JavaEE workshop #9
Kuba Hejda
(Strategy pattern, Microservices architecture, Spring cloud basics)

Previous workshop
-
Web Services
-
Swagger/OpenApi
Contents
- IDEA shortcut: refactoring - Ctrl+Alt+Shift+T
- Strategy pattern
- Monolith vs Microservices architecture
- Spring cloud
-
IDEA shortcut:
- within a class press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+T
- refactoring
Strategy pattern
- we need a different behavior based on the subject type but under the same interface
- example
Application achitecture
- Different approaches for different use-cases
- The decision can affect the success of the whole project
- Not a general rule
- Often based on clients requirements, runtime abilities and the budget
Application achitecture
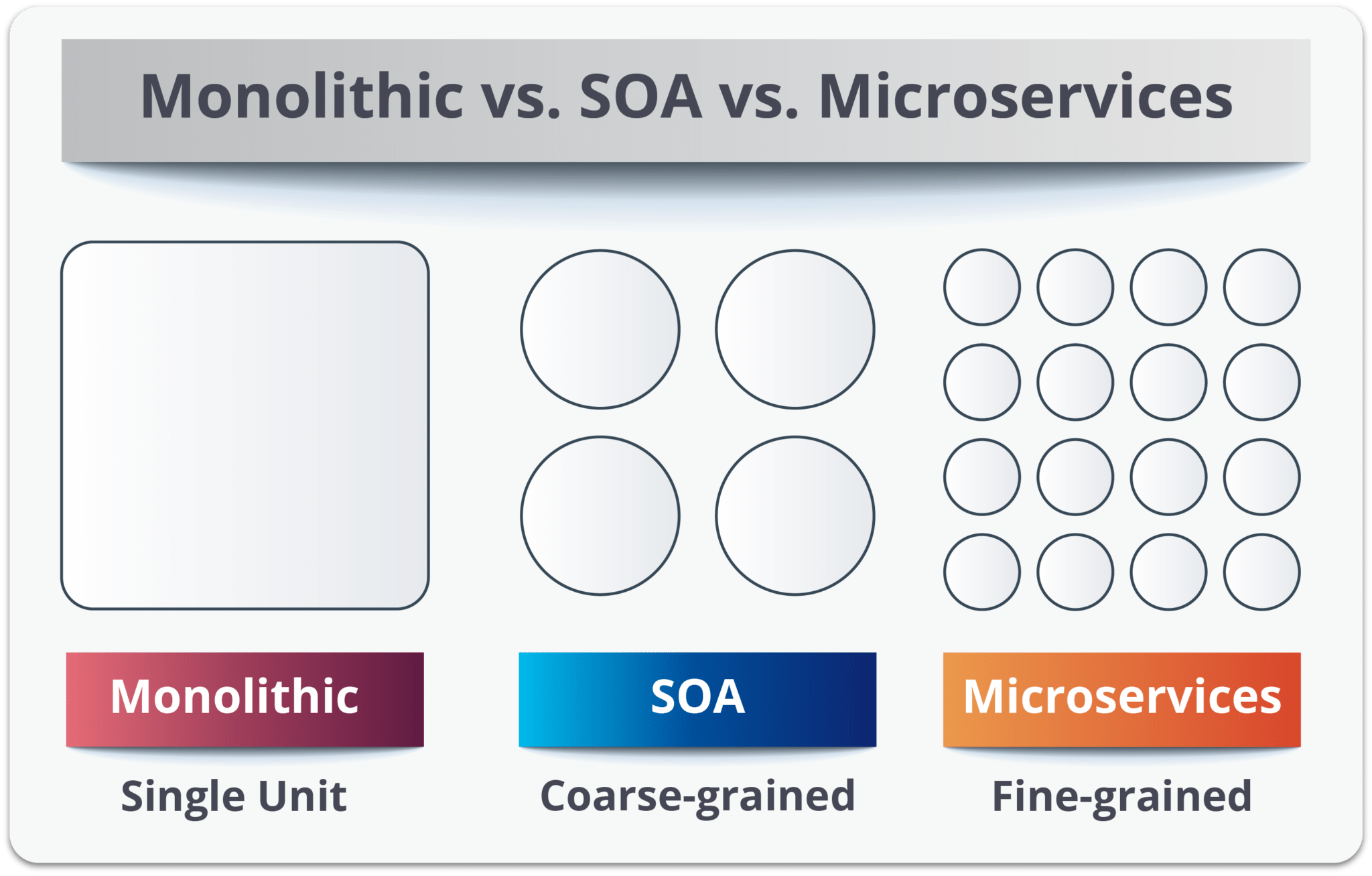
Application achitecture
- Monolith
- advantages
- easier to maintain, learn and develop on smaller projects
- easier deployment and integration
- faster interoperability between modules
- disadvantages
- on larger projects can be a mess, harder to test
- unable to scale only the module which is under load
- on larger projects a lot on conflicts especially in the beginning of the implementation
- advantages
Application achitecture
- Microservices
- advantages
- on larger project each part of the development team can focus on its own service
- great for horizontal scaling, balancing of the load, out-of-the box prepared to run in cloud
- disadvantages
- higher demands on architecture and preparation
- needs more to work properly (load balancing, routing, higher resources), especially in the early stage of the project
- advantages
Spring cloud
- provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus, one-time tokens, global locks, leadership election, distributed sessions, cluster state).
-
