Spring framework
Viktor Martiš
Content
- Spring framework introduction
- IoC
- Spring framework family
- Beans, lifecycle
- Spring framework configuration
- Spring framework in XMS and STATS
Spring framework - introduction
-
popular application development framework for enterprise Java
-
first release October 2002
-
current version 5.0.1.RELEASE
-
what's new in 5.x
-
Features
-
Dependency Injection
-
Aspect-Oriented Programming including Spring's declarative transaction management
-
Spring MVC web application and RESTful web service framework
-
Foundational support for JDBC, JPA, JMS
-
Much more…
-
Spring platform
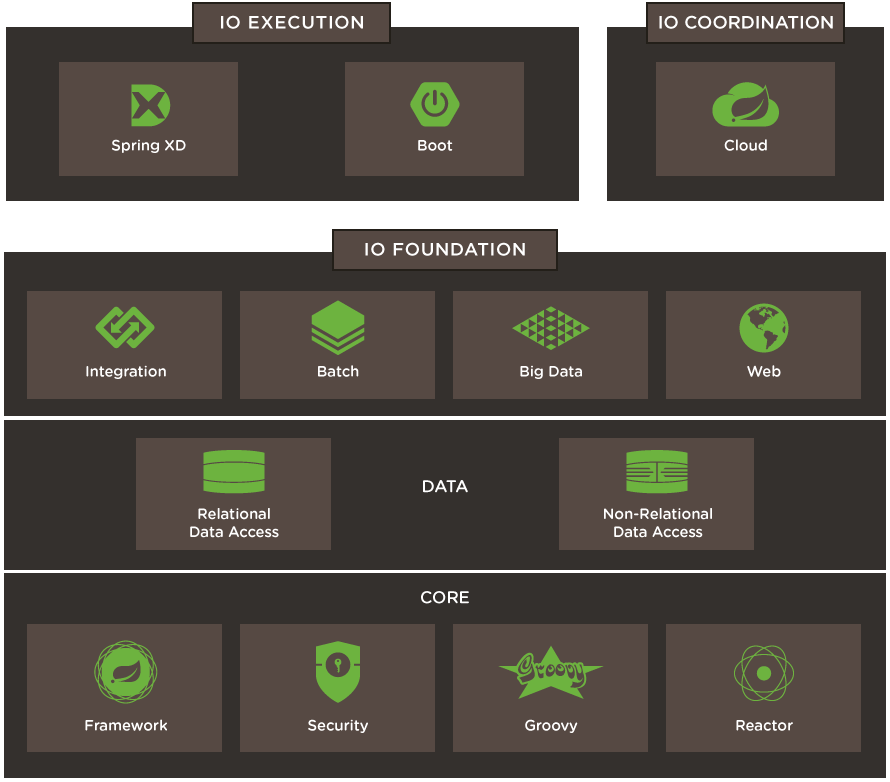
Spring modules
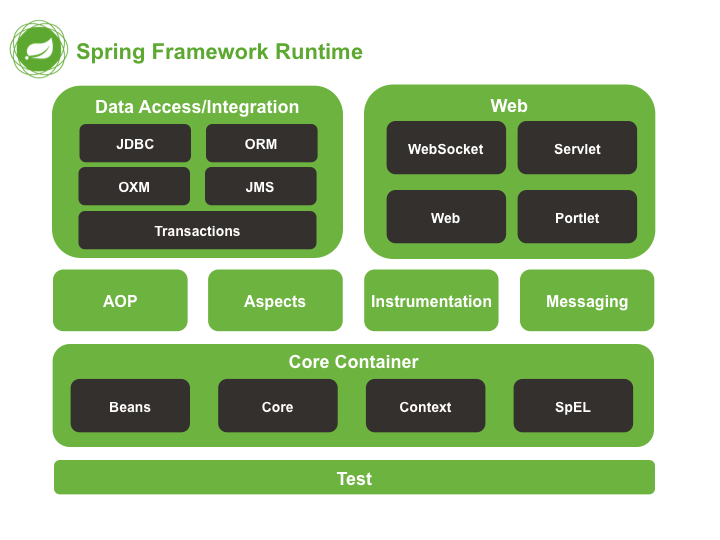
Spring - benefits
- enables developers to develop enterprise-class applications using POJOs.
