Representing Algorithms
Represent algorithms using flow charts
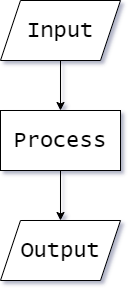
Input-Process-Output
All programs can be broken down into combinations of:
- Inputs
- Processes
- Outputs
Flowcharts
- An algorithm can be represented by a flowchart.
- This is a graphical representation that:
- uses symbols to show each step,
- with arrows showing how to move between each step.
Flowcharts
| Line | An arrow represents control passing between the connected shapes | |
| Process | This shape represents something being performed or done | |
| Sub-routine | This shape represents a subroutine call that will relate to a separate, non-linked flowchart | |
| Input/output | This shape represents the input or output of something into or out of the flowchart | |
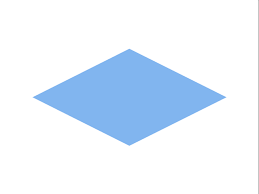
| Decision | This shape represents a decision (Yes/No or True/False) that results in two lines representing the different possible outcomes | |
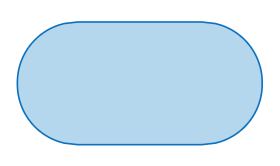
| Terminal | This shape represents the 'Start' and 'End' of the process |



Flowcharts

- All flow charts begin and end with the terminal shape, indicating the start and end of the flow chart.
Flowcharts

- Inputs and outputs are represented by a parallelogram
Flowcharts

- Decision boxes must have two possible outputs:
- True/False
- Yes/No
Flowcharts

- All other processes are represented by a rectangle
Flowcharts

- Where algorithms are decomposed into separate sub-routines, a rectangle with two extra vertical lines is used.
Flowcharts

Questions
- Define the following terms
- Decomposition
- Abstraction
- A programmer is creating software to send and receive encrypted messages via email. Describe how decomposition can be used to allow this problem to be solved.
- A chess club develops a system to store details about games played. For each game, the winner's and loser's names are stored alongside the date that the game was played. Explain how abstraction has been used in the development of this system.
Answers
- Define the following terms
- Decomposition
- Abstraction
- Decomposition is breaking a problem down into smaller sub-problems.
- Once each sub-problem is small and simple enough, it can be tackled individually.
- Abstraction is removing or hiding unnecessary details from a problem, so that the important details can be focused on.
1b Representing Algorithms II
By David James
1b Representing Algorithms II
Computer Science - Fundamentals of Algorithms - Representing Algorithms
- 618



