by JS
Wrocław, 22/11/2014
Topics
- Client-Server
- MVC
- ng
Client
- Handles user interaction
- Forwards functional requests to the server
- Designed to be thin, fast, deliver smoothless experience
- So clients tend to be lightweight
Server
- Does the heavy stuff
- Designed to be the Though Guy
- So servers are full of resources
Client - Server: Language?
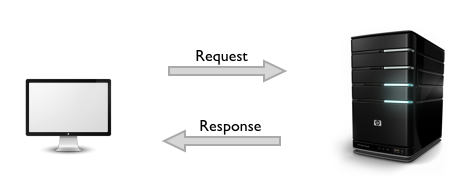
Protocol: HTTP
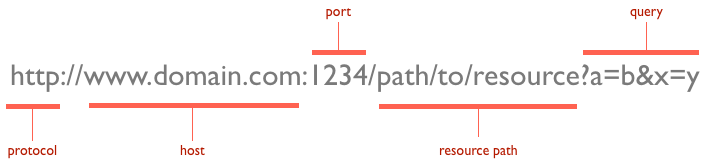
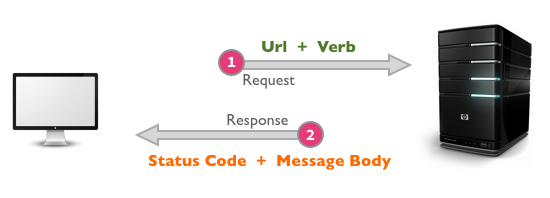
- URLs
- VERBS
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- DELETE
- HEAD
- TRACE
- OPTIONS
- 1XX: Informational Messages
- 2XX: Successful
- 3XX: Redirection
- 4XX: Client Error
- 5XX: Server Error
AJAX
Just another thing to remember
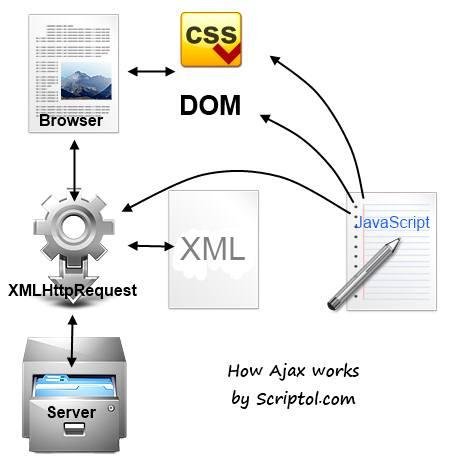
- A as in Asynchronous
- J as in JavaScript
- A as in And
- X as in XML
- There is no full round-trip to the server. No HTTP Request.
- Instead, there is XHR: XmlHTTPRequest that is being sent.
- Asynchronously
- Website doesn't refresh in the browser
Websites: Server Side
- Application is built and displayed to the user
- There are a predefined set of controls/helpers to make HTML/JS rendering easy
- Most events are forwarded to the server to rebuid/update the HTML/JS
- The more the framework is modern, the more server calls are made using AJAX, asynchronously
- Still round-trip to the server is often required to refresh data
- In .NET, two different approaches for Layout: WebForms, MVC
- As for most technological choices, there are pros and cons
- WebForms: easy development using controls, harder maintenance, less control on generated HTML output
- ASP.NET MVC: strict control on the HTML, easier maintenance, longer to write/style/wire-up things
- State vs State-less programming
Server side...
- Complex business logic - protected
- Centralized storage
- Centralized database
- Easy maintenance
- Data behind the firewall
- Easy access: Web Services, Web sockets
- Scalability: You can always add more servers, you can't improve user's browser performance
Client Side
Modern web applications are highly focused on client-side development.
That's because:
- Customer: it's performing better if the workload is distributed to multiple clients rather than cumulated on the server
- Vendor: hardware on client side doesn't cost anything
- Client-side development is getting easier each day
- Saves the network bandwidth
Client Side: Java Script
That's because:
- A lot of JavaScript frameworks have shown up recently (AngularJS, BackboneJS, KnockoutJS, SpineJS, EmberJS, ReactJS....)
- JavaScript has been heavily optimized by all browsers vendors
- JavaScript is implemented by all browsers, on all platforms, what makes it the most accessible technology, like HTML

- Because all client-side frameworks except JS DIED (Microsoft Silverlight, Adobe Flash)
- Because it's cool :]
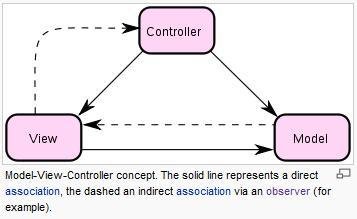
MVC is easy
- Model-View Controller
- Architectural Pattern
- Separates concerns
- Enables testability
- Defines interaction flow
- Model: Data, Data-oriented logic, Business Logic
- View: The output, mostly Visual
- Controller: As its name suggests, controls the user input, chooses which view to render, controlling logic
MVC: 10 beers later

BA-ng BA-ng
< >
AngularJS
Superheroic JavaScript MVW Framework
https://angularjs.org
MVW?
So, what actually MVW stands for?
Having said, I'd rather see developers build kick-ass apps that are well-designed and follow separation of concerns, than see them waste time arguing about MV* nonsense. And for this reason, I hereby declare AngularJS to be MVW framework - Model-View-Whatever. Where Whatever stands for "whatever works for you".
Igor Minar, Google
How to begin?
Get some IDE.
Or use notepad.
That's boring
- People always need to style their app
- There's an easy way to do this
Get Bootstrap*
*http://getbootstrap.com/
First demo time.
AngularJS
- Made by Google
- AngularJS:
- 'Angular' as angular brackets from HTML: <>
- 'JS' as JavaScript
- Designed to take advantage of client-side computation
- Unlike other frameworks, no imperative DOM* manipulation
- Declarative programming for HTML
* Document Object Model
Main concepts
- Data binding
- Dependency injection
- Routing
Main Elements
- modules
- controllers
- binding
- directives
- services
- routing
Noch mal demo.
jQuery vs AngularJS
Demo
Exercise: Automatically add new row to the data grid / html table, when a row is filled in.
Another demo.
$watch How the $apply Runs a $digest
- $watch()
- $apply()
- $digest()
Demo again.
Scalable architecture
Listen to the community
- NodeJS
- Grunt
- Bower
- NPM
- ng-boilerplate
Thanks
ngSlides
By Jakub Szumiato
ngSlides
Short introduction to AngularJS MVC Framework
- 377



