April 1-3, 2019
72nd HPC User Forum
Santa Fe, New Mexico
Terrell Russell, Ph.D.
@terrellrussell
Chief Technologist, iRODS Consortium
Metadata and Archiving
at Scale

Metadata and Archiving
at Scale




Our Membership



















Data Centric. Metadata Driven.
Provides insurance against your changing infrastructure:
- edge devices (sequencers, satellites, supercomputers, etc.)
- storage
- compute
- networking
- authentication




Open Source Data Management
Data Management
"The development, execution, and supervision of plans, policies, programs, and practices that control, protect, deliver, and enhance the value of data and information assets."
Most organizations are still managing their assets with a collection of small scripts, tribal knowledge, vigilance, and hope.
Organizations, instead, need a future-proof solution to managing data and its surrounding infrastructure.

Why Data Management Matters
As data matures and reaches a broader community, data management policy must also evolve to meet these additional requirements.


The Data Lifecycle begins at Data Generation
When data management is involved from the point of data generation,
a system can address other hard problems:
- Data Harmonization
- Data Movement
- Data Integrity
- Geographic Distribution
- Network Capacity
- Network Reliability
- Variety of Data Sources
- Variety of Data Formats

A Small Matter of Policy
Two Simplified Assertions for Today:
- Metadata
- Annotations that mean something:
- to people
- to programs
- Annotations that mean something:
- Archive
- Copies or replicas in a safe/cheaper place
- Discoverable
- Retrievable when appropriate
Both can be handled abstractly through configuration and policy.
Automatic, policy-based solutions are resilient to future changes in technology.

iRODS Core Competencies
The underlying technology categorized into four areas




iRODS Policy Examples
- Data Routing
- Data Movement
- Data Verification
- Data Synchronization
- Data Transformation
- Metadata Capture
- Metadata Application
- Metadata Verification
iRODS Capabilities









