CERVICAL SURFACE ANATOMY
Professor Con Yiannikas

Anatomical Landmarks

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
-
Mastoid tip- 1cm below and anterior-C1
-
Hyoid bone – C3
-
Thyroid Cartilage – C4-5
-
Cricoid cartilage – C6
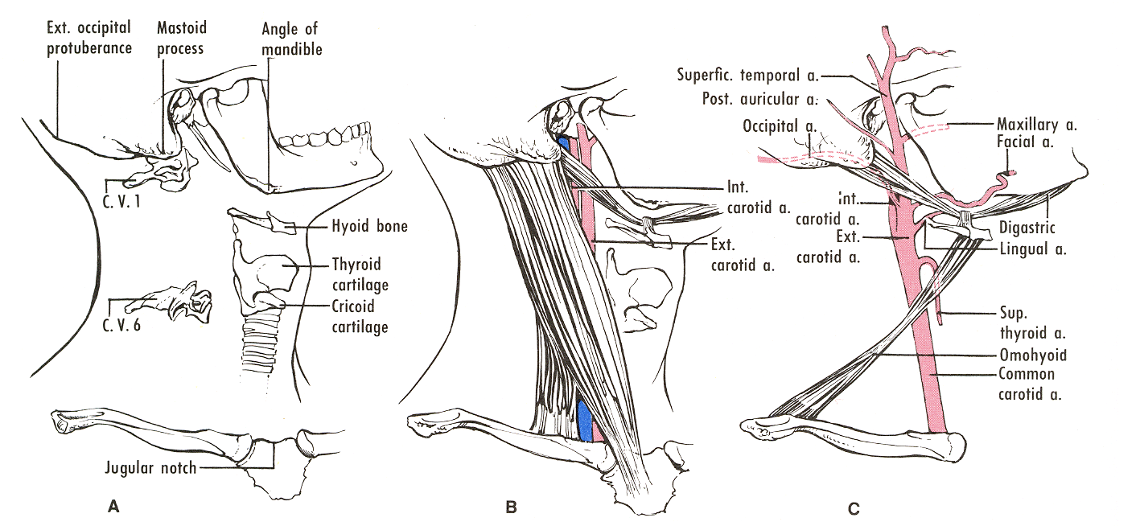
Vertebral Levels
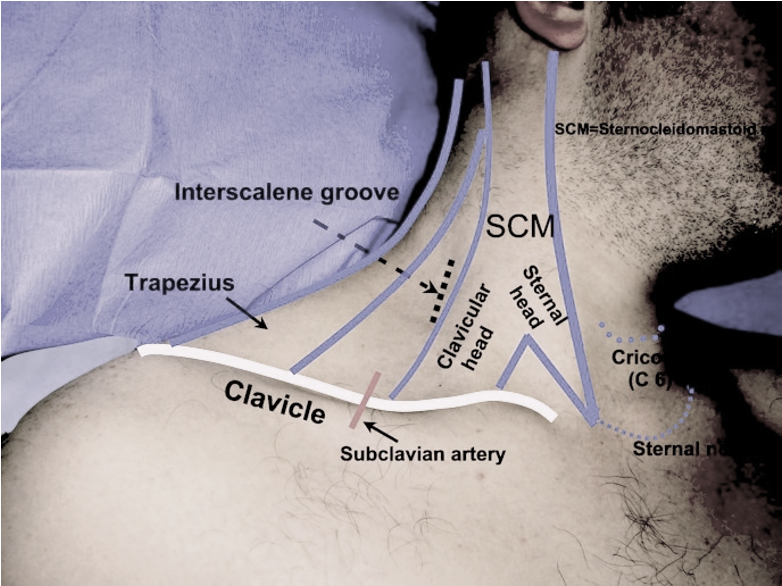
The Interscalene Groove

