High Availability
June 5-7, 2018
iRODS User Group Meeting 2018
Durham, NC
Justin James
Applications Engineer, iRODS Consortium
High Availability





High Availability iRODS - Goal
Our goal is to create a fault tolerant iRODS Zone to achieve high availability.
This design is based on High Availability iRODS System (HAIRS) by Yutaka Kawai at KEK and Adil Hasan at the University of Liverpool.

High Availability iRODS - Overview
To achieve full redundancy within an iRODS Zone, the following iRODS components should be replicated:
- iCAT Database - Implementing redundancy for RDBMS databases is outside the scope for this demonstration
- Catalog Provider (iCAT Server) - Redundancy is achieved by having two iCAT servers behind a load balancer
- Catalog Consumer (Resource Server) - The built-in replication resource hierarchy will provide data redundancy.
- It is also possible to have redundancy within the load balancers that are fronting the iCAT servers. This will not be covered in this demonstration but the following link provides one such solution:

High Availability iRODS - Basic Setup
For this demonstration... 7 virtual servers.
- LoadBalancer.example.org – 192.168.1.150
- ICAT1.example.org – 192.168.1.151
- ICAT2.example.org – 192.168.1.152
- DB1.example.org – 192.168.1.153
- Resource1.example.org – 192.168.1.155
- Resource2.example.org – 192.168.1.156
- CLI1.example.org – 192.168.1.154
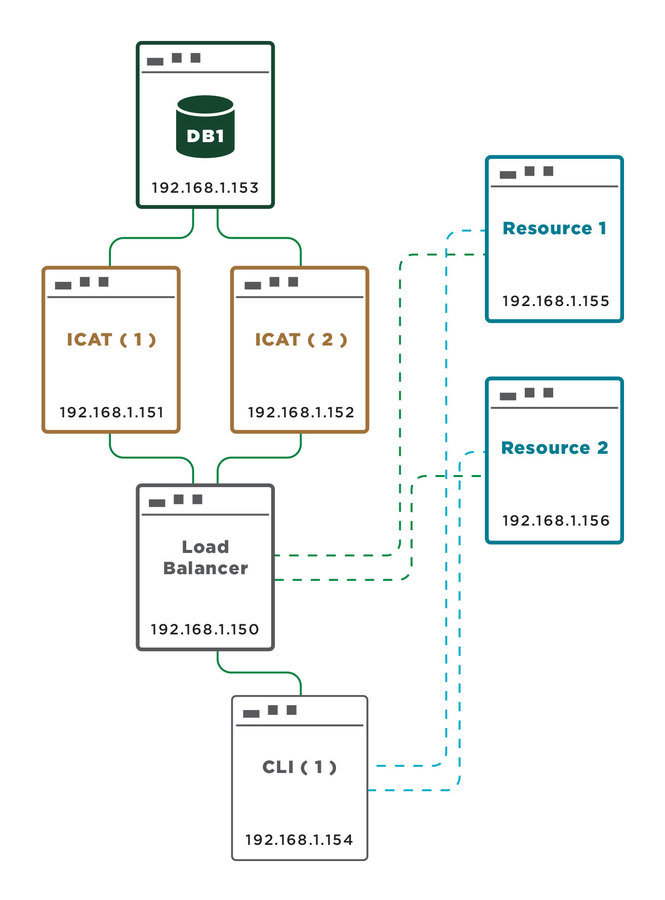

Initial Conditions
We need to have each server set up with the appropriate hostname and IP address.
The LoadBalancer will refer to the two catalog providers as
- ICAT1.example.org and
- ICAT2.example.org
Internally, the two catalog providers will each refer
to themselves as LoadBalancer.example.org
- Their own /etc/hostname should be LoadBalancer.example.org
- This is how other servers will refer to them
Once this is configured, make sure that each server can ping the other servers by IP.

Configuring /etc/hosts
The next step is to make sure each server can map its peers' fully qualified domain names to their IP address.
All components when acting as a client, will access the catalog providers via the load balancer.
The following table lists the hosts that need to be known for each server.
| Server | Needs to Resolve |
|---|---|
| LoadBalancer.example.org | Both catalog providers |
| ICAT(n).example.org | The database server and each catalog consumer |
| Resource(n).example.org | The other catalog consumer and the load balancer |
| DB1.example.org | Each catalog provider |
| CLI1.example.org | Needs access to at least one iRODS server for the primary connection |

/etc/hosts setup
For this example, just update the /etc/hosts files to perform host to IP mapping.
LoadBalancer.example.org:
ICAT1.example.org:
ICAT2.example.org:
127.0.0.1 LoadBalancer.example.org localhost
192.168.1.151 ICAT1.example.org
192.168.1.152 ICAT2.example.org127.0.0.1 LoadBalancer.example.org localhost
192.168.1.153 DB1.example.org
192.168.1.155 Resource1.example.org
192.168.1.156 Resource2.example.org127.0.0.1 LoadBalancer.example.org localhost
192.168.1.153 DB1.example.org
192.168.1.155 Resource1.example.org
192.168.1.156 Resource2.example.org

/etc/hosts setup
Resource1.example.org:
Resource2.example.org
127.0.0.1 Resource1.example.org localhost
192.168.1.156 Resource2.example.org
192.168.1.150 LoadBalancer.example.org
127.0.0.1 Resource2.example.org localhost
192.168.1.155 Resource1.example.org
192.168.1.150 LoadBalancer.example.org