Distributed/versioned configuration, Service registration and discovery, Routing, Service-to-service calls, Load balancing, Circuit Breakers, Global locks, Leadership election and cluster state, Distributed messaging
Spring cloud
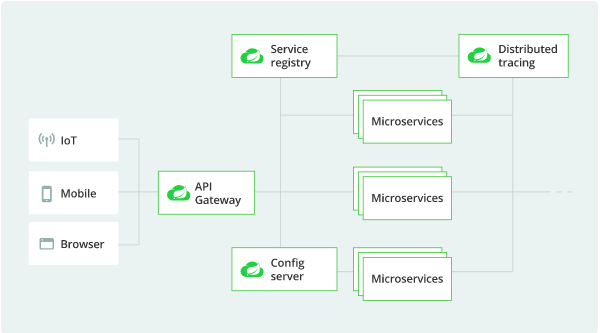
Service registry
- In the cloud, applications can’t always know the exact location of other services.
- A service registry, such as Netflix Eureka, or a sidecar solution, such as HashiCorp Consul, can help. Spring Cloud provides DiscoveryClient implementations for popular registries such as Eureka, Consul, Zookeeper, and even Kubernetes' built-in system.
- There’s also a Spring Cloud Load Balancer to help distribute the load carefully among service instances.
API Gateway
-
With so many clients and servers in play, it’s often helpful to include an API gateway in your cloud architecture.
-
A gateway can take care of securing and routing messages, hiding services, throttling load, and many other useful things.
-
Spring Cloud Gateway gives a precise control of the API layer, integrating Spring Cloud service discovery and client-side load-balancing solutions to simplify configuration and maintenance.
Cloud configuration
-
Many services need different configurations which cannot be stored inside cloud apps
-
The configuration has to be flexible enough to cope with multiple applications, environments, and service instances, as well as deal with dynamic changes without downtime
-
SpringCloudConfig offers solution to these problems, can serve config from the git or filesystem
Tracing
-
Debugging distributed applications can be complex and take a long time.
-
For any given failure, you might need to piece together traces of information from several independent services.
-
Spring Cloud Sleuth can instrument applications in a predictable and repeatable way. And when used in conjunction with Zipkin, you can zero in on any latency problems you might have.
Q&A
ITA-05-Java W09
By IT-absolvent
ITA-05-Java W09
Workshop #9
- 583