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
- The interscalene groove lies immediately behind the lateral border of the clavicular head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of the cricoid cartilage (C6)
- Approximately 1cm above the separation of the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
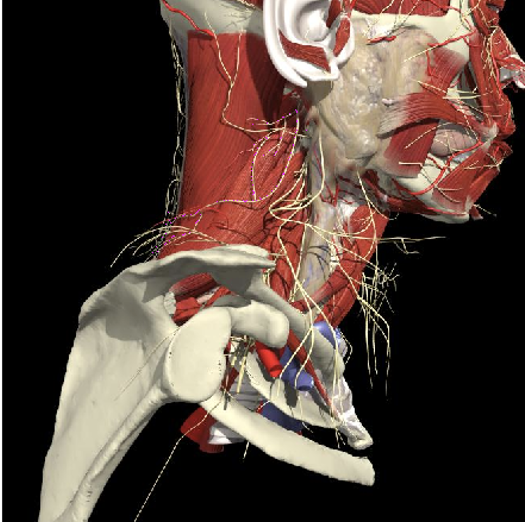
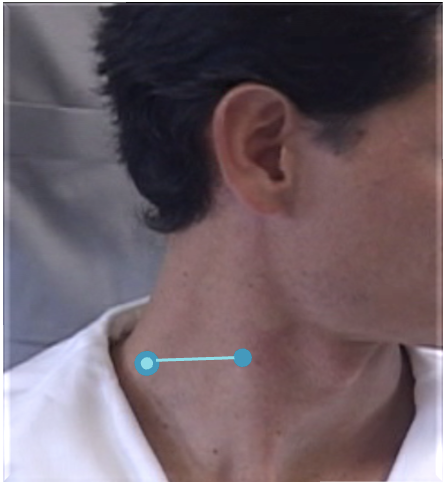
The BP lies inferior to a line from the posterior margin of the sternomastoid at the level of the cricoid cartilage to the midpoint of the clavicle
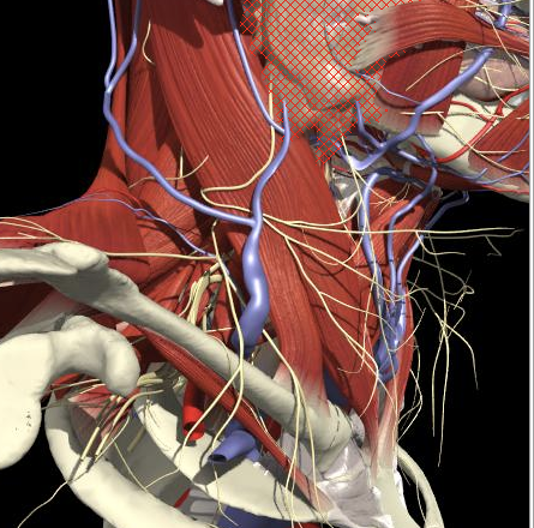
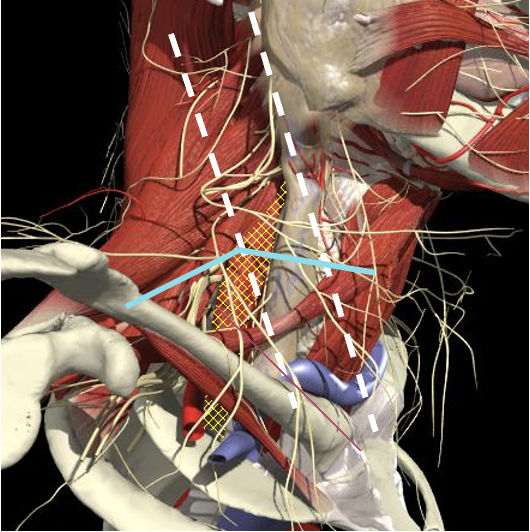
