Computer Networks
- Define what a computer network is.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of computer networks.
- Describe the main types of computer network including:
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN).
Computer Networks
- A computer network is two or more computers or devices that are linked together.
- They are connected either using wires or wirelessly.
- This allows them to communicate with each other and share resources.
- Some additional examples of networked devices are:
- smartphone
- tablets
- games consoles
- wearables

Advantages - Costs
- Reduce hardware costs:
- Share peripheral devices
- Allow a single internet connection to be used by many devices

Advantages - Sharing
- Share information
- Exchange data between computers without using physical media (memory stick, external hard drive)
- Back-up files centrally

Advantages - Security
- Improve security
- Centrally control security
- Maintain the firewall
- Centrally control software updates
- Control which users have access to the network and what resources they can access

Advantages - Mobility
- Improve mobility of users
- Log into any computer and still access the same resources
- Files can be accessed anywhere
- Separate computers are not needed for every user

Disdvantages
- Additional hardware is needed to set up a network and large networks will need a network manager to oversee the system.
- If one machine is infected with malware, it can quickly spread to the other machines on the network.
- Hackers may target a network to gain access to many computers.
- If there is a file server that fails, users will not be able to access their files.

Types of Computer Network
- Personal area network (PAN)
- Local area network (LAN)
- Wide area network (WAN)
Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Connects devices over a very small area
- Range is a few metres (approx. 10 m)
- Usually Bluetooth (short-wave radio)
- Headphones, printer, speakers...
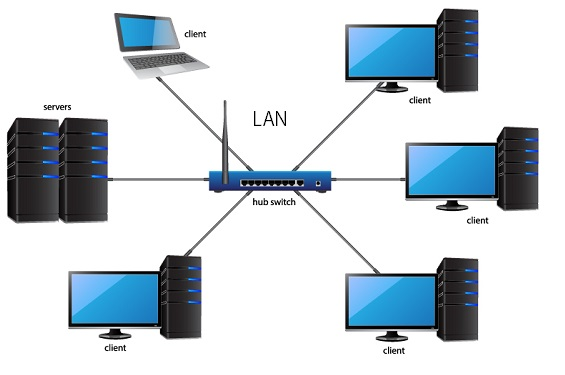
Local Area Network (LAN)
- Connects devices over a small area, usually one site
- Home, school, company office
- The hardware is usually owned by the organisation using the network
- Often uses wired and wireless connections
Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Used by large organisations to connect multiple LAN's over a large geographical area.
- The largest WAN is the Internet.
- The infrastructure (hardware) are usually hired/leased from a telecommunication company.
- Banks are a good example of a WAN, multiple branches all around the country, each has its own local area network connected back to the head office using a wide area network.
- State two advantages of using a computer network.
- State two disadvantages of using a computer network.
- Describe the characteristics of a LAN.
- Give one example of a type of technology used in a PAN.
- Identify two differences between a LAN and a WAN.
Questions
- State two advantages of using a computer network.
Answers
- Sharing hardware devices
- Sharing an internet connection
- Storing files centrally
- Managing software centrally
- Managing security centrally
- Backups managed centrally
- State two disadvantages of using a computer network.
Answers
- Additional hardware is needed to set up the network
- Networking hardware can be expensive
- Malware can spread easily between networked devices
- If a central file server fails, users cannot access their files
- Larger networks will need to be overseen by a network manager
- Describe the characteristics of a LAN.
Answers
- A network in a small geographical area, such as a home, school, office on a single site.
- The hardware is usually owned by the organisation that uses it.
- Often uses both wired and wireless connections.
- Give one example of a type of technology used in a PAN.
Answers
- Bluetooth
- Identify two differences between a LAN and a WAN.
Answers
- A LAN is a network covering a small geographic area; a WAN covers a wide geographic area.
- The networking hardware in a LAN is usually owned and maintained by the organisation that uses it; the connections in a WAN are usually hired or leased from a telecommunications company.
5a Computer Networks
By David James
5a Computer Networks
Computer Science - Computer Networks - Computer Networks
- 952



