COMP2521
Data Structures & Algorithms
Week 4.2
AVL Trees
Author: Hayden Smith 2021
In this lecture
Why?
- Rebalancing methods often have an O(n) worse case, and we want to find something with O(log(n)) worst case.
What?
- AVL Tree Overview
- Examples
- Pseudocode
AVL Tree
AVL trees fix imbalances as soon as they occur. It aims to have the tree reasonably maintain balance with an O(log(n)) cost.
General Method:
- Store information on each node (amortisation) about it's height/balance
- Do repairs on tree balance locally, not on overall structure
Invented by Georgy Adelson-Velsky and Evgenii Landis (1962)
AVL Tree Method
A tree is unbalanced (height) when:
This tree can be repaired by rotation:
- If left subtree is too deep, rotate right
- If right subtree is too deep, rotate left
This process would normally be O(n) as you have to traverse all nodes to figure out the height of any particular sub-tree.
However, we will store the balance data on each node (height or balance) which will make things faster, but also mean more to maintain.
AVL Tree Structure(practical)
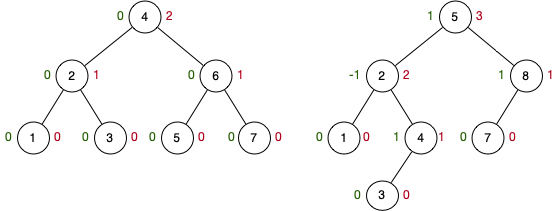
Red numbers are height. Typically stored on node.
Green numbers are balance. Stored or calculated based on immediate children.
Rule: Rotate whenever tree |balance| > 1
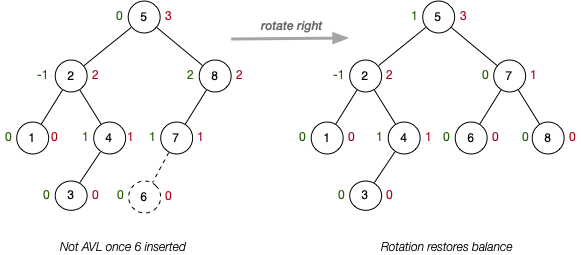
AVL Tree Structure(practical)
Insertion of 6 will trigger a rotate right on 8.
AVL Insertion Algorithm
Pseudocode
Pseudocode
insertAVL(tree, item):
if tree is empty:
return new node containing item
else if item = data(tree):
return tree
if item < data(tree):
left(tree) = insertAVL(left(tree),item)
else if item > data(tree):
right(tree) = insertAVL(right(tree),item)
LHeight = height(left(tree))
RHeight = height(right(tree))
if (LHeight - RHeight) > 1:
if item > data(left(tree)):
left(tree) = rotateLeft(left(tree))
tree = rotateRight(tree)
else if (RHeight - LHeight) > 1:
if item < data(right(tree)) then
right(tree) = rotateRight(right(tree))
tree=rotateLeft(tree)
return tree
AVL Tree Performance
- Average/worst-case search performance of O(log(n))
- Finite time spent on maintaining height data in each node
- Finite time spent rebalancing locally when there is imbalance
- Trees are always height-balanced. Subtree depths differ by +/- 1
- May not be weight-balanced, as subtrees may differ in size (even if height only varies by 1)
Feedback

Feedback

COMP2521 21T2 - 4.2 - AVL Trees
By haydensmith
COMP2521 21T2 - 4.2 - AVL Trees
- 1,923