Brachial Plexus
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
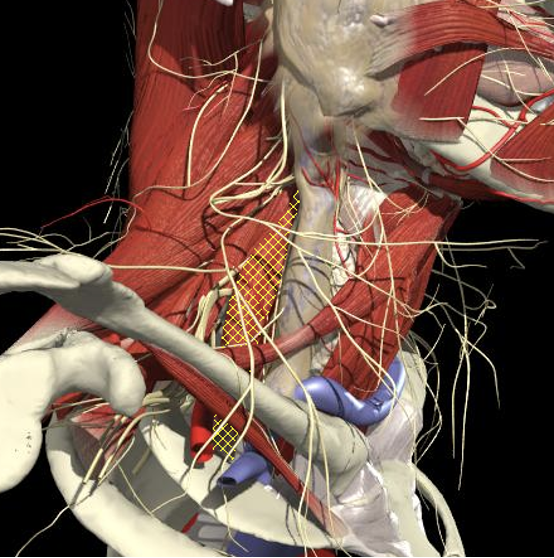
Interscalene groove
Interscalene Groove and Plexus
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
-
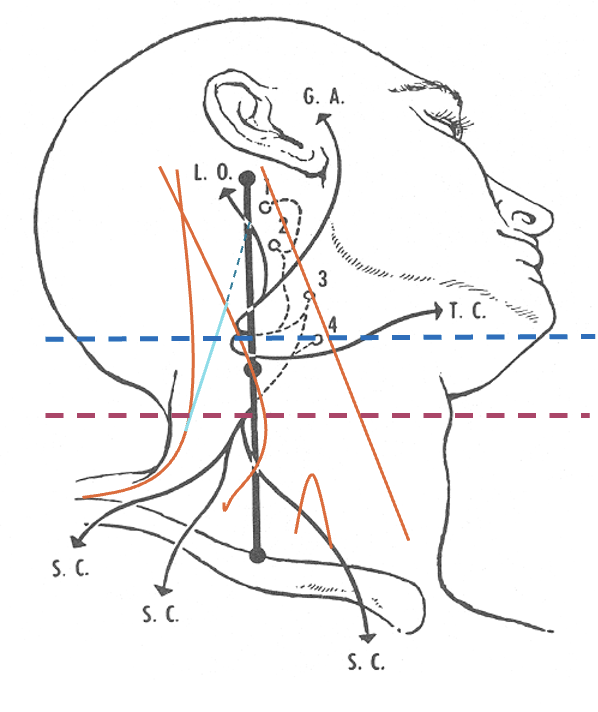
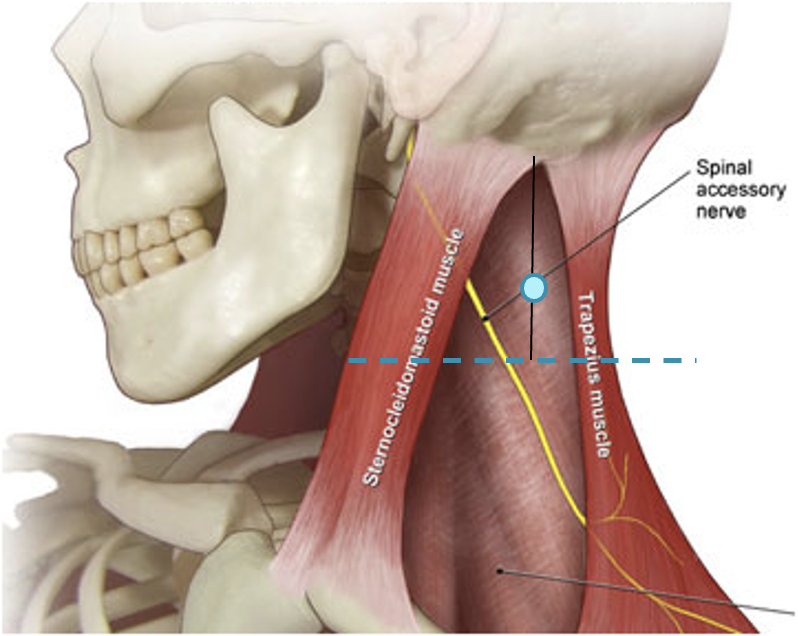
Accessory nerve
-
Lies on LS, enters 1cm cranial to EP posterior border of SCM and runs on line to between middle and lower third of trapezius.
-
-
Should inject splenius and levator over 1cm above EP
-
Cervical plexus cutaneous branches
-
Mid point of posterior border
-
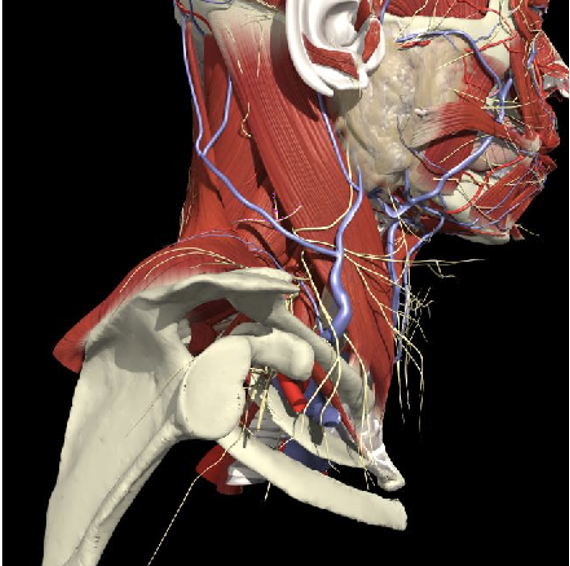
Nerves in Posterior Triangle