Deployment Patterns

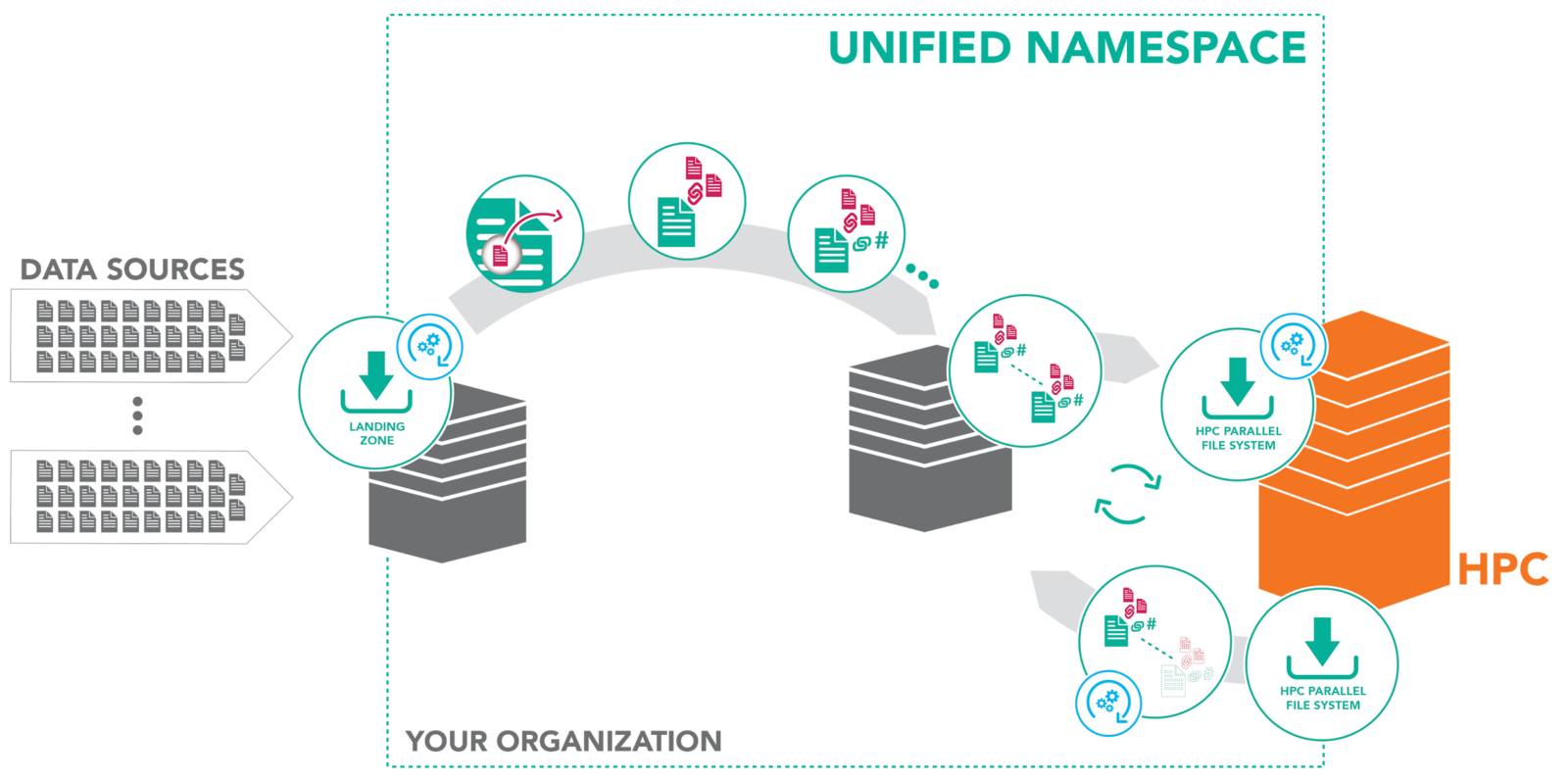
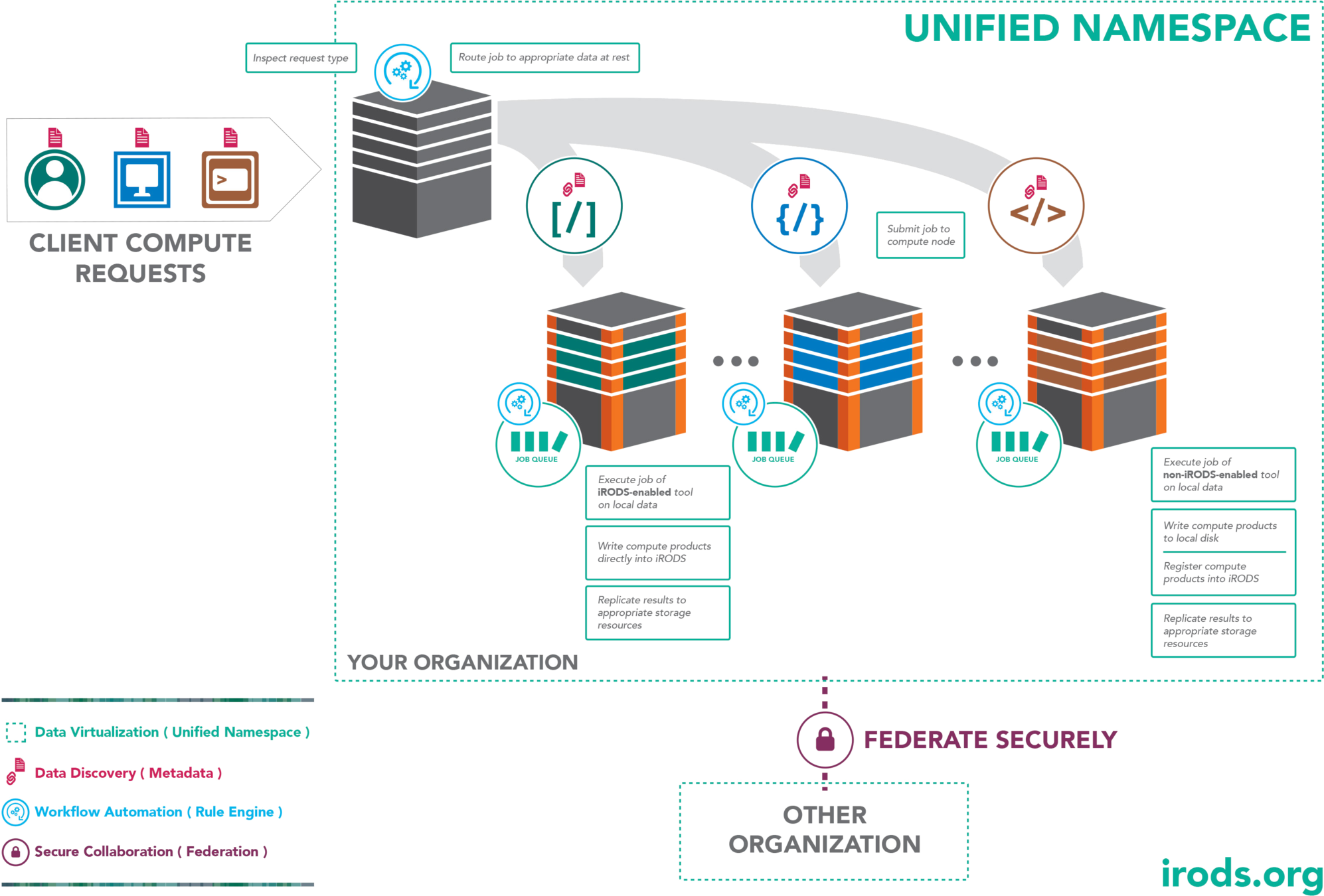
Data to Compute