- organized in a modular fashion.
- easy tesing
- web framework is a well-designed web MVC framework
- "Lightweight" IoC containers
- provides a consistent transaction management
-
Inversion of control (IoC) is a programming technique in which object coupling is bound at run time by an assembler object and is typically not known at compile time using static analysis. In order for the assembler to bind objects to one another, the objects must possess compatible abstractions.
- is a concept in application development
- "don’t call me, I’ll call you"
- one form is Dependency Injection (DI)
Inversion of control
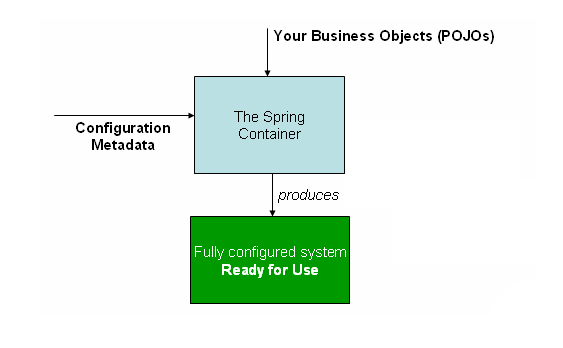
INVERSION OF CONTROL
-
The Spring container is at the core of the Spring Framework.
-
The Spring container uses dependency injection (DI) to manage the components that make up an application.
-
The container will create the objects, wire them together, configure them, and manage their complete lifecycle from creation till destruction.
-
The container gets its instructions on what objects to instantiate, configure, and assemble by reading configuration metadata provided. The configuration metadata can be represented either by XML, Java annotations, or Java code.
DEPENDENCY INJECTION CONTAINERS
- Spring BeanFactory Container
This is the simplest container providing basic support for DI. There are a number of implementations of the BeanFactory interface that come supplied straight out-of-the-box with Spring. The most commonly used BeanFactory implementation is the XmlBeanFactory class.
- Spring ApplicationContext Container
The ApplicationContext includes all functionality of the BeanFactory, it is generally recommended over the BeanFactory. It adds more enterprise-specific functionality such as the ability to resolve textual messages from a properties file and the ability to publish application events to interested event listeners.
Beans
-
The objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans.
A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. These beans are created with the configuration metadata that you supply to the container, for example, in the form of XML <bean/> definitions, in class form @Bean annotation, which you have already seen in previous chapters.
BEANS - DEFINITION
-
The bean definition contains the information called configuration metadata which is needed for the container to know the followings:
- How to create a bean
-
Bean's lifecycle details
-
Bean's dependencies
Bean definition - FactoryBean
- Factory pattern for bean creation
- Split creation logic from configuration class
- Testable
BEANS - LIFECYCLE
The life cycle of a Spring bean is easy to understand.
When a bean is instantiated, it may be required to perform some initialization to get it into a usable state.
When the bean is no longer required and is removed from the container, some cleanup may be required.
BEANS - LIFECYCLE - INITIALIZATION
The org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean interface specifies a single method:
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;In the XML-based configuration metadata, you can use the init-method attribute to specify the name of the method that has a void no-argument signature.
<bean id="..." class="..." init-method="init"/>Annotate the method with @PostConstruct
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
...
}BEANS - LIFECYCLE - DESTRUCTION
The org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean interface specifies a single method:
In the XML-based configuration metadata, you can use the destroy-methodattribute to specify the name of the method that has a void no-argument signature.
Annotate the method with @PreDestroy
void destroy() throws Exception;<bean id="..." class="..." destroy-method="destroy"/>@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
...
}BEANS - MULTIPLE LIFECYCLE MECHANISMS
-
Multiple lifecycle mechanisms configured for the same bean are called in the following order:
Initialization: -
Methods annotated with @PostConstruct
-
afterPropertiesSet() as defined by the InitializingBean callback interface
-
A custom configured init() method
Destruction:
-
Methods annotated with @PreDestroy
-
destroy() as defined by the DisposableBean callback interface
-
A custom configured destroy() method
BEANS - SCOPES
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| singleton | This scopes the bean definition to a single instance per Spring IoC container (default). |
| prototype | This scopes a single bean definition to have any number of object instances. |
| request * | This scopes a bean definition to an HTTP request. |
| session * | This scopes a bean definition to an HTTP session. |
| global-session * | This scopes a bean definition to a global HTTP session. |
Prototype scope bean
- can't be autowired in singleton bean
- available from:
- ApplicationContext.getBean()/getBeans()
- ObjectFactory<T>
DEPENDENCY INJECTION & AUTOWIRING
When writing a complex Java application, application classes should be as independent as possible of other Java classes to increase the possibility to reuse these classes and to test them independently of other classes while doing unit testing.