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Accessory nerve
Inject levator above this point
Cervical plexus
Midpoint of SCM (EP)
Middle and lower third of Trapezius
Nerves in Posterior Triangle
Landmarks
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
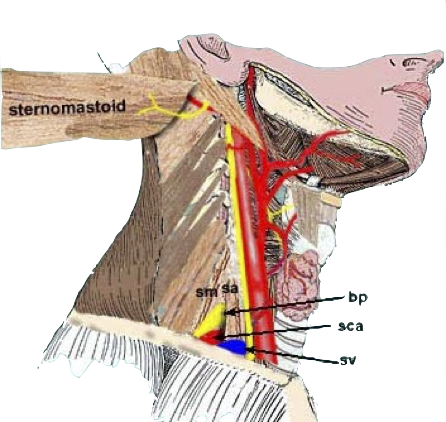
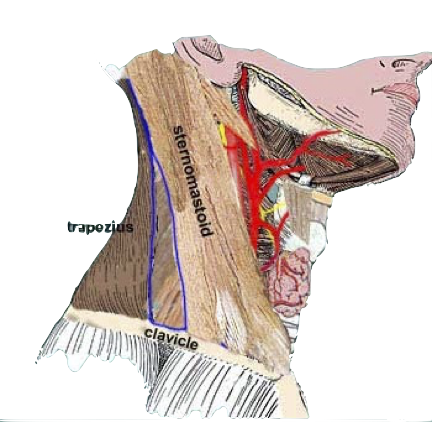
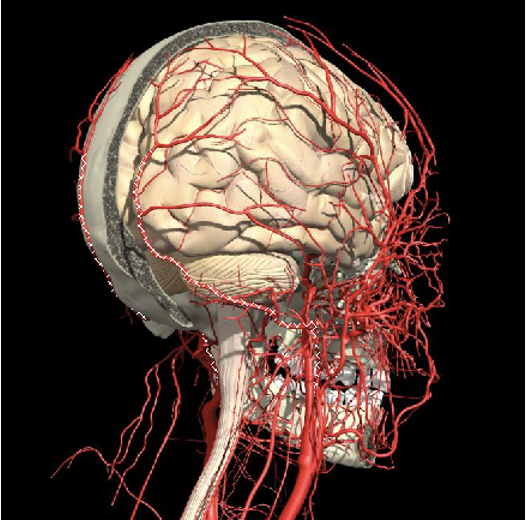
- Carotid artery
-
Midpoint anterior border of SCM
-
-
Vertebral artery
- Occipital bone or C2 towards midline is safe
-
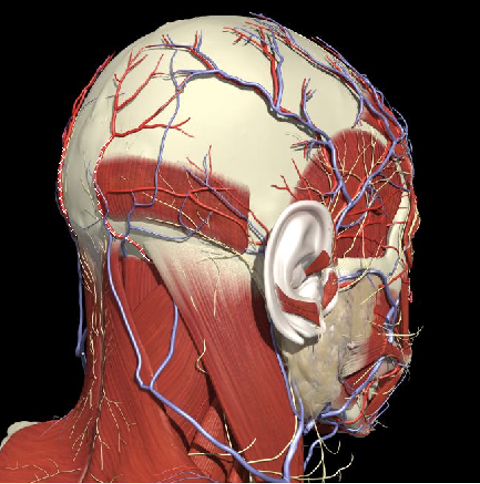
Occipital artery
-
Avoid apex of posterior triangle
-
Arteries
Structures to Avoid

