SCRUM

scrum
By:
Ian Munene
Cornellius Ngondo
what is scrum?

scrum
scrum is a framework for developing and sustaining complex projects.

scrum
interesting fact: all sizes and complexity
Text
product may refer to a product, service or any other deliverable

scrum
Text
principles
processes
aspects
SCRUM FRAMEWORK

scrum
Text
what impacts projects?

scrum
Text
what impacts projects?
- time

scrum
Text
what impacts projects?
- time among others such as -
- cost
- scope
- quality
- resources
- organizational capabilities
- other limitations

scrum
Text
what impacts projects
successful implementation and good results has numerous and significant business benefits to an organization
to achieve this, choose and use an appropriate project management framework

scrum
Text
and thus scrum :-)

scrum
Text
so what is scrum?
- popular agile methodology
- adaptive, iterative, fast, flexible and effective
- ensures transparency in communication
- creates collective accountability and progress
- framework supports all sorts of projects

scrum
Text
why is scrum better than other project management techniques?

scrum
Text
scrumteams are?
| Cross-Functional | Self-Organized |
|---|---|
| Empowered | use sprints |

scrum
Text
created
stakeholder meeting

scrum
Text
history of scrum
- developed in the 1980s - Hirotaka takeuchi and ikujiro Nonaka
- defined a flexible and all inclusive approach to product dev strategy
- described an innovative and holistic approach to product dev: a holistic/rugby approach
- from case studies in the industry then

scrum
Text
history of scrum
- product dev should not be a sequential relay race
- rather it should be analogous to the rugby game

scrum
Text
history of scrum


scrum
Text
history of scrum
features of scrum analogous to rugby are:
- to score, the team moves together
- to restart the game (after a try) the team huddles up again

scrum
Text
history of scrum
- later Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber elaborated on the scrum concept and its applicability to software dev in 1995, Austin Texas (OOP conf)
- since then, constantly changing, being modified and refined by experts in various fields

scrum
Text
<why use scrum>

scrum
Text
Key


scrum
Text
highly adaptable
- iterative delivery and incorporating change on the stride

scrum
Text
customer centric
- customers have a say in literally every step/phase of the project

scrum
Text
continuous delivery of value
- iterative dev ensures quick shipping of deliverables as quickly as customer expects

scrum
Text
early delivery of value
- prioritized backlog ensures that the most urgent of customer req are met first

scrum
Text
continous feedback
- continous feedback is provided through daily standups

scrum
Text
transparency
- all resources such as sprint burndown chart and backlog board/scrum board are made public/shared with everyone
- leads to an open working environment

scrum
Text
transparency
- sprint review meetings demonstrate potentially shippable features/products keeping them fully involved and aware of project status

scrum
Text
continous improvement
- deliverables are always being improved from sprint to sprint

scrum
Text


scrum
Text
sustainable pace
- people involved can work at a sustainable pace which in theory they can continue indefinitely

scrum
Text
effecient development process
- through minimizing non essential work and time boxing

scrum
Text
motivation
- through daily standups
faster prob resolution
- crossfunctional teams and daily standups ensure that problems can be identified and solved ASAP

scrum
Text
collective project ownership
- personalizes the project creating a feeling of need to push it to completion

scrum
Text
how fast and scalable is scrum?

scrum
Text
- to be effective, scrum teams should ideally have a total of six to ten members
- common misconception that its used for small projects only
- multiple scrum teams can be formed when members exceed ten e.g 2007 - 2009 (yahoo)

scrum
Text
who coordinates multiple scrum teams?
convene scrum of scrums process which:
- facilitates coordination among the teams
- enables effective implementation in larger/complex projects
- manages projects of different sizes spanning even different geographical locations

scrum
Text
what is a scrum of scrums
- meeting where all the scrums are rep
- reps provide details as to progress
- challenges encountered are discussed
- coordinate activities

scrum
Text
factors determining freq of the SoS meetings
-
complexity of the projects
-
size of the projects
-
level of inter-team dependency

