Building Modern Enterprise Searching Platform: Introduction & Concept
Han Yi
2018.06.07
Three major Enterprise data oriented systems
- OLTP system, mostly based on relational database: Oracle, MySQL, etc
- Core search engine, commonly Elasticsearch/Solr
- OLAP system, like hadoop ecosystem
General vs Enterprise purpose search engine
- Data source types: Web, image, document, multimedia, database, log, data from other commercial systems
- Data retrieval: Public / Internal
- Data update frequency: Near real time
- Data integrity: No / High
- Sort: Relevancy, time, business attributes
- Allow SEO: Yes / No
- Result control: Full automatic / Strong customized
- Index structure: Web / Variable due to business requirement
Methodology to design & build modern eCommerce search engine
Business driven
- Need to deeply understand Business Vision, Domain Knowledge, and Technology of Information Retrieval
Continuous feedback
- Have more understanding on source data, and user intention of search
- Keep on collecting feedback from user and react fast
Challenges
- Relational database data model
- Index model needs to be flexible to satisfy query requirement
- Advanced search
- API integration
- Performance
- Endless expectation on conversion rate
Information Retrieval Basics
- Target data types
- Structured data
- Unstructured data
- Semistructured data
Information Retrieval Basics
- Basic query types: Boolean Query
- Linear searching: grep (Global Regular Expression Print)
- Non-linear searching: Incidence Matrix

Information Retrieval Basics
- Advanced query: Ad hoc Query
- One time query to for user information need
- Information need != query

Information Retrieval Basics
- Effectiveness Assessment
- Precision
- Recall

Information Retrieval Basics
- Inverted Index
- Dictionary
- Posting list (Inverted List)

Information Retrieval Basics
- Building Inverted Index
- Index data structure
- Dictionary data structure
- Indexing algorithm
- Distributed indexing
- Dynamic indexing
- Index Compression
Information Retrieval Basics
- Tolerant Retrieval
- Wildcard query
- Spelling correction
- Phonetic correction
Information Retrieval Basics
- Relevancy & Score
- Term Weighting
- Vector Space Model
Information Retrieval Basics
- Evaluation
- measurement
- test collections
- unranked result
- ranked result
- user utility
Information Retrieval Basics: Building Index
- Steps to create Inverted Index
- Raw document analysis
- Tokenization (based on language, also can be used for language identification)
- Linguistic preprocessing
- Physical index building
Information Retrieval Basics: Raw Doc Analysis
- Raw document analysis
- Raw document collection
- Char sequence generation
- Indexing granularity
- Precision vs Recall
- Business specific requirement
Information Retrieval Basics: Token Analysis
-
Tokenization
- Token
- Type
- Term
- Stop word deletion
- Stop word list extraction from collection frequency
- Token normalization
- Equivalence, case-folding, language specific
- Stemming & lemmatization (resolve flection)
- Stem vs Root
- Pragmatic analysis (语用分析)
Information Retrieval Basics: Index Data Structure
-
Example 1: Skip list pointer — Fast post list intersection (Boolean Query)
- step list sqrt(P), P is length of post list

-
Example 2: Positional index — Fast phrase search
- Commonly less than 4 words
angels: 2: {36,174,252,651}; 4: {12,22,102,432}; 7: {17};
fools: 2: {1,17,74,222}; 4: {8,78,108,458}; 7: {3,13,23,193};
fear: 2: {87,704,722,901}; 4: {13,43,113,433}; 7: {18,328,528};
in: 2: {3,37,76,444,851}; 4: {10,20,110,470,500}; 7: {5,15,25,195};
rush: 2: {2,66,194,321,702}; 4: {9,69,149,429,569}; 7: {4,14,404};
to: 2: {47,86,234,999}; 4: {14,24,774,944}; 7: {199,319,599,709};
tread: 2: {57,94,333}; 4: {15,35,155}; 7: {20,320};
where: 2: {67,124,393,1001}; 4: {11,41,101,421,431}; 7: {16,36,736};Information Retrieval Basics: Index Data Structure
-
Blocked sort-based Indexing
- First pass to create termID-docID pairs
- Second pass to sort pairs based on termID and docID
- Final pass to organize docIDs for each term into a posting list
Information Retrieval Basics: Index Construction
-
Single-pass in-memory Indexing
- Adds posting directly to its postings list. Instead of first collecting all termID-docID pairs and then sorting them
- Run faster because there is no sorting required, and it saves memory because we keep track of the term a postings list belongs to, so the termIDs of postings need not be stored
Information Retrieval Basics: Index Construction
-
Distributed Indexing
- Term-partitioned index
- Document-partitioned index

Information Retrieval Basics: Index Construction
Information Retrieval Basics: Tolerant Retrieval
- Wildcard query
- Example: hel*, *llo, he*o
- N-gram index
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "ngram",
"text": "Quick Fox"
}
[ Q, Qu, u, ui, i, ic, c, ck, k, "k ", " ", " F", F, Fo, o, ox, x ]Information Retrieval Basics: Tolerant Retrieval
- Spelling correction
- Isolated term: hallo wolrd
- Edit (Levenshtein) distance
- N-gram overlap
- Isolated term: hallo wolrd
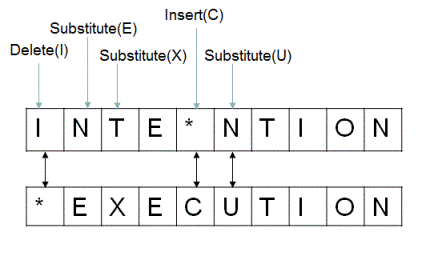

Information Retrieval Basics: Tolerant Retrieval
- Spelling correction
- Context sensitive: flew form Heathrow
- Check searching based on top ranked terms
- Context sensitive: flew form Heathrow
Information Retrieval Basics: Tolerant Retrieval
- Phonetic correction
- Syllable Analysis (commonly 4 at most)
- Soundex

Information Retrieval Basics: Classic Ranking
- Parametric Index
- a document may contain multiple "fields"
- a "Zone" means text type field
- Build inverted index for each zone
-
Ranked boolean retrieval
- Example: Bool query scoring by weighted zone matching

- Term frequency and weighting
- tf: term frequency in specific zone
- cf: term frequency in documents of whole index
- df: document frequency that contains specific term of whole index
- idf: inverse document frequency
- weighting of specific term: tf-idf = tf x idf
Information Retrieval Basics: Classic Ranking


- Vector space model
Information Retrieval Basics: Classic Ranking


- Document/Search Similarity
Information Retrieval Basics: Classic Ranking


vs
- Example: search "car insurance" (tf as weighting)
[0.707, 0, 0.707, 0]
Information Retrieval Basics: Evaluation
- Evaluation
- test collection
- commonly 50 documents at least
- test cases
- in queries
- relevancy standards
- user feedback
- test collection
Information Retrieval Basics: Evaluation
- Open source data collection
Information Retrieval Basics: Evaluation
- Evaluation on unranked searching results
- Precision vs Recall
-
Evaluation on ranked searching results
- Precision vs Recall for top K items
Information Retrieval Basics: Evaluation
- System measurement
- index time
- index size
- query time
- friendliness of API
- User utility
- for design: study on user satisfaction
- for improvement: clickstream mining, A/B testing
Thanks

Building Modern Enterprise Searching Platform: Introduction & Concept
By hanyi8000
Building Modern Enterprise Searching Platform: Introduction & Concept
- 2,149