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Vertebral Artery
Landmarks
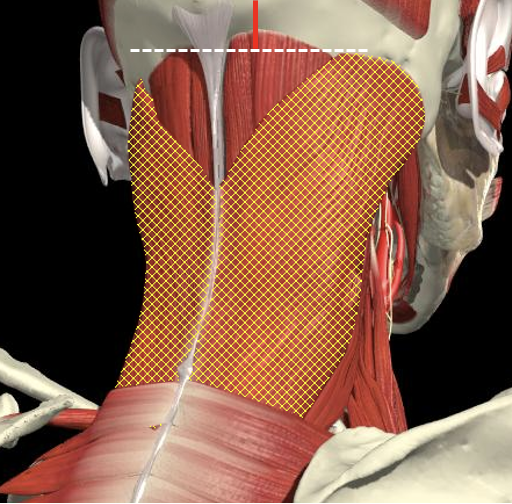
Splenius Capitis/Cervicis

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
- Midway between the inion and mastoid process
- From the same attachment forward is SCM
- Runs obliquely to spinal processes of C7 to T3
- Cervicis runs lateral border and underneath capitus anterior to levator scapulae.
Surface Anatomy
Splenius EMG

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
¿Splenius?

Cervical Dystonia
Surface Anatomy
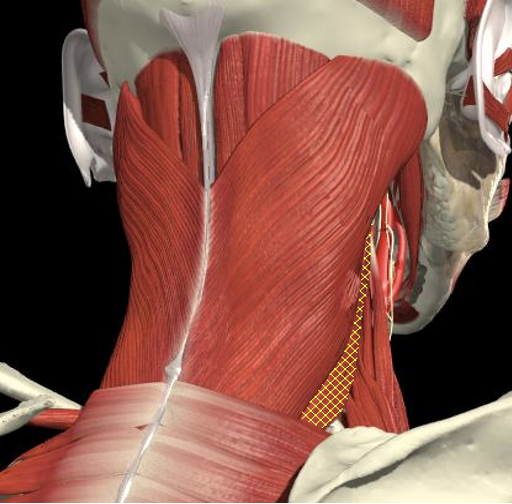
Longissimus Capitis

Cervical Dystonia
Surface Anatomy
Surface Anatomy

- Inserts into mastoid and occipital bone, and is underneath splenius capitis and over the lateral border of semispinalis capitis.
- It is the layer below splenius capitus and medial to it and underneath it is the lateral border is semispinalis capitus.
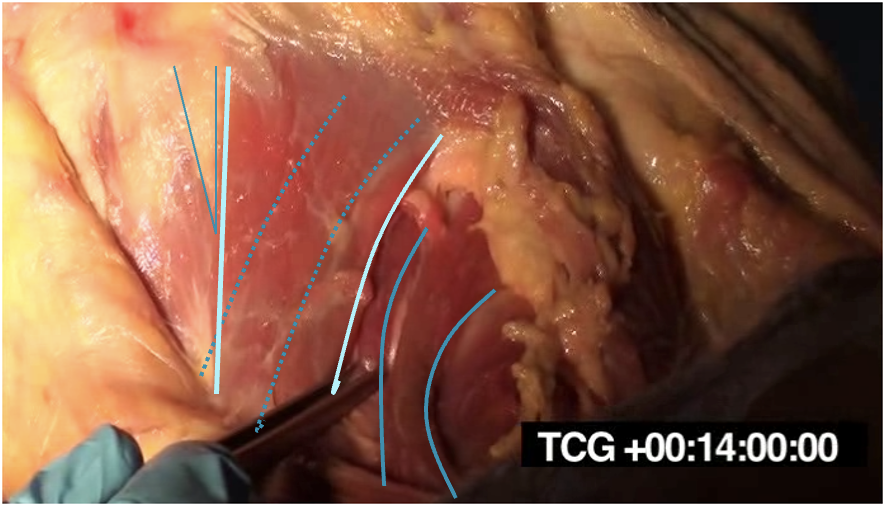
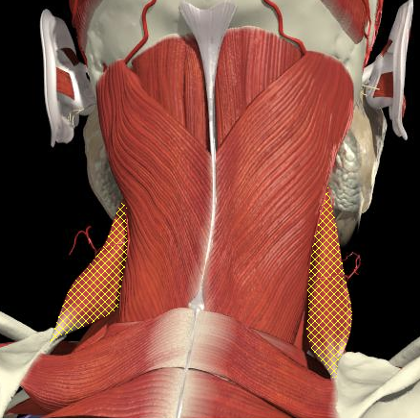
Levator Scapulae