scrum
Text
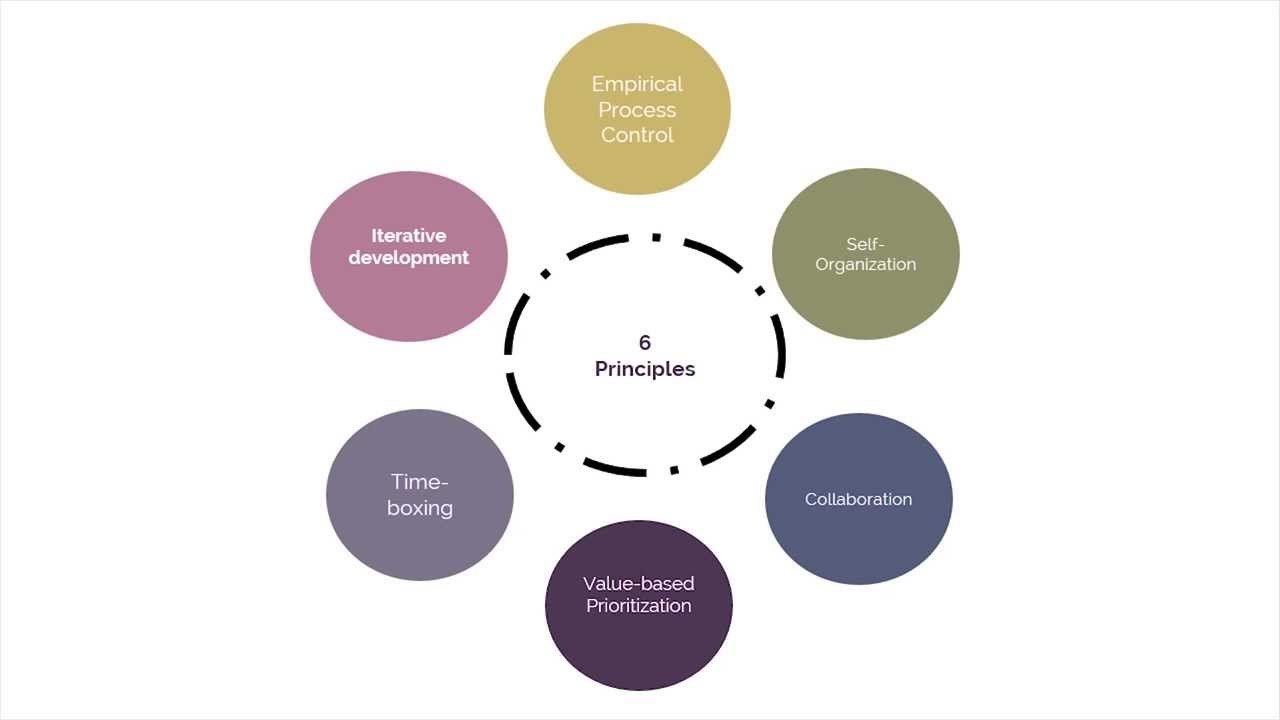
Scrum Principles

scrum
Text
Scrum Principles
- they are the core guidelines for applying the scrum framework and should be used in all scrum projects
- they are non-negotiable which are they?

scrum
Text

scrum
Text
empirical process control
the main ideas here are:
- transparency
- adaptation
- inspection

scrum
Text
self organization
- self organize rather than work under command and control

scrum
Text
collaboration
advocates PMgmnt as a shared value creation process
three core dimensions of collaboration
- awareness
- articulation
- appropriation (owning)

scrum
Text
value based prioritization
maximum business value (what is most urgent?)