Compute to Data
Filesystem Synchronization
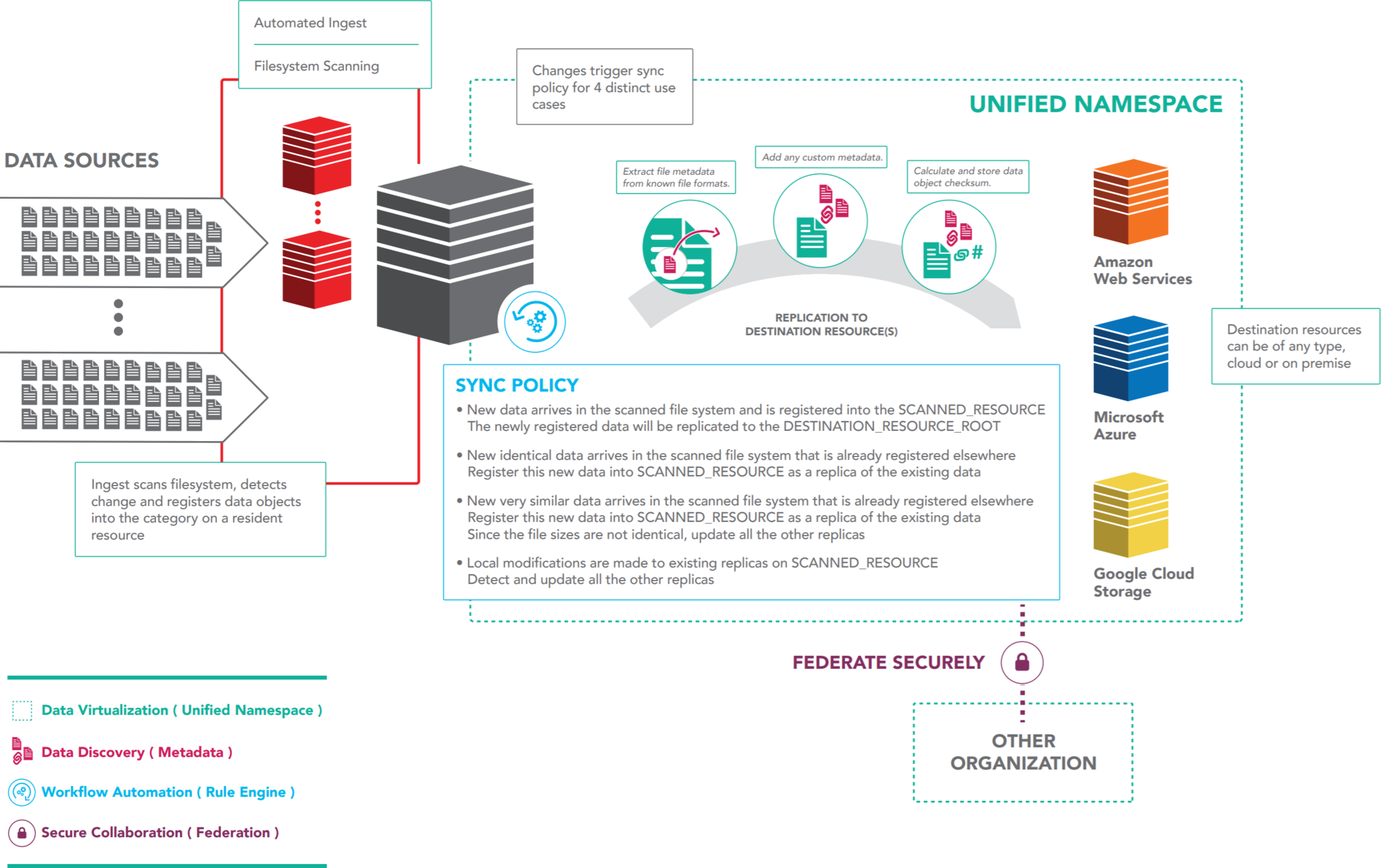
The Data Management Model