Cervical Dystonia
Surface Anatomy
Posterior Triangle Surface Anatomy
- Runs from C1-4
- Inject in midline of posterior triangle above 2cm above EP (midpoint of SCM) and 3-4 cm below mastoid
- Below splenius capitus
Levator Scapulae

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Posterior Surface Anatomy
- Line from acromium to midline and inferior
- Feel the edge of the spine
- Above and below is infra and supraspinatus fossae
- Follow spine to midline (T3 level)
- Above that along the medial border
- Line obliquely from there to transverse process of C1-4 (below and anterior to splenius capitus)
Levator Scapulae EMG

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Lateral neck
Scapula
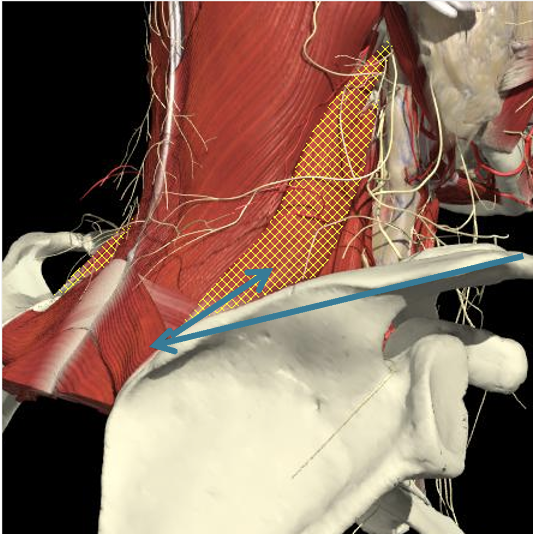
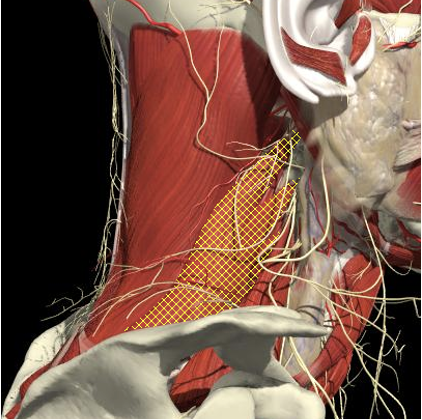
Scalenes

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
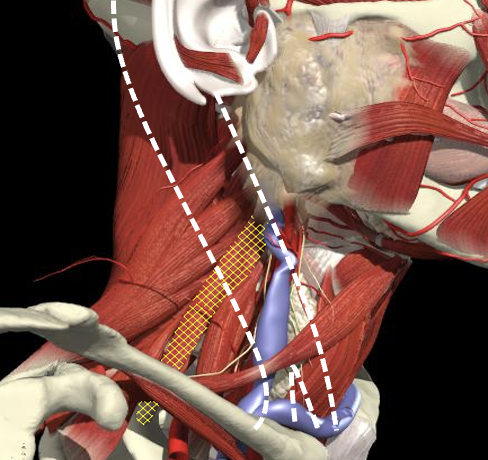
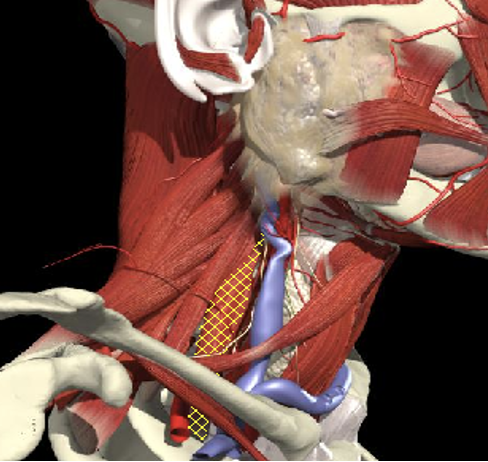
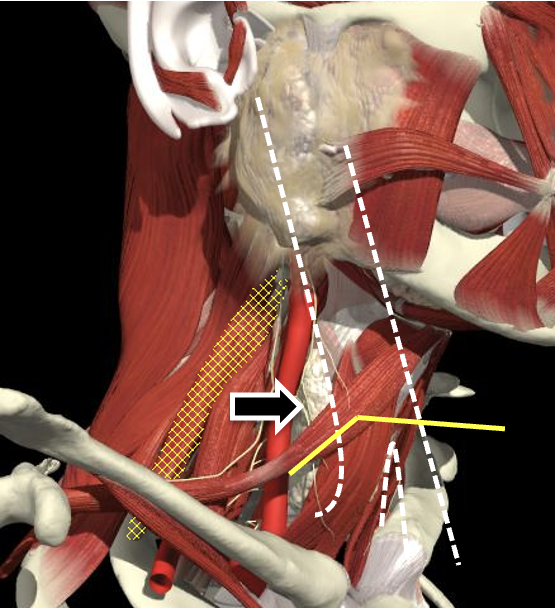
- The scalenus anterior and medius muscles lie immediately anterior and posterior to the plexus in the interscalene region and then insert onto the first rib.
- The upper, middle and lower trunks are enclosed within the interscalene fascial sheath as they emerge between the scalene muscles.
Scalenus Medius