Dependency Injection (or sometime called wiring) helps in gluing these classes together and same time keeping them independent.
Types of configuration
- XML
- Annotations
- Java based configuration - preferred
ANNOTATION BASED CONFIGURATION
Starting from Spring 2.5 it became possible to configure the dependency injection using annotations. So instead of using XML to describe a bean wiring, you can move the bean configuration into the component class itself by using annotations on the relevant class, method, or field declaration.
Annotation injection is performed before XML injection, thus the latter configuration will override
the former for properties wired through both approaches.
ANNOTATION BASED CONFIGURATION
Annotation wiring is not turned on in the Spring container by default. So, before we can use annotation-based wiring, we will need to enable it in our Spring configuration file. So consider to have following configuration file in case you want to use any annotation in your Spring application.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>ANNOTATION BASED CONFIGURATION
| @Autowired | The @Autowired annotation can apply to bean property setter methods, non-setter methods, constructor and properties. |
| @Qualifier | The @Qualifier annotation along with @Autowired can be used to remove the confusion by specifiying which exact bean will be wired. |
| @Required | The @Required annotation applies to bean property setter methods. |
| JSR-250 Annotations | Spring supports JSR-250 based annotations which include @Resource, @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations. |
ANNOTATION BASED CONFIGURATION
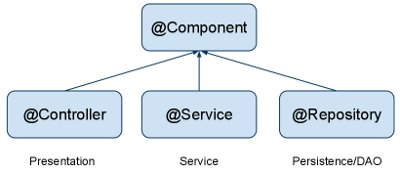
| @Component | generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component |
| @Service | stereotype for service layer |
| @Repository | stereotype for persistence layer |
| @Scope | indicates the name of a scope to use for instances of the annotated type. |
Java based configuration option enables you to write most of your Spring configuration without XML but with the help of few Java-based annotations explained below.
Annotating a class with the @Configuration indicates that the class can be used by the Spring IoC container as a source of bean definitions.
The @Bean annotation tells Spring that a method annotated with @Bean will return an object that should be registered as a bean in the Spring application context.
- @Configuration
- @Import
- @Bean
- @ComponentScan
- ...(spring MVC config, tx config)
- Links
- segregate parts of your application configuration and make it only available in certain environments.
@Configuration
@Profile("production")
public class ProductionConfiguration {
// ...
}- Activation by spring.profiles.active Environment property or command line using the switch --spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb or by calling SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles(…)
- Comprehensive support for Authentication And Authorization
- Protection against common attacks
- Servlet API Integration
- Optional integration with Spring MVC
- Optional Spring Data Integration
- WebSocket Support 4
Spring framework in STATS
- version 4.3.4.RELEASE (latest 4.x - 4.3.13.RELEASE)
- spring-core
- spring-context-support
- spring-context
- spring-tx - remove
- A little unclear to find all @Configuration
- should be unified -> package and class name suffix
- or replace @Configuration with @Import into class main config class StatsApplicationConfig.
- Profiles
- development
Spring framework in XMS
-
version 4.3.4.RELEASE (latest 4.x - 4.3.13.RELEASE)
- spring-core
- spring-expression
- spring-beans
- spring-context
- spring-context-support
- spring-aop ???
- spring-web ???
- spring-tx ???
- Spring security - version 3.2.5.RELEASE (lastest 4.x - 4.2.3.RELEASE)
- Mixed of XML + Java based config
- Profiles
- sso
XMS - spring security
-
XmsWebSecurityConfig
- depends on "sso" profile
Testing with spring - XMS/STATS
- mixed Mockito tests + Spring tests
- mess - there are no rules
Spring framework
By IT-absolvent
Spring framework
- 546



