C++
基礎資料結構
struct
資料包裝
c++ struct
c++ 的struct 可以將資料包裝起來形成新的型別
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct NewType{
int a;
string b;
};
int main(){
NewType x;
x.a = 0;
x.b = "AAAAA";
return 0;
}c++ struct
可以在struct
裡面寫函數
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct NewType{
int a;
string b;
string get(string c){
return to_string(a) + " " + b + c;
}
};
int main(){
NewType x;
x.a = 7122;
x.b = "AAAAA";
cout << x.get("BB") << '\n';
// 7122 AAAAABB
return 0;
}c++ struct
建構子
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct NewType{
int a;
string b;
NewType(){
a = 7122;
b = "AAAAA";
}
};
int main(){
NewType x;
cout << x.a << x.b << '\n';
// 7122AAAAA
return 0;
}c++ struct
帶參數建構子
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct NewType{
int a;
string b;
NewType(int _a, string _b){
a = _a;
b = _b;
}
};
int main(){
NewType x(7122, "AAAAA");
cout << x.a << x.b << '\n';
// 7122AAAAA
return 0;
}Stack
堆疊
stack
- 先進後出
- Push: 放東西進去
- Pop: 拿東西出來
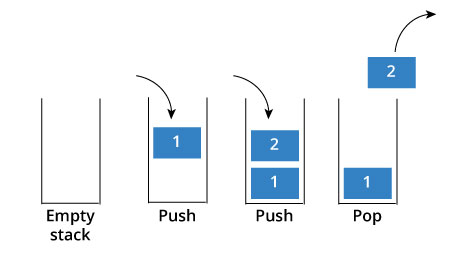
陣列實作
最大的缺點是陣列大小固定
但stack的大小有可能不斷變大
struct stack{
int arr[1005];
int _top;
stack(){
_top = -1;
}
void push(int data){
arr[_top++] = data;
}
void pop(){
--_top;
}
int top(){
return arr[_top];
}
};
// ...
stack st;
st.push(7122);C++ 內建stack
- #include <stack>
- push: \(O(1)\)
- pop: \(O(1)\)
- top: \(O(1)\)
- size: \(O(1)\)
stack
宣告: stack<資料型態> 名稱;
看起來舒服多了
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
stack<int> st;
st.push(7122);
st.push(7123);
cout << st.size() << '\n';
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << '\n';
return 0;
}Stack 經典題
題解
- 火車站其實就是一個stack
- 火車進站和出站的操作就變成push和pop
- 根據出站順序模擬stack的操作判斷是否合法
範例答案
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[1005];
int main(){
int n;
while (cin >> n && n){
while (cin >> a[0] && a[0]){
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
int cnt = 1;
stack<int> st;
bool ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
while (cnt < a[i]) st.push(cnt++);
if (cnt == a[i]) ++cnt;
else if (st.size() && st.top() == a[i]) st.pop();
else{
ans = false;
break;
}
}
cout << (ans ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}Queue
佇列
Queue
- 就像排隊,先進先出
- push: 放東西進去
- pop: 拿東西出來
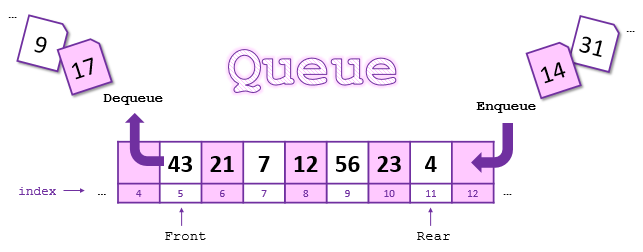
陣列實作
比stack來說會有更多空間上的問題
例如右邊的作法在經過MAXQ次push後就超過陣列範圍了
const int MAXQ = 1005;
struct queue{
int arr[MAXQ];
int _front, _rear;
queue(){
_front = _rear = 0;
}
void push(int data){
arr[_rear++] = data;
}
void pop(){
++_front;
}
int front(){
return arr[_front];
}
};
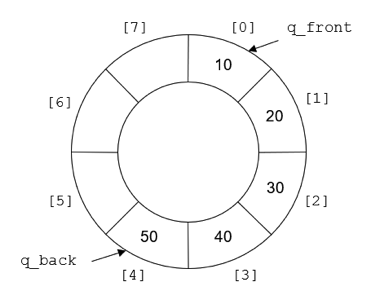
陣列實作2
環狀陣列可以解決這個問題
const int MAXQ = 1005;
struct queue{
int arr[MAXQ];
int _front, _rear;
queue(){
_front = _rear = 0;
}
void push(int data){
arr[_rear] = data;
_rear = (_rear + 1) % MAXQ;
if(_rear == _front)
cout << "full!!\n";
}
void pop(){
_front = (_front + 1) % MAXQ;
}
int front(){
return arr[_front];
}
};
C++ 內建queue
- #include <queue>
- push: \(O(1)\)
