COMP2521
Data Structures & Algorithms
Week 9.1
Heaps & Priority Queues
Author: Hayden Smith 2021
In this lecture
Why?
- Heap structures are tree-like structures used for things like priority queues - which are really common
What?
- Heaps
- Heap insert and delete
- Priority Queues
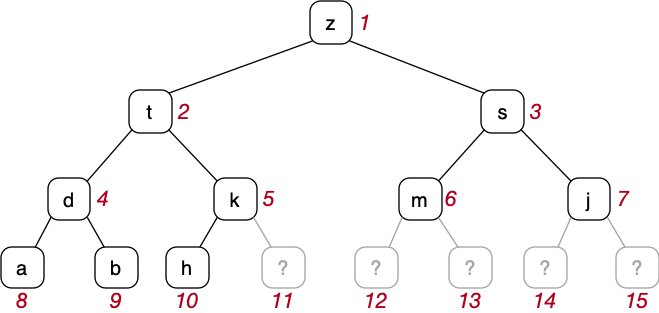
Heaps
Heaps can be conceptualised as dense tree structures where:
- Tree maintains a general order with higher elements up the top
- New items are added in level order to the next available position on the bottom row. After added, they then "drift up" to appropriate level in tree
- items are always deleted by removing root (top priority)
- Since heaps are dense trees, depth = floor(log2N)+1
Heaps
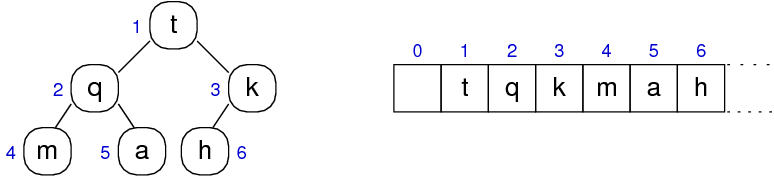
BSTs are typically implemented as linked data structures.
Heaps are often implemented via arrays (assumes we know max size)
Simple index calculations allow navigation through the tree:
- left child of Item at index i is located at 2i
- right child of Item at index i is located at 2i+1
- parent of Item at index i is located at i/2
Heap Structure
typedef struct HeapRep {
Item *items; // array of Items
int nitems; // #items in array
int nslots; // #elements in array
} HeapRep;
typedef HeapRep *Heap;
Heap newHeap(int N)
{
Heap new = malloc(sizeof(HeapRep));
Item *a = malloc((N+1)*sizeof(Item));
assert(new != NULL && a != NULL);
new->items = a; // no initialisation needed
new->nitems = 0; // counter and index
new->nslots = N; // index range 1..N
return new;
}
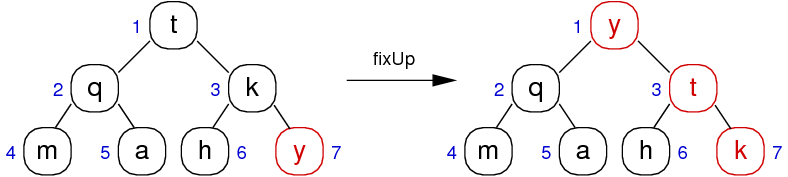
Heap Inserting
Insertion is a two-step process
- Add new element at next available position on bottom row
(but this might violate heap property; new value larger than parent) - Reorganise vales along path to root to restore heap property
Heap Inserting
void HeapInsert(Heap h, Item it) {
// is there space in the array?