scrum
Text
time boxing
describes how time is a limiting constraint in scrum
ensures sprint planning and coordination of activities. time boxed activities include:
- sprints
- daily standups
- sprint planning meetings
- sprint review meetings

scrum
Text
iterative dev
- how to better manage change
- how to build s/w that satisfy the customer

scrum
Text
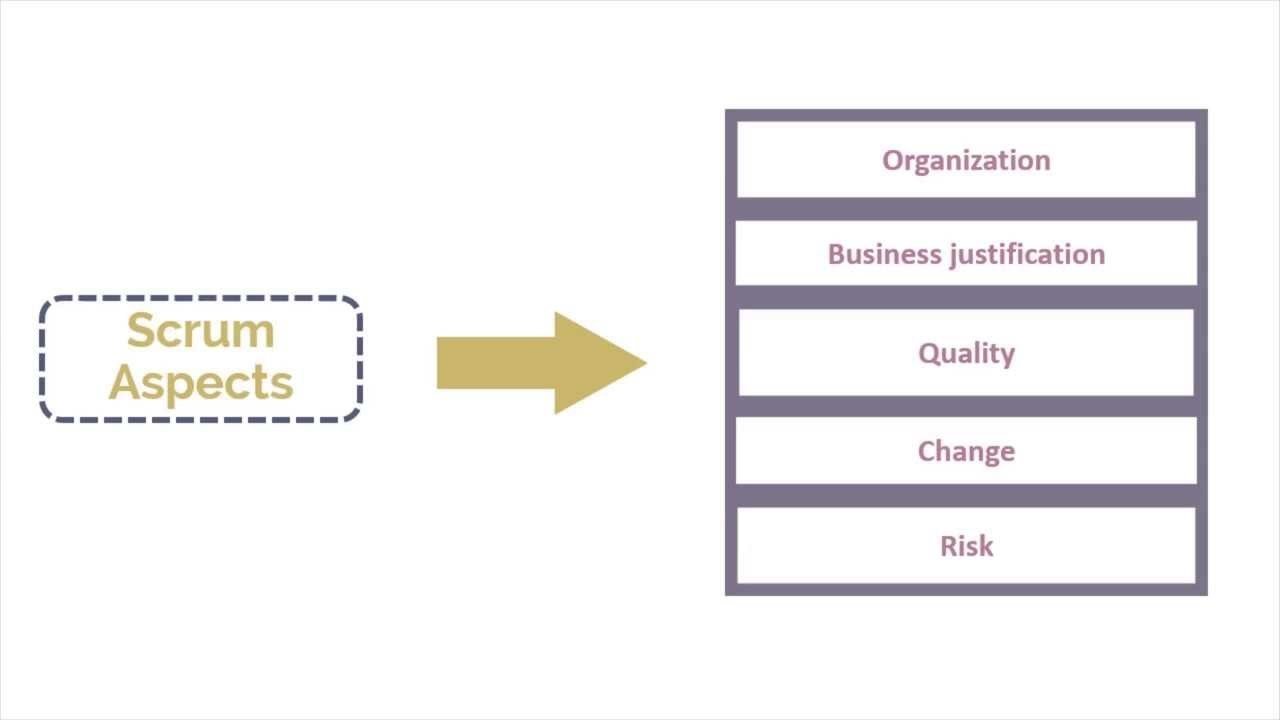
scrum aspects

scrum
Text

scrum
Text
organization
involves understanding defined roles and responsibilities
they are in two broad categories
- core roles (working on product, fully committed to project)
- non-core roles (nor responsibe for outcome of project) e.g stakeholders, vendors, scrum guidance body, chief product owner

