JavaEE workshop #6
Kuba Hejda
(flyway, JPA - advance, DTO)

Agenda
- Flyway
- Builder design patern
-
JPA
- Entity lifecycle
- JPQL and criteria API
- Relations
- Fetch type
- Named queries
- DTO and transformations
Design pattern: Builder
- object creation pattern
- solution to the telescoping constructor anti-pattern, that occurs when the increase of object constructor parameter combination leads to an exponential list of constructors
Flyway
- Spring boot configuration, Spring documentation
- migrations
- Alternative - liquibase
JPA architecture
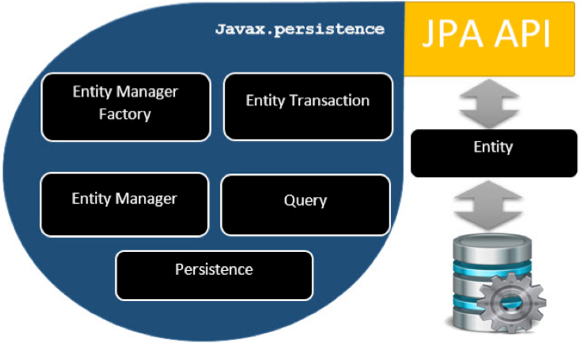
JPA Architecture
| EntityManagerFactory | This is a factory class of EntityManager. It creates and manages multiple EntityManager instances. |
| EntityManager | It is an Interface, it manages the persistence operations on objects. It works like factory for Query instance. |
| Entity | Entities are the persistence objects, stores as records in the database. |
| EntityTransaction | It has one-to-one relationship with EntityManager. For each EntityManager, operations are maintained by EntityTransaction class. |
| Persistence | This class contain static methods to obtain EntityManagerFactory instance. |
| Query | This interface is implemented by each JPA vendor to obtain relational objects that meet the criteria. |
JPA Entity Lifecycle
- managed vs detached
- entity updates in active transaction are persisted
- lazy loading works only in active transaction
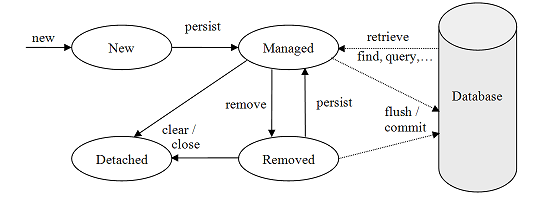
JPA - EntityManager
| find(Class<T> entityClass, Object primaryKey) | Find by primary key. |
| getReference(Class<T> entityClass, Object primaryKey) | Get an instance, whose state may be lazily fetched. |
| persist(Object entity) | Make an instance managed and persistent. |
| merge(T entity) | Merge the state of the given entity into the current persistence context. |
| remove(Object entity) | Remove the entity instance. |
| refresh(Object entity) | Refresh the state of the instance from the database, overwriting changes made to the entity, if any. |
| flush() | Synchronize the persistence context to the underlying database. |
| createQuery(String qlString) | Create an instance of Query for executing a Java Persistence query language statement. |
| createNamedQuery(String name) | Create an instance of Query for executing a named query (in the Java Persistence query language or in native SQL). |
JPA - @MappedSuperclass
- Designates a class whose mapping information is applied to the entities that inherit from it. A mapped superclass has no separate table defined for it.
@MappedSuperclass
public class AbstractEntity {
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", columnDefinition = "serial")
@Id
private Long id;JPA - Inheritance Strategies
- SINGLE_TABLE
- makes all classes fields (both super and sub classes) and map them down into a single table
- JOINED_TABLE
- share the referenced column which contains unique values to join the table
- TABLE_PER_CONCRETE_CLASS
- create a table for each sub entity. Table will contain null records
@Entity
@Inheritance( strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
public class User {
JPA - Relations
- Unidirectional vs bidirectional
- Side owner
- Relation types
- One to One
- One to Many
- Many to One
- Many to Many
JPA - entity Relationships
//unidirectional example
@Entity
public static class Classroom {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String number;
@OneToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "classroom_id")
private Blackboard blackboard;
...JPA - entity Relationships
-
@OneToMany
- If doesn’t have a mirroring @ManyToOne association on the child side, the @OneToMany association is unidirectional. If there is a @ManyToOne association on the child side, the @OneToMany association is bidirectional
- with @JoinColumn hibernate doesn't create database join table.
JPA - entity Relationships
- @OneToMany with Joining table
@Entity
public class Classroom {
@Id
public Long id;
@OneToMany
@JoinTable(
name="ClassroomStudents",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn( name="classroom_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn( name="student_id")
)
public Set<Student> students;
}
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
public Long studentId;
}JPA - entity Relationships
- @OneToMany with direct foreign key on subentity
@Entity
public class Classroom {
@Id
public Long id;
@OneToMany
@JoinColumn(
name = "classroom_id",
referencedColumnName = "id"
)
public Set<Student> students;
}
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
public Long studentId;
}JPA - entity Relationships
@Entity(name = "Person")
public static class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
public Person() {
}
}
@Entity(name = "Phone")
public static class Phone {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String number;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "person_id",
foreignKey = @ForeignKey(name = "PERSON_ID_FK")
)
private Person person;
...