assert(h->nitems < h->nslots);
h->nitems++;
// add new item at end of array
h->items[h->nitems] = it;
// move new item to its correct place
fixUp(h->items, h->nitems);
}
// force value at a[i] into correct position
void fixUp(Item a[], int i) {
while (i > 1 && less(a[i/2], a[i])) {
swap(a, i, i/2);
i = i / 2; // integer division
}
}
void swap(Item a[], int i, int j) {
Item tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}Heap Inserting
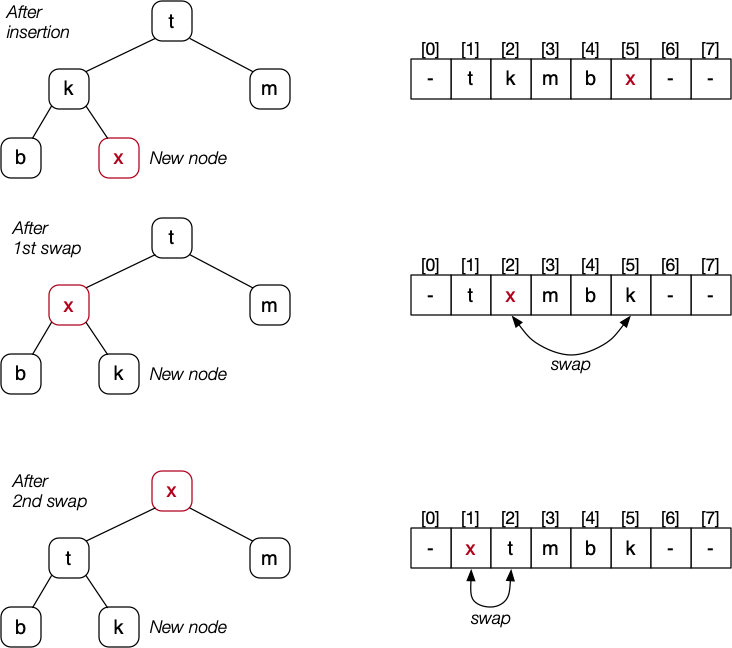
Heap Deletion
Deletion is a three-step process:
- Replace root (always root) value by bottom-most, rightmost value
- Remove bottom-most, rightmost value
- Reorganise values along path from root to restore heap
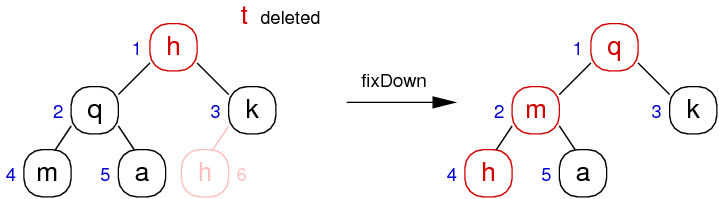
Heap Deletion
Item HeapDelete(Heap h) {
Item top = h->items[1];
// overwrite first by last
h->items[1] = h->items[h->nitems];
h->nitems--;
// move new root to correct position
fixDown(h->items, 1, h->nitems);
return top;
}
// force value at a[i] into correct position
// note that N gives max index *and* # items
void fixDown(Item a[], int i, int N) {
while (2 * i <= N) {
// compute address of left child
int j = 2 * i;
// choose larger of two children
if (j < N && less(a[j], a[j+1])) j++;
if (!less(a[i], a[j])) break;
