Introduction to NoSQL

Chandan Jhunjhunwal
Session-1: 14-05-2017
https://github.com/indyarocks/
@ChandanJ


Agenda
- History of databases
- CAP Theorem
- RDBMS vs NoSQL
- ACID vs BASE
- NoSQL Solutions
- DynamoDB

History of DB
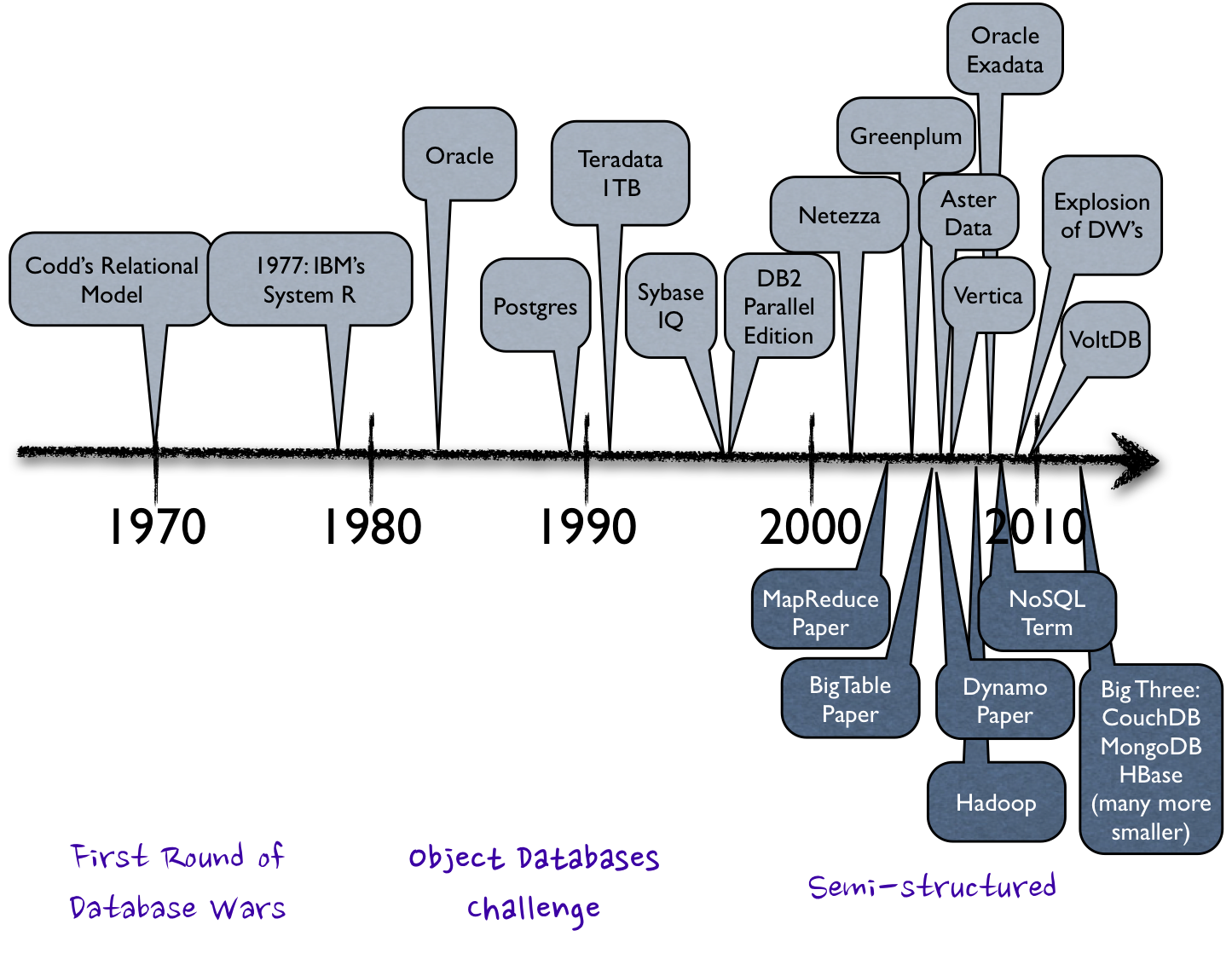
Source: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/416653403000976761/