}JPA - entity Relationships
@Entity(name = "Employee")
public static class Employee {
@Id
private Long id;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(
name = "r_employee_project",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "id_employee"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "id_project")
)
private List<Project> projects = new ArrayList<>();
...
}
@Entity(name = "Project")
public class Project {
@Id
private Long id;
...
}JPA - named queries
- @NamedQuery annotation define query with a predefined unchangeable query string
- improve code organization by separating the JPQL query strings from POJO
@Entity
@Table
@NamedQuery(query = "Select e from Employee e where e.eid = :id", name = "find employee by id")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int eid;
private String ename;
private double salary;
private String deg;Query query = entitymanager.createNamedQuery("find employee by id");
query.setParameter("id", 1204);
List<Employee> list = query.getResultList( );JPA - Eager vs. Lazy Loading
- Eager fetching - fetching the whole record while finding the record using Primary Key.
- Lazy fetch - It checks for the availability of underlying entity/entities and holds the primary key. When getter for this property is called within transaction on a managed entity, then the attribute is loaded dynamically
- Fetch join - enables the fetching of an association as a side effect of the execution of a query
Swagger / OpenAPI
- A way to communicate how the API should look like
- Why ?
- contract first
- code-generation
- documentation
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.6.9</version>
</dependency>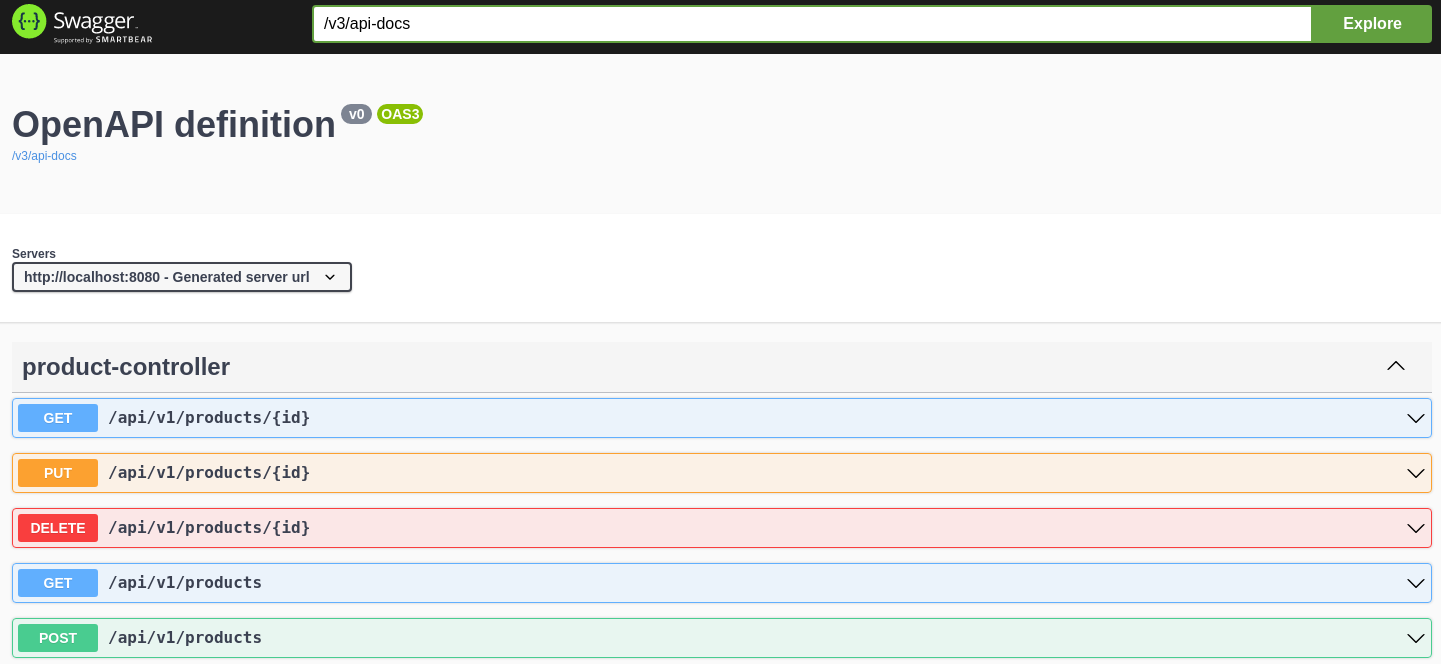
Q & A
ITA 08 - Workshop 06
By IT-absolvent
ITA 08 - Workshop 06
Workshop #6
- 400