- pop: \(O(1)\)
- front: \(O(1)\)
- size: \(O(1)\)
queue
宣告: queue<資料型態> 名稱;
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
queue<int> q;
q.push(7122);
q.push(7123);
cout << q.size() << '\n';
q.pop();
cout << q.front() << '\n';
return 0;
}Stack實作Queue
資料結構課?
stack a
stack b
rear
front
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
stack a
stack b
rear
front
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
push(7)
stack a
stack b
rear
front
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
pop()
stack a
stack b
rear
front
2
3
4
5
6
7
pop()
stack a
stack b
rear
front
3
4
5
6
7
pop()
stack a
stack b
rear
front
7
6
5
4
pop()
實作
用兩個stack就可以完成了。
每個元素只會進出這兩個stack各一次,因此push, pop的時間複雜度都是\(O(1)\)
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct queue{
stack<int> a, b;
void push(int data){
a.push(data);
}
void pop(){
front();
b.pop();
}
int front(){
if (b.size())
return b.top();
while(a.size()){
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
};
c++ vector
動態變長陣列
Segmentation fault
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// long long a[10000000]; // 放這裡比較好
int main(){
long long a[10000000]; // 函數中陣列不能開太大
for(int i = 0; i<10000000; ++i)
a[i] = 1LL*i*i;
return 0;
}一般動態陣列
- 指標
- malloc / calloc / new
- 速度快,但使用上很噁心
int *p = malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
free(p);
int *q = new int[1000];
delete[] q;vector 動了!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<long long> a(10000000);
for(int i = 0; i<10000000; ++i)
a[i] = 1LL*i*i;
return 0;
}c++ vector
- #include <vector>
- 可以像一般陣列一樣使用[]存取
- 可以在尾端增加/減少元素 \(O(1)\)
常用操作
- vector<型態> 名稱(初始長度, 初始值)
- 括號部分可以省略
- push_back(資料): 在尾端加入資料
- \(O(1)\)
- pop_back(): 移除尾端資料
- \(O(1)\)
- back(): 最後回傳尾端資料
- size(): 陣列長度
- clear(): 將所有元素移除
- \(O(1)\)
push_back()
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> v(10, 5);
for(size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
cout << v[i] << ' ';
cout << '\n';
v.clear();
v.push_back(7122);
v.push_back(7123);
for(auto x: v)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}疊代器 iterator
- 類似指標,但不一樣
- 初學者先知道它的存在就行了
疊代器 iterator
vector<int> v(10, 5);
for(vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it){
cout << *it << '\n';
*it = 6;
}
for(auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it){
cout << *it << '\n';
}stack 加速
- c++ 內建的stack速度其實比vector慢
- 但是我們可以透過一些方法讓stack用vector實作
stack<int> A;
stack<int, vector<int>> BHeap
堆
Heap 性質
- 一棵二元樹,每個節點的左右小孩的值都小於等於自己
32
27
11
13
12
11
Binary tree 名詞定義
Parent
Left Child
Right Child
me
Complete binary tree
Complete binary tree
- 一棵二元樹,各層節點全滿,除了最後一層
- 最後一層節點全部靠左。
性質
- 高度為\(\lceil \log_2 n \rceil\)
- 從上到下,左到右依序編號
對於編號\(i\)的節點- left child的編號是
\(i*2+1\) -
right child的編號是
\(i*2+2\) - parent 的編號是
\(\lfloor (i-1)/2 \rfloor\)
- left child的編號是
0
1
2
3
4
Binary Heap
二元堆積
Binary Heap
- 滿足Heap性質的
complete binary tree - 可以存在陣列中
- 用vector!