Cervical Dystonia
Surface Anatomy
Surface Anatomy
Scalenus medius is behind and above a line from the posterior margin of the sternomastoid at the level of the cricoid cartilage to the midpoint of the clavicle.

Scalenes

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
Scalenes EMG

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
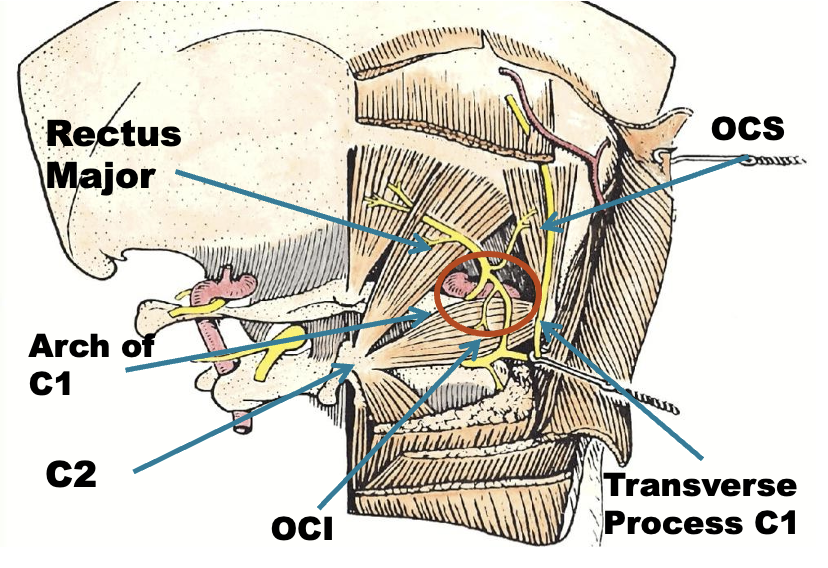
Sub-Occipital Triangle

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
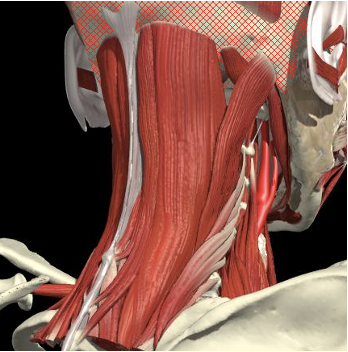
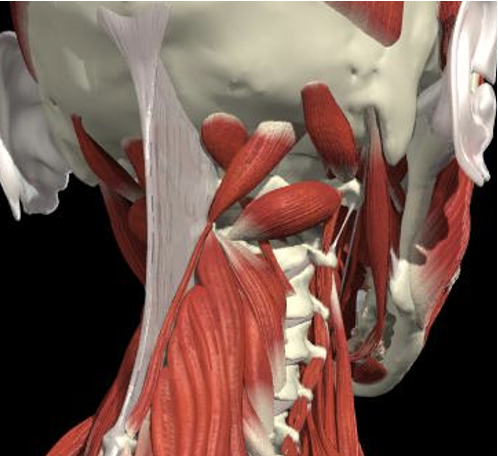
Splenius Capitis
Semispinalis
Rectus Minor Major
Obliquus Superior
Obliquus Inferior
-
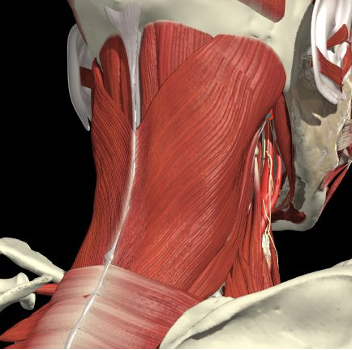
Triangle between C1 transverse process (below and behind mastoid), C2 and occiput.
-
Pass through Trapezius, Splenius capitus (more lateral) and semispinalis capitus (more medial) to reach it.
Sub-Occipital Triangle