swap(a, i, j);
// move one level down the heap
i = j;
}
}
Heap Complexity
- For insertion:
- Add new item at end of array ⇒ O(1)
- Move item up into correct position ⇒ O(log2n)
- Summary: O(log(n))
- For deletion:
- Replace root by item at end of array ⇒ O(1)
- Move new root down into correct position ⇒ O(log2n)
- Summary: O(log(n))
Priority Queue
Heap behaviour is exactly behaviour required for Priority Queue :
- join(PQ,it): ensure highest priority item at front of queue
- it = leave(PQ): take highest priority item from queue
typedef Heap PQueue;
void join(PQueue pq, Item it) { HeapInsert(pq,it); }
Item leave(PQueue pq) { return HeapDelete(pq); }Priority Queue
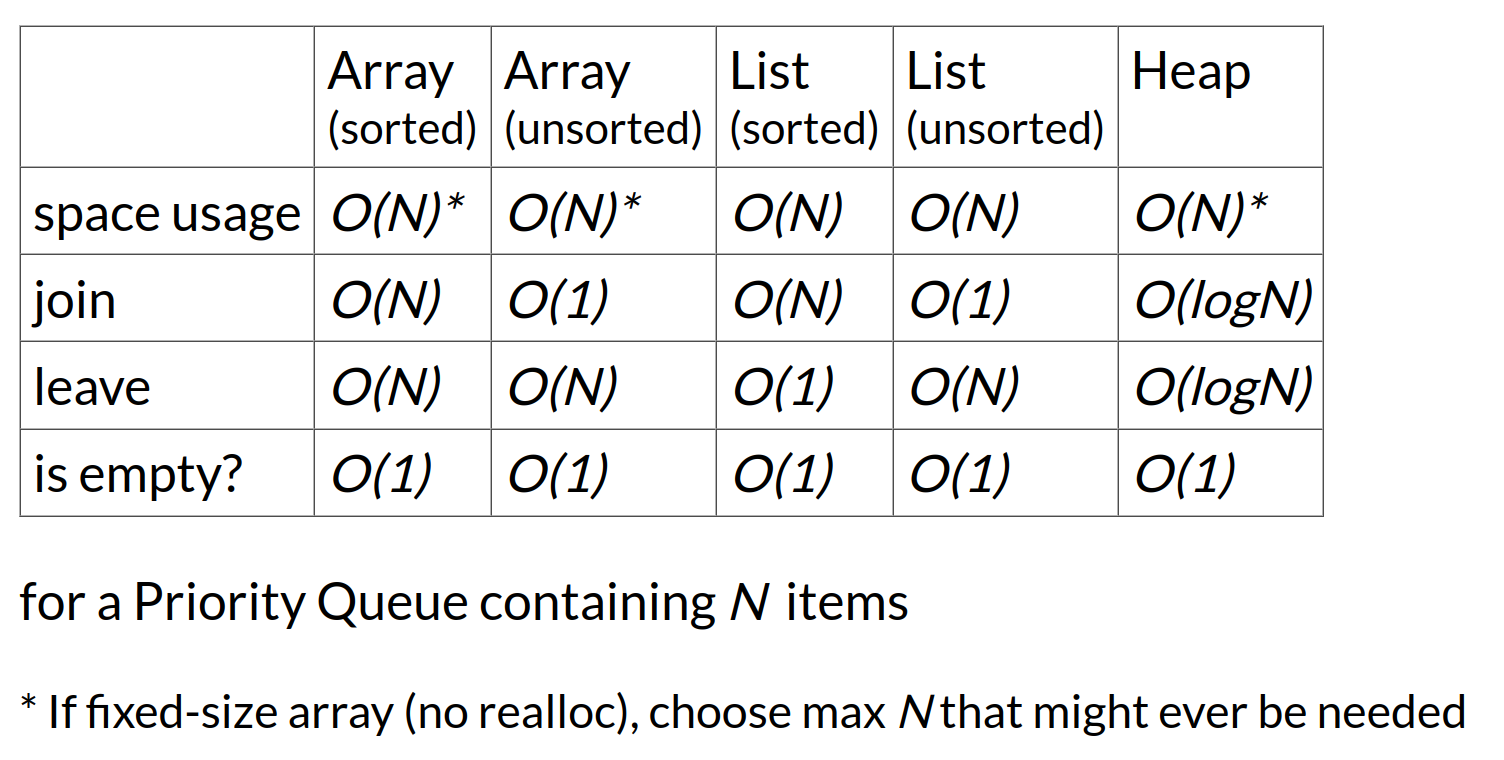
Implementation Comparison
Heap Sort
We can use a heap for sorting very easily:
-
Step 1: build a heap in the array
- iterates N times, each time doing fixUp()
- each fixUp() is O(logN), so overall O(NlogN)
-
Step 2: use heap to build sorted array
- iterates N times, each time doing swap() and fixDown()
- swap() is O(1), fixDown() is O(logN), so overall O(NlogN)
Cost of heapsort = O(NlogN)
Feedback

COMP2521 21T2 - 9.1 - Heaps & Priority Queues
By haydensmith
COMP2521 21T2 - 9.1 - Heaps & Priority Queues
- 1,235