scrum
Text
core roles
- product owner
- scrum master
- scrum team

scrum
Text
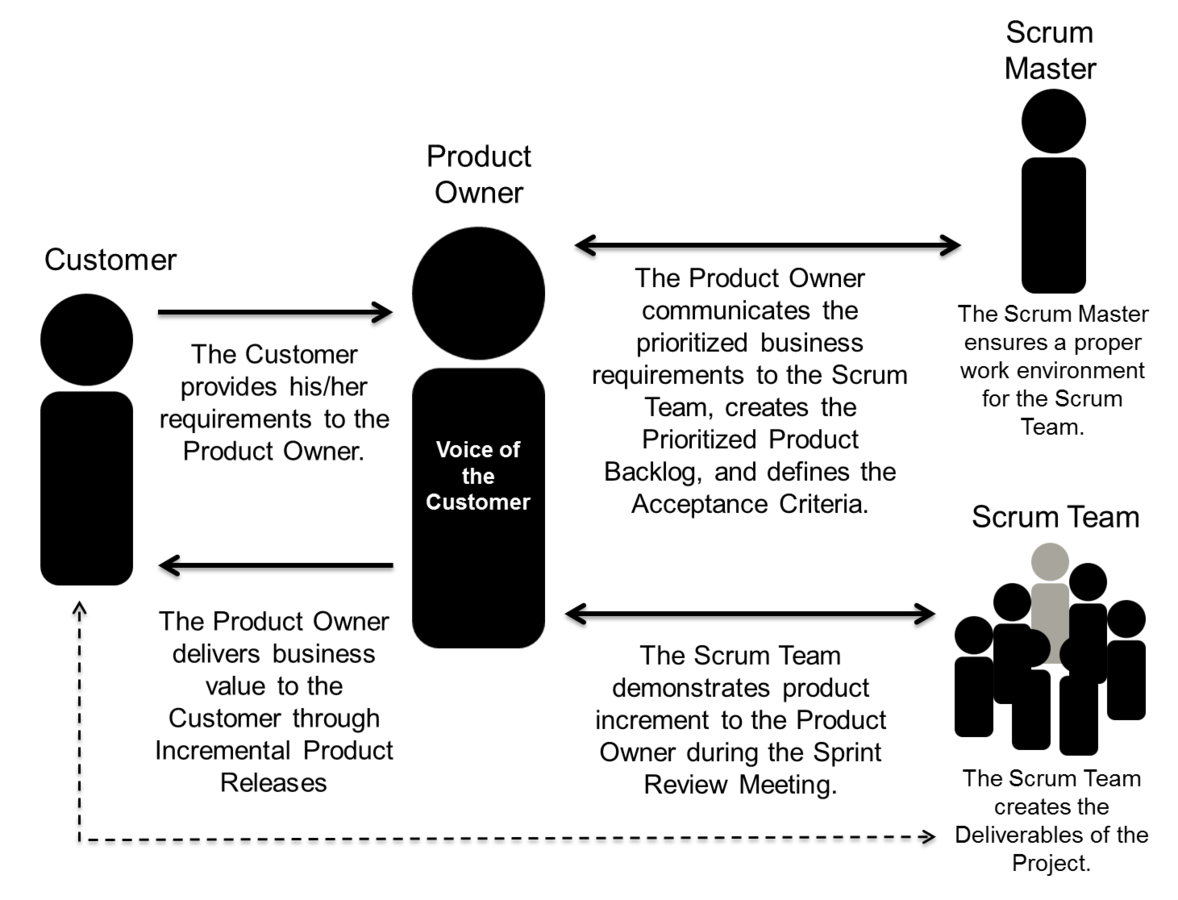
product owner
achieves maximum business value for the product
articulates customer requirements
represents the voice of customer

scrum
Text
scrum master
ensures scrum team is provided with appropriate env
guides, facilitates and teaches scrum practices
clears blockers

scrum
Text
scrum team
create the product deliverables
responsible for understanding and implementing the product owner's vision

scrum
Text

scrum
Text
recap?
stand up and stretch :-)
- scrum principles?
- scrum aspects?