Cervical Dystonia
Anatomy
- The C2 level is a plane 2.5 cm below the mastoid process
Obliquus Capitis Superior
Rectus Capitis Major
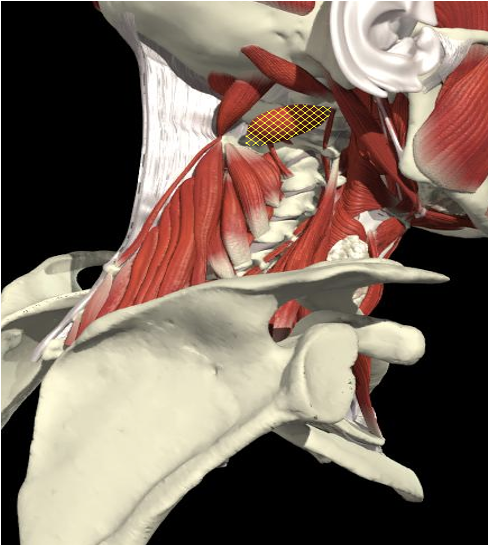
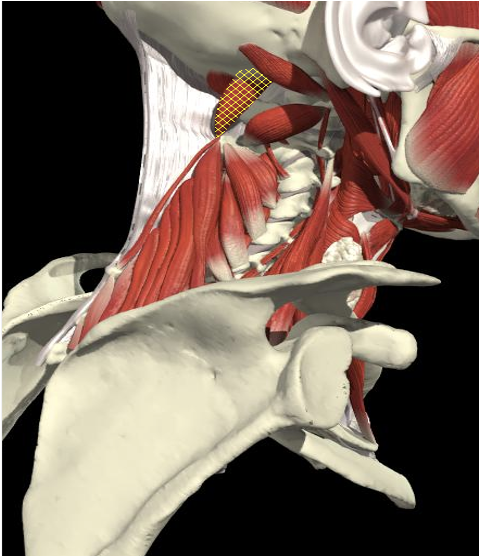
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
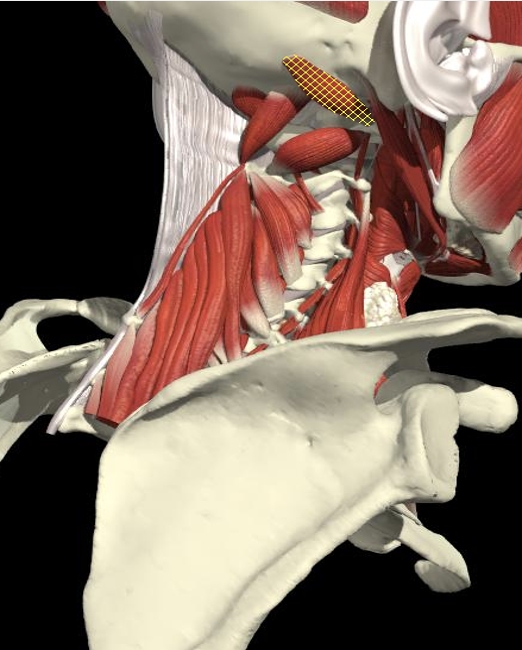
Obliquus Capitis
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
- Midway between the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid and the dorsal midline.
- Depth of 3.0-3.5 cm.
CD_Surface Anatomy
By Integra
CD_Surface Anatomy
- 100