/etc/hosts setup
DB1.example.org:
CLI1.example.org
127.0.0.1 CLI1.example.org localhost
192.168.1.155 Resource1.example.org
192.168.1.156 Resource2.example.org
192.168.1.150 LoadBalancer.example.org127.0.0.1 DB1.example.org localhost
192.168.1.151 ICAT1.example.org
192.168.1.152 ICAT2.example.org
Configuring the Load Balancer
In our test setup we use HAProxy to perform software level HTTP and TCP load balancing.
HAProxy can be downloaded on Ubuntu 16.04 systems using the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y haproxy
Configuring the Load Balancer
Next we will configure the load balancer to use TCP routing. Incoming requests on port 1247 will be redirected in a round-robin fashion to one of the two catalog providers.
Save the following contents into /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 256
defaults
mode tcp
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
frontend irods-in
bind *:1247
default_backend servers
backend servers
option tcp-check
tcp-check connect
tcp-check send PING\n
tcp-check expect string <MsgHeader_PI>\n<type>RODS_VERSION</type>
server ICAT1.example.org 192.168.1.151 check port 1247
server ICAT2.example.org 192.168.1.152 check port 1247
Configuring the Load Balancer
To determine if a particular catalog provider is up and running, any string can be sent (in the above case we send "PING") to port 1247 and iRODS will respond with text beginning with "<MsgHeader_PI>". This is used as a health check on the iRODS server.
This is sufficient to determine if an iCAT instance is up or down.
Restart haproxy:
sudo service haproxy restart
Installing and Configuring DB
Install PostgreSQL on DB1.example.org:
Configure the PostgreSQL database for iRODS:
myuser@DB1:~$ sudo apt-get install postgresqlmyuser@DB1:~$ sudo su - postgres
postgres@DB1:~$ psql
psql (9.5.12)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# CREATE USER irods WITH PASSWORD 'testpassword';
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE "ICAT";
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE "ICAT" TO irods;
GRANT
postgres=# \q

Installing and Configuring DB
Update /etc/postgresql/9.3/main/postgresql.conf to allow remote connections from any host.
Update /etc/postgresql/9.3/main/pg_hba.conf to allow users from 192.168.1.X addresses to connect to the ICAT database with the irods user.
Restart PostgreSQL:
listen_addresses = '*' # what IP address(es) to listen on;host ICAT irods 192.168.1.0/24 md5myuser@DB1:~$ sudo service postgresql restart
Install iRODS on the Catalog Providers
First, test that the iCAT server can connect remotely to the database server.
Install iRODS on each catalog provider.
Enter DB1.example.org as the DB server when prompted.
myuser@ICAT1:~$ sudo apt-get install irods-server irods-database-plugin-postgres
myuser@ICAT1:~$ sudo /var/lib/irods/packaging/setup_irods.pymyuser@ICAT1:~$ sudo apt-get install postgresql-client-9.3
myuser@ICAT1:~$ psql -d ICAT -h 192.168.1.153 -U irods -W
Password for user irods:
psql (9.3.13)
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256)
Type "help" for help.
ICAT=>
Note: Ignore the error about being unable to put a file into iRODS on the second iCAT installation. Go ahead and start the server with ~irods/irodsctl start. The root cause of the error will be addressed when we delete the resource on the iCAT servers.

Install iRODS on the Catalog Consumers
myuser@Resource1:~$ sudo apt-get install irods-server
myuser@Resource1:~$ sudo /var/lib/irods/packaging/setup_irods.pyInstall iRODS on each catalog consumer.
When prompted for the address of the catalog provider, enter LoadBalancer.example.org which will resolve to the load balancer.

Create Resources
Now we will create a resource tree using a replication resource.
Login to iRODS under the administrator account (default is irods).
You can do this on either catalog providers or consumers.
Run the following commands to create a replication hierarchy and delete the default resource.
Verify the resource hierarchy:
iadmin mkresc BaseResource replication
iadmin mkresc Resource1 'unixfilesystem' Resource1.example.org:/var/lib/irods/Vault
iadmin mkresc Resource2 'unixfilesystem' Resource2.example.org:/var/lib/irods/Vault
iadmin addchildtoresc BaseResource Resource1
iadmin addchildtoresc BaseResource Resource2
iadmin rmresc demoResc
iadmin rmresc Resource1Resource
iadmin rmresc Resource2Resource$ ilsresc --tree
BaseResource:replication
|____Resource1
|____Resource2
Update Default Resources
We have removed demoResc which was on the catalog provider.
Let's update the default resources in all of the /etc/irods/core.re files.
acSetRescSchemeForCreate {msiSetDefaultResc("BaseResource","null"); }
acSetRescSchemeForRepl {msiSetDefaultResc("BaseResource","null"); }

Setup a Client
Install iRODS CLI on CLI1.example.org:
Create ~/.irods/irods_environment.json and have it connect to the LoadBalancer.example.org and use BaseResource as the default resource.
Run iinit to confirm the connection succeeds.
myuser@CLI1:~$ sudo apt-get install irods-icommands{
"irods_default_resource": "BaseResource",
"irods_host": "LoadBalancer.example.org",
"irods_port": 1247,
"irods_user_name": "rods",
"irods_zone_name": "tempZone"
}
Testing
- Put a file into iRODS
- Verify that it has been stored on both catalog consumers.
- Verify that it has been stored on both catalog consumers.
- Bring one catalog consumer down
- Run iget to retrieve the data object just uploaded.
- You may have to select the replica number (iget -n) when retrieving the data object.
- If a resource resident on a catalog consumer is not yet marked 'down' in the catalog, your request may still be routed to the server that cannot answer.
- Run iget to retrieve the data object just uploaded.
- Bring one catalog provider down
- Verify that the iCommands still work.

UGM 2018 - High Availability
By iRODS Consortium
UGM 2018 - High Availability
iRODS User Group Meeting 2018 - Advanced Training Module
- 1,728

