
Blood Clot Prevention, or Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) prevention after orthopedic surgery
Why and Who needs it ?
Immobilization after surgery interrupts the venous blood flow and eliminates the calf pumping protective mechanism against clotting
Blood clots from the leg veins may travel to the lungs, causing Pulmonary Embolism, (PE)
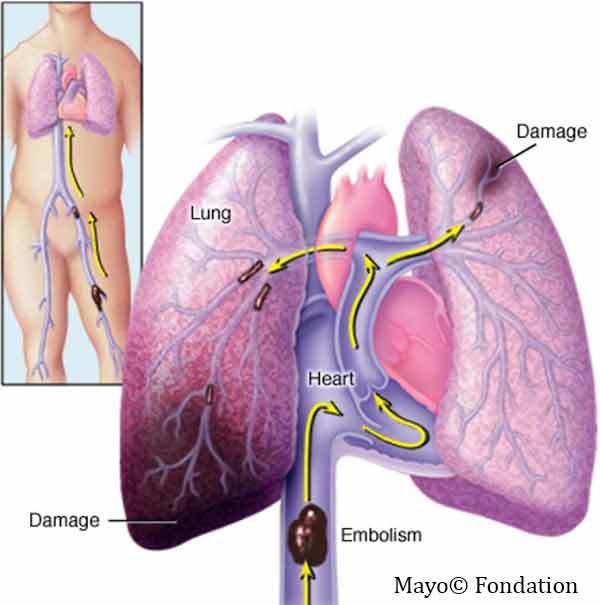
PE caries a high risk of death , if untreated
How to use the scoring system?
For each Risk Factor, assign a scoring point, based on the following tables.
Calculate your final score, which reflect your risk of blood clots.
For scoring more or equal to 2, start prophylaxis with heparin, coumadin, or one of the novel anticoagulants
-
The following get 1 point
-
-
Age 41-60 years
-
Minor surgery
-
History of major surgery within 1 month
-
Pregnancy or postpartum within 1 month
-
Varicose veins
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
-
Swelling of legs
-
Obesity (body mass index [BMI] >25 kg/m 2)
-
Oral contraceptives, patch, or hormone replacement therapy
The following get 2 point
-
Age older than 60 years
-
Malignancy or current chemotherapy or radiation therapy
-
Major surgery (>45 min)
-
Laparoscopic surgery (>45 min)
-
Confined to bed longer than 72 hours
-
Immobilizing cast shorter than 1 month
-
Central venous access for less than 1 month
-
Tourniquet time longer than 45 minutes
The following get 3 points
-
Age older than 75 years
-
History of DVT or PE
-
Family history of thrombosis
-
Factor V Leiden/activated protein C resistance
-
Medical patient with risk factors of myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
-
Congenital or acquired thrombophilia
The following get 5 points
-
Major, elective lower extremity arthroplasty, Total knee and total hip replacement
-
Hip, pelvis, or leg fracture within 1 month
-
Stroke within 1 month
-
Multiple trauma within 1 month
-
Acute spinal cord injury with paralysis within 1 month
deck
By Irina Staicu
deck
DVT prophylaxis post orthopedic surgery
- 519



