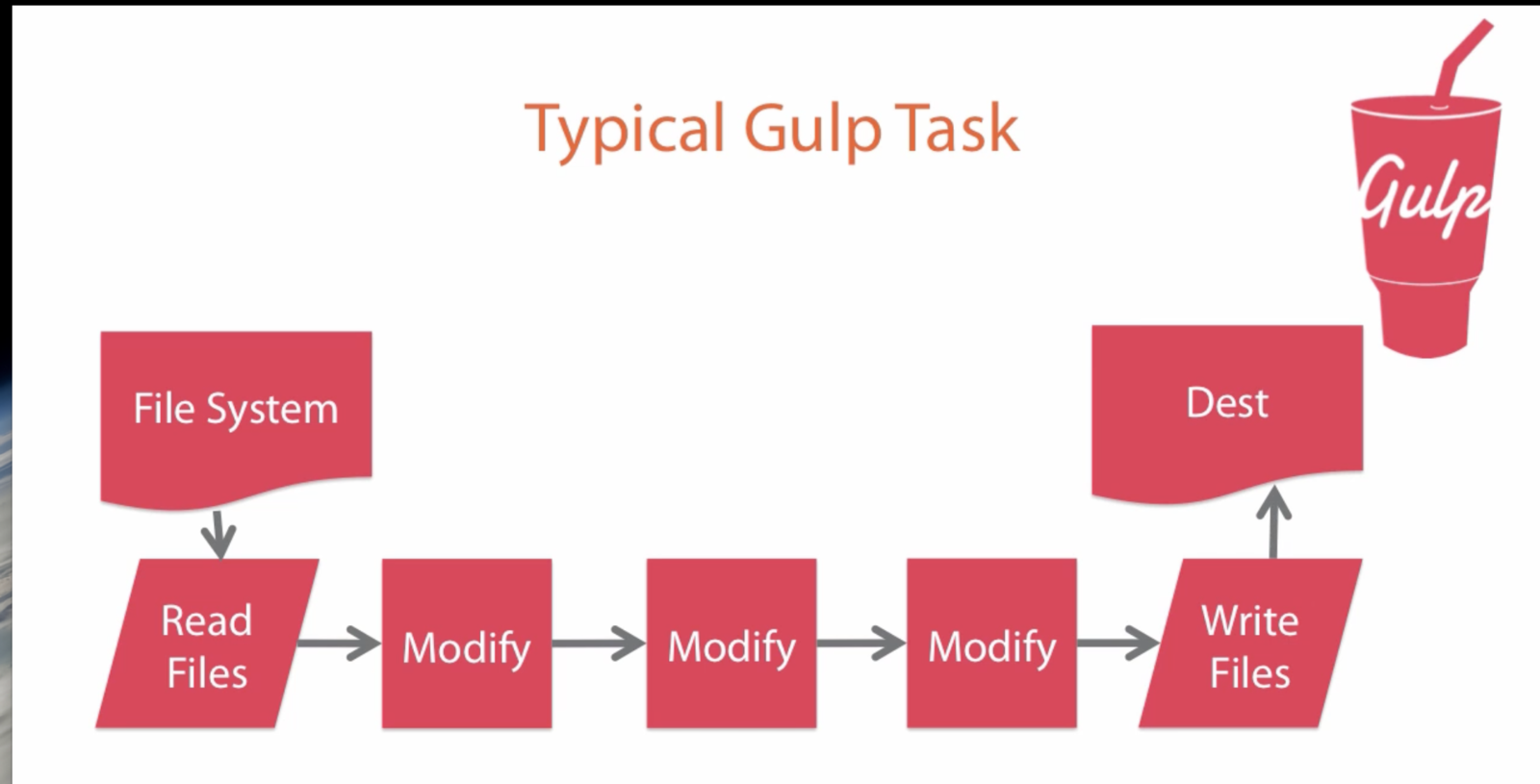
- Code over configuration - you write the tasks out in code
-
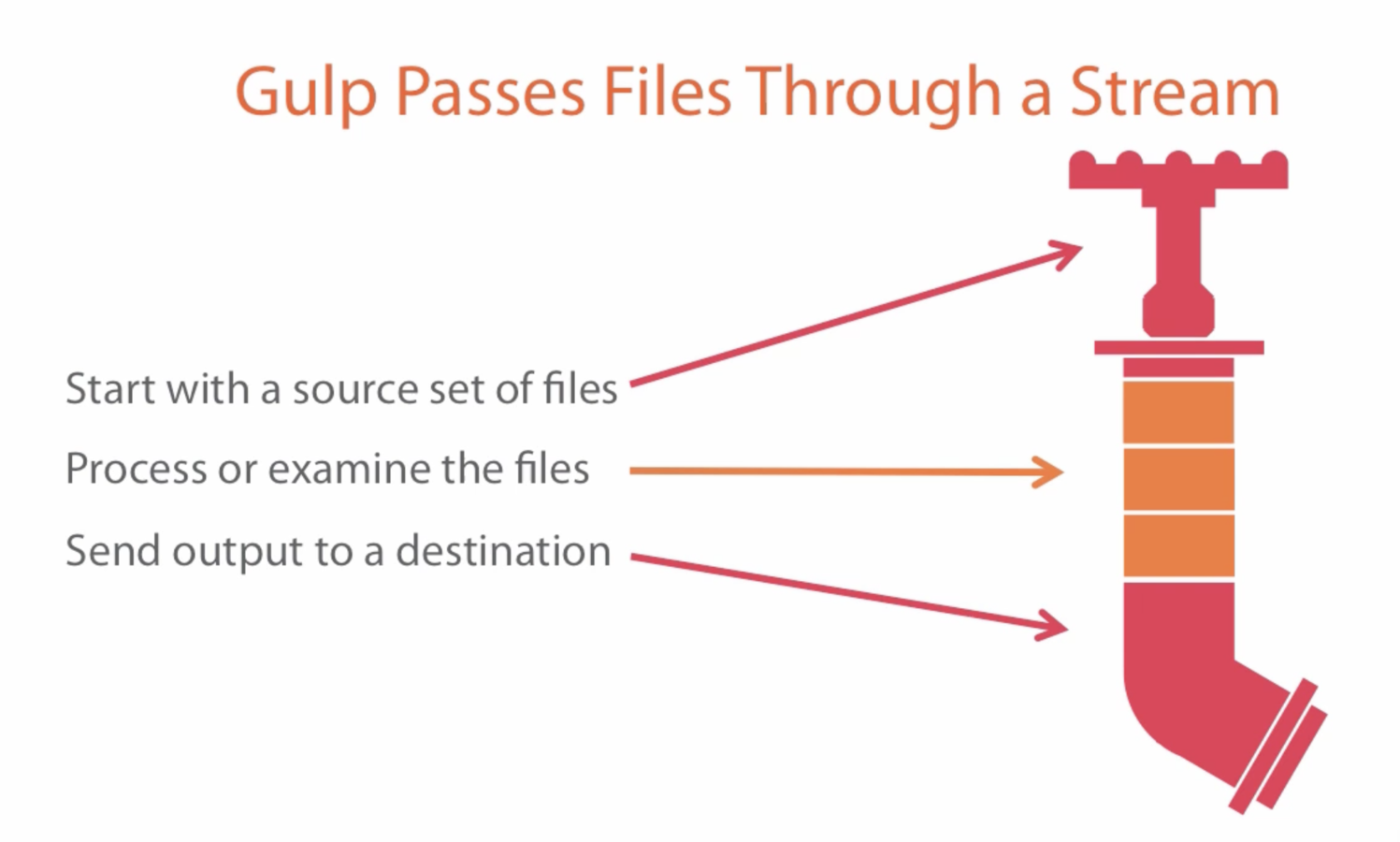
Stream based - files are read in, processed then written out - 1100+ plugins
- Uses node more readily
1

Advantages of gulp
- Easier learning curve
- More readable
- Easier to write
- Easier to debug
- Faster as it uses streams
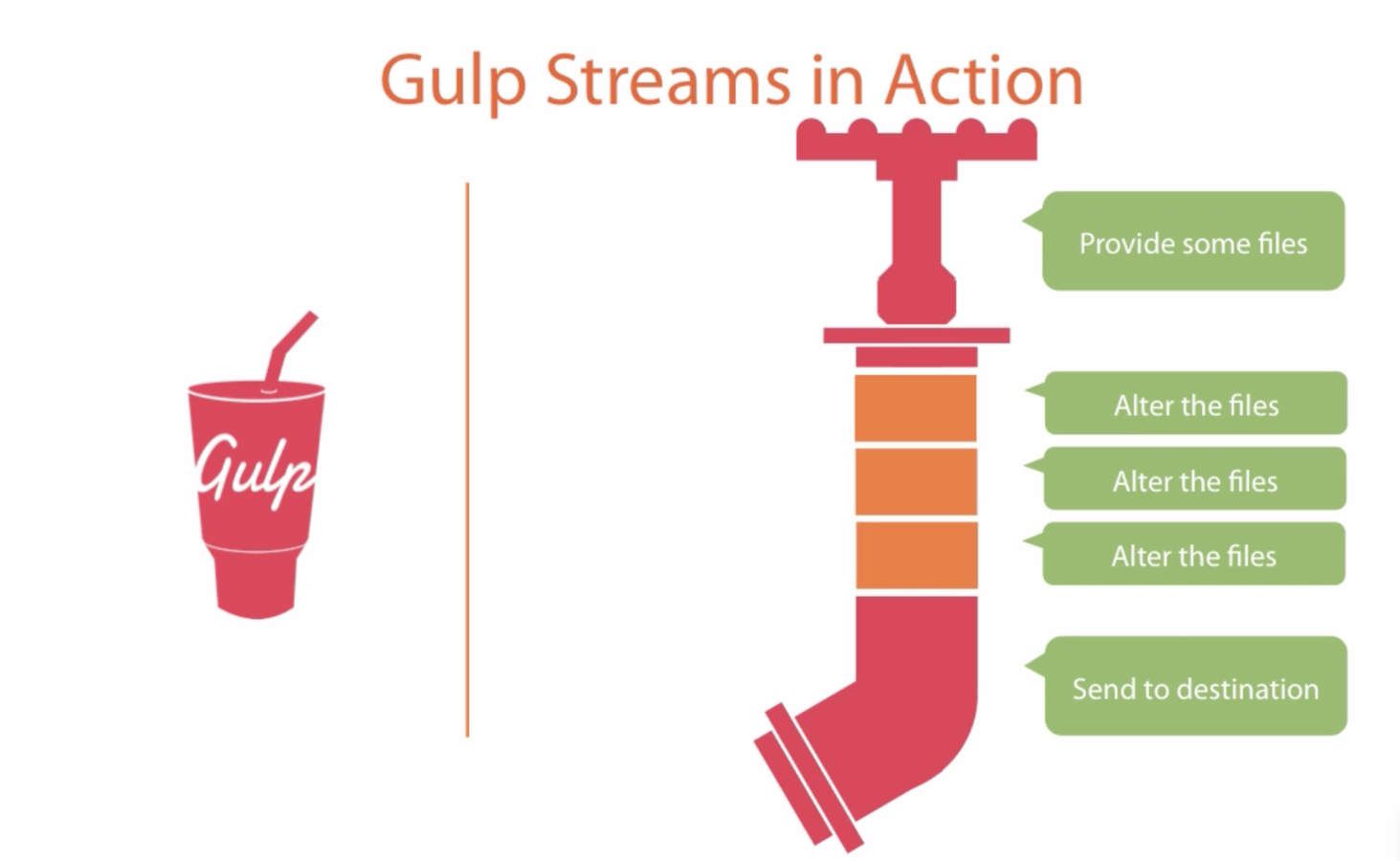
Gulp APIs
- Task - gulp.task
- Watch - gulp.watch
- Source - gulp.src
- Destination - gulp.dest
gulp.task
Function:
Defines a task, its dependencies and the code it is to execute.
Dependencies must run before the task.
Tasks all run asynchronously