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 13 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 27 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
binary heap
struct binary_heap{
vector<int> tree;
void push(int data){
// TODO
}
void pop(){
// TODO
}
int top(){
return tree[0];
}
};Binary Heap
- push
- 放在陣列最後面
- 不斷跟parent比
如果比parent值大就交換 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 12 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 27 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 5 |
|---|
| 12 |
Binary Heap
- push
- 放在陣列最後面
- 不斷跟parent比
如果比parent值大就交換 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 13 | 11 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 27 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 5 |
|---|
| 11 |
binary heap: push
void push(int data){
tree.push_back(data);
int id = tree.size() - 1;
while (id != 0){
int parent_id = (id - 1) / 2;
if (tree[id] > tree[parent_id]){
swap(tree[id], tree[parent_id]);
id = parent_id;
} else {
break;
}
}
}Binary Heap
- pop(刪除最大值)
- 用最後一項去取代
- 不斷跟左右小孩比較
和較大的那個交換位置 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 13 | 11 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 27 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 5 |
|---|
| 11 |
Binary Heap
- pop(刪除最大值)
- 用最後一項去取代
- 不斷跟左右小孩比較
和較大的那個交換位置 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 13 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
Binary Heap
- pop(刪除最大值)
- 用最後一項去取代
- 不斷跟左右小孩比較
和較大的那個交換位置 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 13 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
Binary Heap
- pop(刪除最大值)
- 用最後一項去取代
- 不斷跟左右小孩比較
和較大的那個交換位置 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 13 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 13 |
Binary Heap
- pop(刪除最大值)
- 用最後一項去取代
- 不斷跟左右小孩比較
和較大的那個交換位置 - 做到不能做為止
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 11 |
| 0 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 1 |
|---|
| 13 |
| 2 |
|---|
| 12 |
| 3 |
|---|
| 11 |
| 4 |
|---|
| 11 |
binary heap: pop
void pop(){
int id = 0;
while(true){
int left_id = id * 2 + 1;
int right_id = id * 2 + 2;
if (left_id >= tree.size()) break;
int next_id = left_id;
if (right_id < tree.size())
if (tree[left_id] < tree[right_id])
next_id = right_id;
if (tree.back() < tree[next_id]){
tree[id] = tree[next_id];
id = next_id;
} else {
break;
}
}
tree[id] = tree.back();
tree.pop_back();
}複雜度
- push: \(O(\log n)\)
- pop: \(O(\log n)\)
- top: \(O(1)\)
c++ priority_queue
優先佇列
priority_queue
- c++ 內建的binary heap
- #include <queue>
- push()
- pop()
- top()
- size()
priority_queue
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(7122);
pq.push(654);
pq.push(8764);
pq.push(855);
while(pq.size()){
cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
}
return 0;
}自定義小於
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct CMP{
bool operator()(int a, int b){
return a > b;
}
};
int main(){
// 有點長
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, CMP> pq;
pq.push(8764);
pq.push(7122);
while(pq.size()){
cout << pq.top() << '\n';
pq.pop();
}
return 0;
}綜合練習
C++基礎資料結構
By jacky860226
C++基礎資料結構
- 404