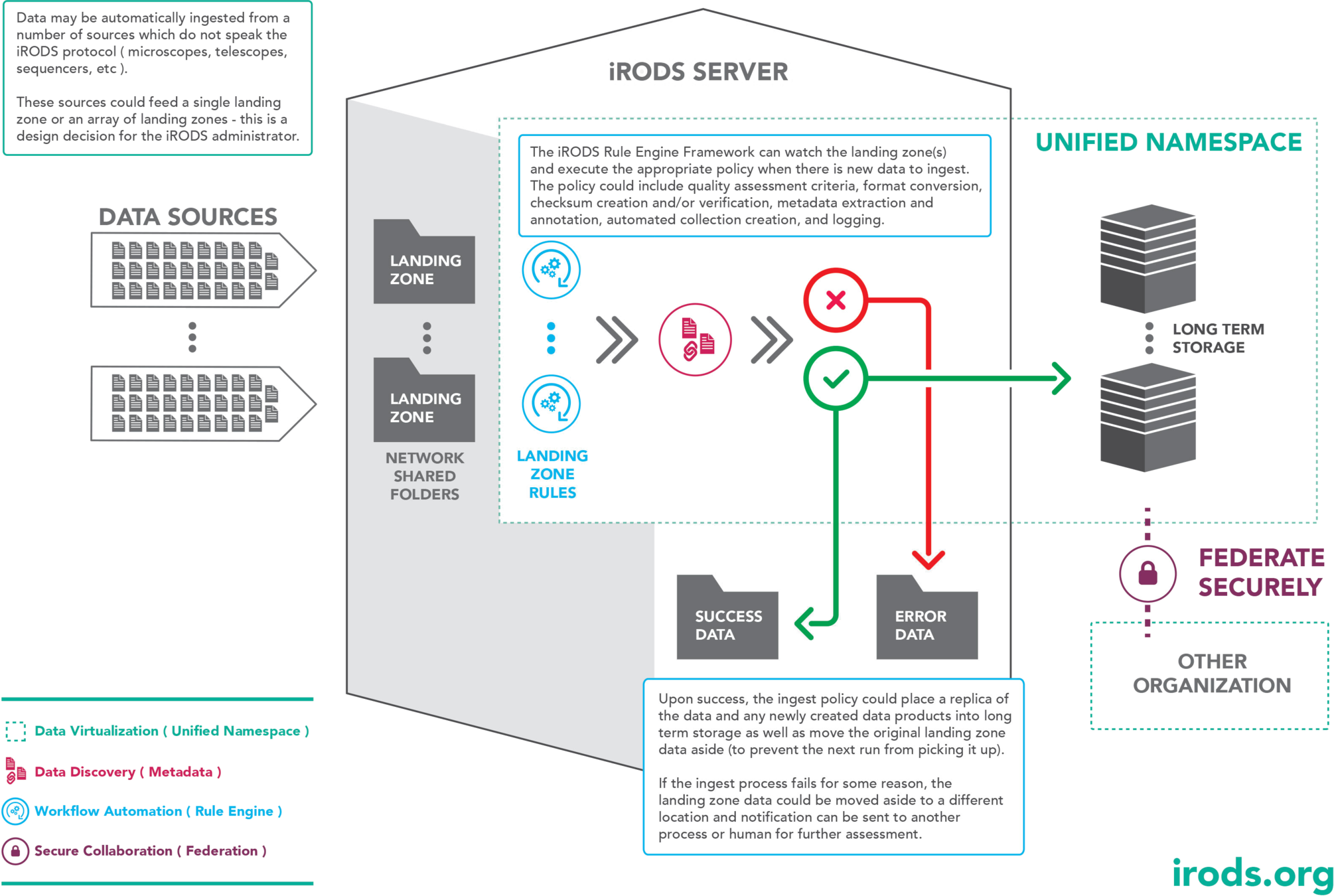
Automated Ingest - Landing Zone


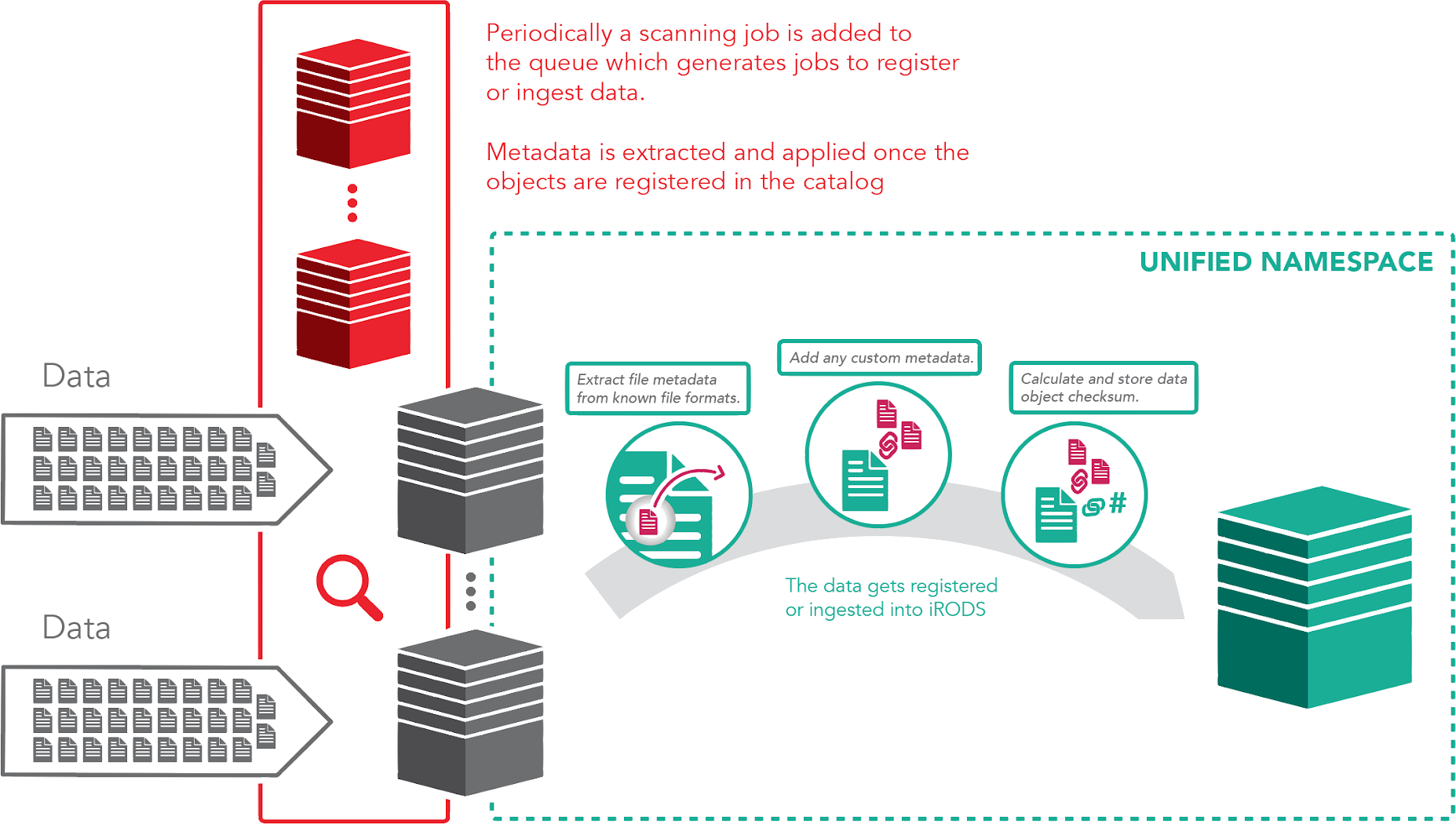
Automated Ingest - Filesystem Scanning


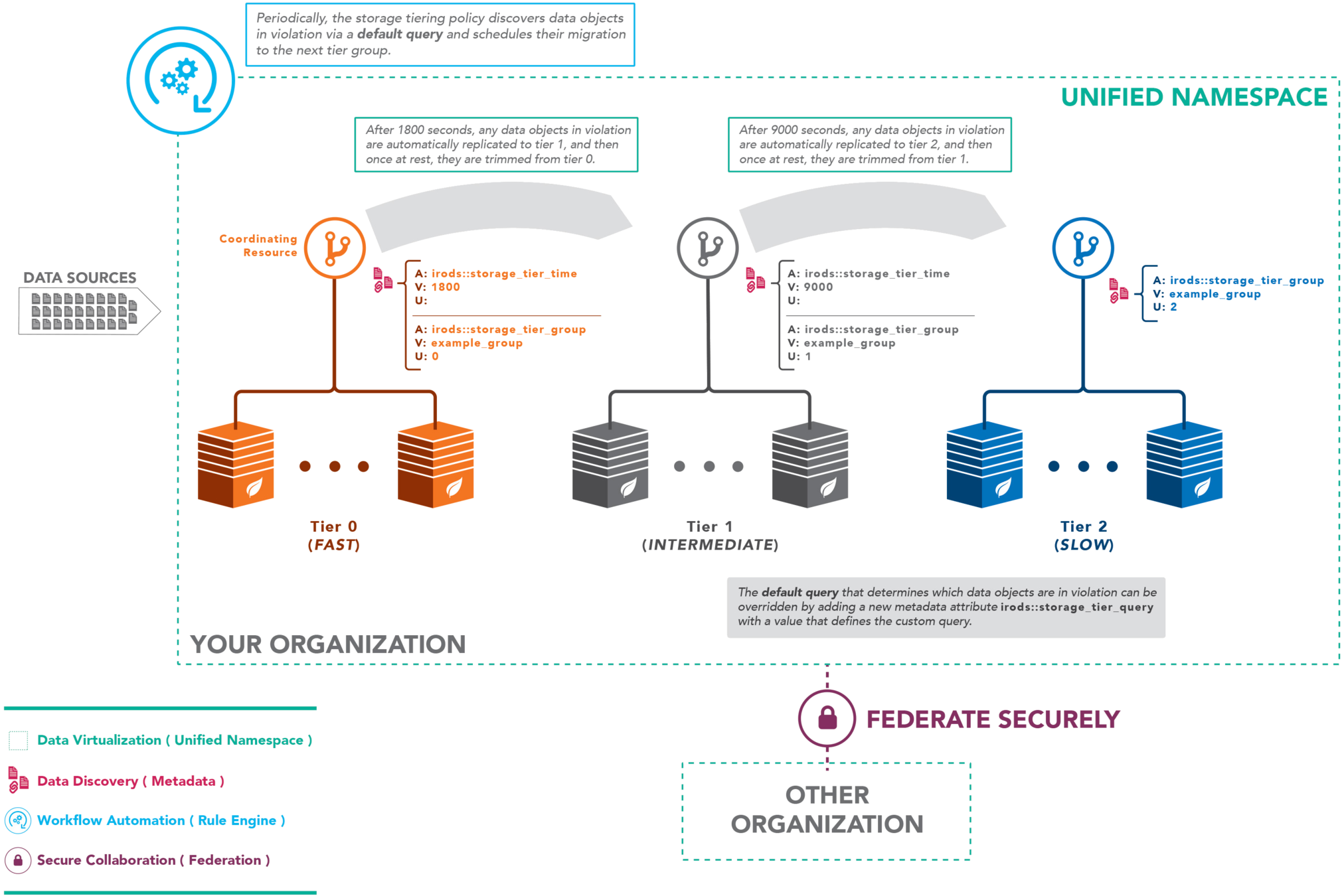
Storage Tiering


Data to Compute



Compute to Data



Take Aways
- Automatic, policy-based solutions are more future-proof as technology continues to change
- Having a programmatic interface (to the iRODS Rule Engine, via Policy Enforcement Points) means action(s) can be taken on your data based on the metadata:
- Ingest
- Metadata Extraction
- Data Verification
- Storage Tiering
- Indexing
- Publication
- Auditing / Reporting
- Metadata templates allow for validation and verification
- Match your domain-specific vocabulary and taxonomies
- Reference outside standards
- Prove compliance with required formats
- Publish to make data discoverable
Ongoing and Upcoming Work
- Cacheless S3
- NFSRODS / CIFSRODS
- RDMA (RoCE) integration
Resources
iRODS Open Source Code
iRODS Overview and Diagrams
https://irods.org/documentation
iRODS Software Documentation
iRODS Training Materials and Presentations
iRODS User Group Meeting
Questions?
Thank you.
iRODS Consortium
@irods
Terrell Russell, Ph.D.
@terrellrussell
HPC User Forum - Metadata and Archiving at Scale
By iRODS Consortium
HPC User Forum - Metadata and Archiving at Scale
- 2,236