Syntax:
Example:
gulp.task(name, [dependencies], fn)
gulp.task('js', function() {
return gulp.src(['js/*.js'])
.pipe(concat('all.js'))
.pipe(minify())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dist/'));
});gulp.src
Function:
Takes a file system glob and emits files that match it
Glob - file pattern match for the source files you want to enter into the stream
Syntax:
Example:
gulp.src(glob, [options])gulp.task('js', function() {
return gulp.src(['js/*.js'], {base: 'js/'})
.pipe(concat('all.js'))
.pipe(minify())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dist/'));
});gulp.dest
Function:
- Piped files are written into the system
- optionally specified options to apply to the output folder
Syntax:
Example:
gulp.dest(folder, [options])gulp.task('js', function() {
return gulp.src(['js/*.js'], {base: 'js/'})
.pipe(concat('all.js'))
.pipe(minify())
.pipe(gulp.dest('dist/'));
});gulp.watch
Function:
This function watches the files that match the glob pattern for changes and executes the task or callback specified as the last argument.
Syntax:
Example:
gulp.watch(glob, [options], [tasks] or callbacks)gulp.task('watch', function() {
gulp.watch(paths.scripts, ['lint']);
});Gulp Build System
By Hannah Koske
Gulp Build System
A brief explanation of the gulp build system.
- 182
