
JavaEE workshop #6
Viktor Martiš
(Factory pattern, JPA, spring-data-jpa)
Previous workshop
- Logging
- Bean lifecycle
- Exception handling
- Testing
Content
- Factory pattern
- JPA
- spring-data-jpa
Design pattern - factory
- creation patterns
- 3 concepts
- Factory
- Factory method
- Abstract factory
- differences
- object/relational mapping facility for managing relational data in Java applicationBullet Two
-
consists of four areas:
-
The Java Persistence API
-
The query language
-
The Java Persistence Criteria API
-
Object/relational mapping metadata
-
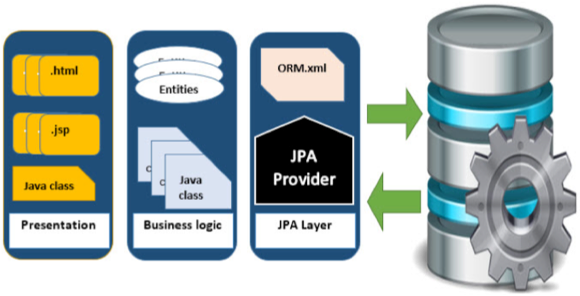
JPA Providers
- JPA is open source API
- Hibernate, Eclipselink, Toplink, OpenJpa etc.
- Spring Data JPA - not JPA provider but framework over JPA
JPA architecture
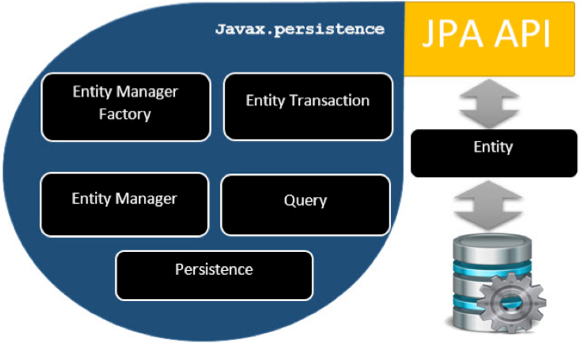
JPA Architecture
| EntityManagerFactory | This is a factory class of EntityManager. It creates and manages multiple EntityManager instances. |
| EntityManager | It is an Interface, it manages the persistence operations on objects. It works like factory for Query instance. |
| Entity | Entities are the persistence objects, stores as records in the database. |
| EntityTransaction | It has one-to-one relationship with EntityManager. For each EntityManager, operations are maintained by EntityTransaction class. |
| Persistence | This class contain static methods to obtain EntityManagerFactory instance. |
| Query | This interface is implemented by each JPA vendor to obtain relational objects that meet the criteria. |
JPA mapping - annotations
| @Entity | Specifies to declare the class as entity or a table. |
| @Table | Specifies to declare table name. |
| @Basic | Specifies non constraint fields explicitly. |
| @Embedded | Specifies the properties of class or an entity whose value instance of an embeddable class. |
| @Id | Specifies the property, use for identity (primary key of a table) of the class. |
| @GeneratedValue | Specifies, how the identity attribute can be initialized such as Automatic, manual, or value taken from sequence table. |
| @Transient | Specifies the property which in not persistent i.e. the value is never stored into database. |
JPA mapping - annotations
| @Column | Used to specify column or attribute for persistence property. |
| @SequenceGenerator | used to define the value for the property which is specified in @GeneratedValue annotation. It creates a sequence. |
| @TableGenerator | Used to specify the value generator for property specified in @GeneratedValue annotation. It creates a table for value generation. |
| @AccessType | Used to set the access type. If you set @AccessType(FIELD) then Field wise access will occur. If you set @AccessType(PROPERTY) then Property wise assess will occur. |
| @JoinColumn | Used to specify an entity association or entity collection. This is used in many- to-one and one-to-many associations. |
JPA mapping - annotations
| @UniqueConstraint | Used to specify the field, unique constraint for primary or secondary table. |
| @ColumnResult | References the name of a column in the SQL query using select clause. |
| @ManyToMany, @ManyToOne, @OneToMany, @OneToOne |
Used to define a many-to-many relationship between the join Tables. |
| @NamedQueries | Used for specifying list of named queries. |
| @NamedQuery | Used for specifying a Query using static name. |
Java bean validation - JSR-303
- constraints in the form of annotations placed on a field, method, or class
- Hibernate validator - reference implementation 1.1
public class Car {
@NotNull
private String manufacturer;
@NotNull
@Size(min = 2, max = 14)
private String licensePlate;
@Min(2)
private int seatCount;
// ...
}JPA - bean conventions
-
Bean contains the default constructor.
-
Non-Boolean property contains getter and setter methods.
-
Boolean property contain setter and is method.
-
Getter method of any property should start with small lettered ‘get’ (java method convention).
-
Setter method of any property should start with small lettered ‘set’ (java method convention).
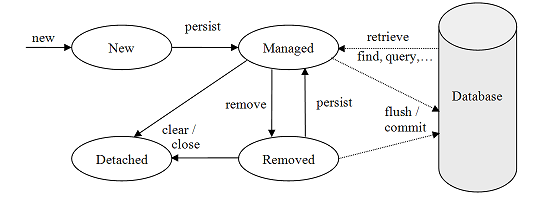
JPA Entity Lifecycle
- managed vs detached
- entity updates in active transaction are persisted
- lazy loading works only in active transaction
JPA - JPQL
- Java Persistence Query Language defined in JPA specification.
- based on SQL syntax
- won’t affect the database directly
- SQL like syntax
- SQL works directly against relational database tables, JPQL works with Java classes and instances
- aggregate functions (COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX)
- BETWEEN, LIKE
Query query = entitymanager.createQuery("Select UPPER(e.ename) from Employee e ORDER BY e.ename ASC");
List<String> list = query.getResultList();JPA - criteria API
- alternative way for defining JPA queries
- useful for building dynamic queries
EntityManager em = ...;
CriteriaBuilder cb = em.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Country> cq = cb.createQuery(Country.class);
Root<Country> country = cq.from(Country.class);
cq.select(country);
TypedQuery<Cuntry> q = em.createQuery(cq);
List<Country> allCountries = q.getResultList()JPA links
- http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/partpersist.htm
- http://www.tutorialspoint.com/jpa/
- http://www.java2s.com/Tutorials/Java/JPA/index.htm
- http://www.slideshare.net/thjanssen/performance-tuning-with-jpa-21-and-hibernate-geecon-prague-2015
- http://www.slideshare.net/osa_ora/jpa-21-performance-tuning-tips
- https://blogs.oracle.com/theaquarium/entry/jpa_2_1_entity_graphs
- http://www.cs.au.dk/~csj/files/dDB/slides/Hibernate%20and%20ORM%20overview.pdf
- https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/persistence-cache001.htm#GKJIO
- http://www.thoughts-on-java.org/jpa-21-entity-graph-part-1-named-entity/
- http://www.radcortez.com/jpa-entity-graphs/
- provides repository support for JPA
- Uses Hibernate underhood
- tutorial 1
- tutorial 2
Spring boot + data-jpa
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot
/spring-boot-starter-data-jpa -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.postgresql/postgresql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.2.8</version>
</dependency>
#application.properties
spring.jpa.database=POSTGRESQL
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.default_schema=ita2019
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost/ita2019
spring.datasource.username=ita2019
spring.datasource.password=ita2019
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.initialization-mode=never- data layer of n-tier architecture
- Interface extends Repository or any child e.g. JpaRepository
- can be extended
Q & A
ITA-05-Java W6
By IT-absolvent
ITA-05-Java W6
Workshop #6
- 498