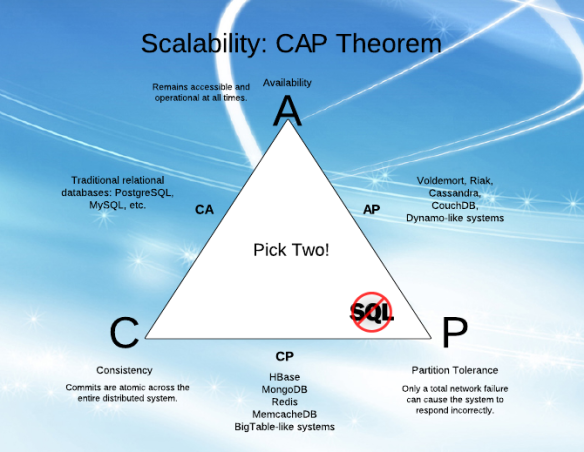
CAP Theorem(Distributed DataStore)
- Consistency: Every read fetches the most recent write or an error
- Availability: Every read fetches a set of data without a guarantee of the latest data
- Partition tolerance: Distributed data store
Misconception: You don't have to abandon one of the three all the time. The choice is really between consistency and availability only when network partition or failure happens

CAP Theorem(Distributed DataStore)
Availability
Consistency
Business Decision

CAP Theorem
Source: https://dzone.com/articles/better-explaining-cap-theorem
Source: https://dzone.com/articles/better-explaining-cap-theorem

RDBMS vs NoSQL(Not only SQL)
- Relational Schema
- Scalable Reads
- Custom high-availability
- Flexible queries
- Consistency
- ACID
- Chooses consistency over availability
- Schema free
- Scalable writes/reads
- Auto high-availability
- Limited queries
- Eventual consistency
- BASE
- Chooses availability over consistency
RDBMS
NoSQL

- Atomicity - All or nothing
- Consistency - One valid state to another valid state
- Isolation - Sequential concurrent execution
- Durability - Persistence even in case of failure
ACID
CREATE TABLE customer_account (CR INTEGER, DR INTEGER, CHECK(CR + DR = 100));
- Basic Availability - Available even if the data may be inconsistent
- Soft state: The state of system could change over time, so even if there is no input, there may be changes going on due to 'eventual consistency', thus the state of the system is always 'soft'
- Eventual consistency: The system will become consistent 'eventually' once it stops receiving inputs.
BASE

- Column database - Cassandra, HBase
Use-case: Scaling, Keeping unstructured, non-volatile information - Document database: MongoDB, CouchDB
Use-case: Nested information, JSON data - Key-value database: Redis, Memcached
Use-case: Caching, Queueing - Graph database: Neo4j
Use-case: Handling complex relational information
NoSQL Solutions

NoSQL Solutions
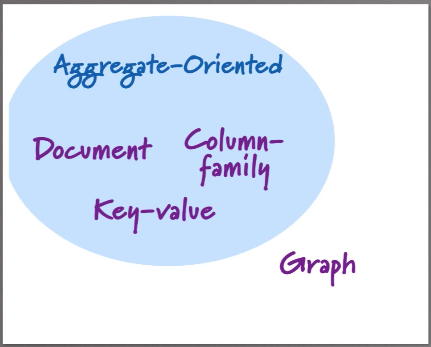
Source: Martin Fowler NoSQL Distilled

DynamoDB
- A highly scalable and fully managed NoSQL database as a service by Amazon
- No hassle of setting up replication(3x), cluster scaling, hardware provisioning, configuration etc
- Supports document and key-value data
- Scale up or down tables throughput capacity without downtime or performance degradation
- AWS CloudWatch Monitoring
- Seamless integration with DynamoDB Streams, EMR, Redshift etc
- Simple API

Thank You!

References
Introduction to DynamoDB
By Chandan Jhunjhunwal
Introduction to DynamoDB
- 785