scrum
Text
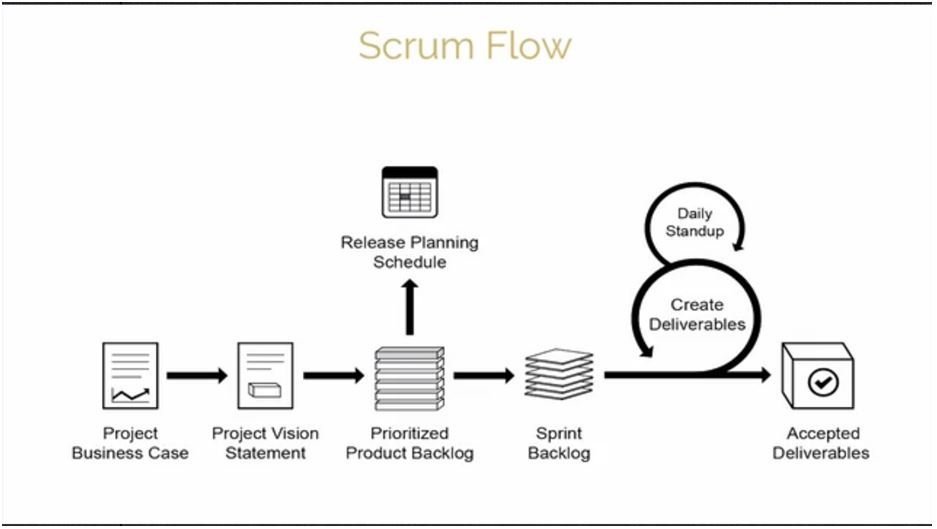
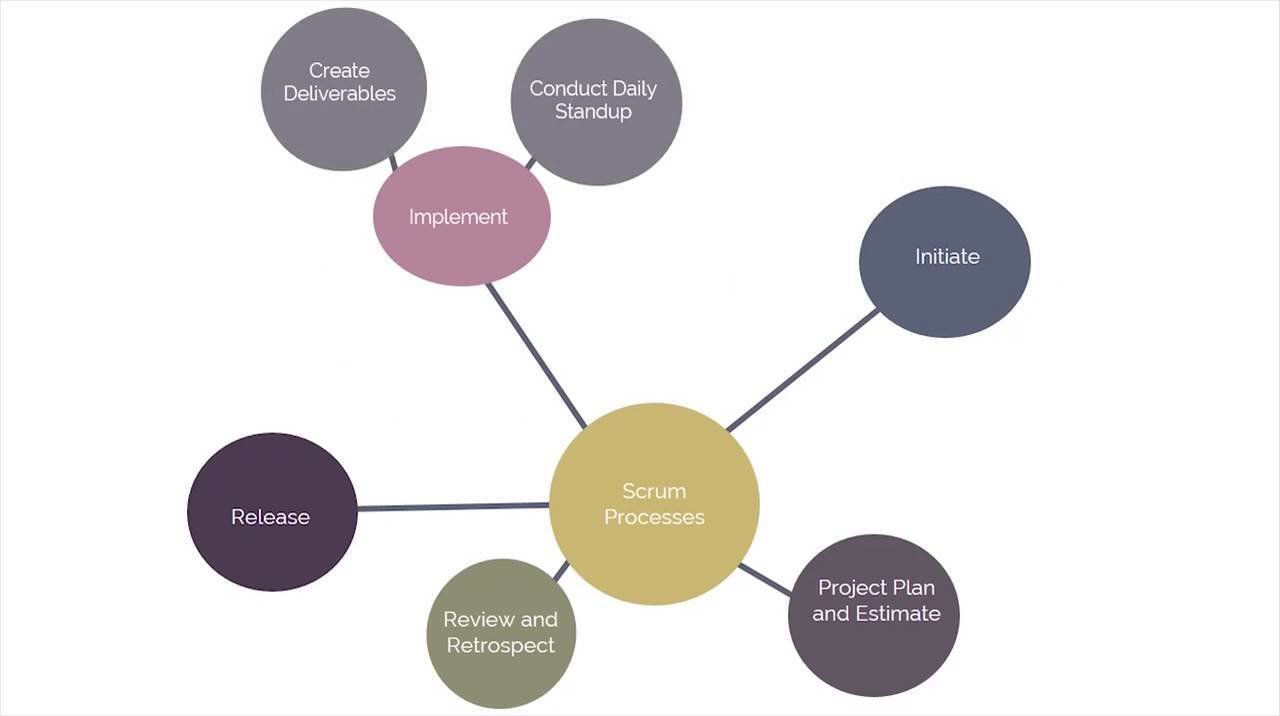
scrum processes

scrum
Text
19 processes grouped into five phases brace yourselves

scrum
Text

scrum
Text
initiate
project vision statement
- project vision statement is created
- product owner is established/identified

scrum
Text
initiate
scrum master, stakeholder identification
- scum master is identified

scrum
Text
initiate
form a team
- selection of team
- PO has the primary responsibility for selecting team (often collaborates with scrum master)

scrum
Text
initiate
develop epic(s)
- user stories are developed

scrum
Text
initiate
create a prioritized product backlog
- epics and unrefined user stories are refined to make a prioritized product backlog
- done criteria is established

scrum
Text
project plan & estimate
create user stories
- from the initiate phase (epics)
- written by PO to ensure customer reqs are understood and clear
- user stories are incorporated into prioritized product backlog

scrum
Text
project plan & estimate
approve estimate &commit epics
- estimation of the effort required
- should not be estimated in terms of hrs
- estimate by relative size i.e medium, large, small or fib sequence

scrum
Text
project plan & estimate
create tasks
- approved user stories broken down to tasks. task list created

scrum
Text
project plan & estimate
estimate tasks
- estimation of the effort required for each task (scrum core team in a task estimation workshop)

scrum
Text
project plan & estimate
create sprint backlogs
- scrum core team hold sprint planning meetings
- sprint backlog contains all work to be completed in the sprint

scrum
Text
implement
create deliverables
- scrum core team creates deliverables from sprint backlog
- scrumboard is used to measure and track activities being carried out

scrum
Text
implement
create daily standups
- same time, every day (religiously)
- discuss what was done to help the PJ on the prev day and what will be done today.

scrum
Text
implement
groom prioritized backlog
- prioritized product backlog is continiously updated and maintained

scrum
Text
review & retrospect
convene scrum of scrums
- where coordination is necessary for large projects

scrum
Text
review & retrospect
demonstrate & validate sprint
- demonstration of scrum deliverables
- intends to secure approval of features/product by the PO

scrum
Text
review & retrospect
retrospect sprint
- scrum team and scrum master meet to discuss lessons learnt
- lessons are documented to be applied to future sprints

scrum
Text
release
ship deliverables
- accepted deliverables identified and shipped

scrum
Text
release
retrospect project meeting
- scrum core team and stakeholders convene to retrospect project
- identify document and internalize the lessons learnt

scrum
Text
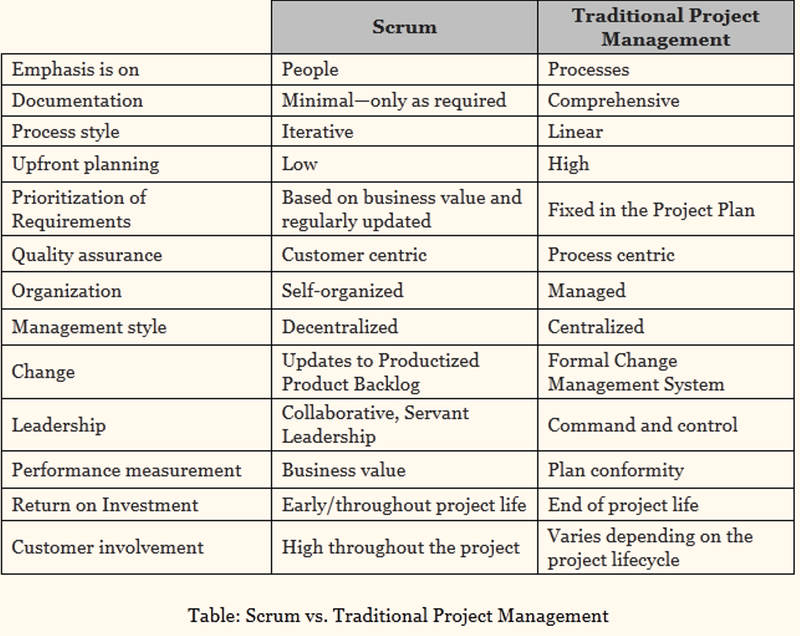
scrum vs traditional project management

scrum
Text
SCRUM
By ian munene
SCRUM
the scrum body of knowledge a guide to the use of the scrum methodology in the workplace
- 1,037



