React.js

Jaroslav Kubicek
Content
- What you know about JS?
- jQuery - why and why not?
- React.js fundamentals
- Building React.js component tree
- How to deal with application state

- abtracting us from ugly browser native interface
jQuery - when we need it
$.get('http://example.com').then(processData);var httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
httpRequest.open('GET', 'http://example.com');
httpRequest.send();
httpRequest.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (httpRequest.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE) {
if (httpRequest.status === 200) {
processData(httpRequest.responseText);
}
}
};- helping with DOM manipulation
jQuery - when we need it
$(document).on('click', '#button', function () {
var count = $(this).data('clicked-count');
$('#input').value(count);
});- Single page application
- It's just helper library, not framework
- things that jQuery doesn't solve:
- modularity & composability
- managing application state
- splitting application logic and model from visual presentation
jQuery - when it's not sufficient anymore
We need more...

React.js
- Have one job - and it's doing it well
- View in MVC
- abstract us from ugly DOM with really simple interface
- doesn't solve managing application state*

How you should feel right now...
React.js - basics
var CustomButton = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<div className="my-button">
<button>Click me!</button>
</div>
);
}
});
var RootComponent = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<CustomButton />
</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<RootComponent />,
document.getElementById('my-spa')
);React.js - props
class RootComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello {this.props.name}!</h1>
</div>
);
}
}
RootComponent.propTypes = {
name: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired
};
ReactDOM.render(
<RootComponent name={'Jouda'} />,
document.getElementById('my-spa')
);React.js - events
class ButtonSend extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this._onClick = this._onClick.bind(this);
}
_onClick(event) {
doStuffWithSyntethicEvent(event);
this.props.onFormSend();
}
render() {
return (
<button type="submit" onClick={this._onClick}>Submit</button>
);
}
}React.js - state
class CustomButton extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {count: 0};
this._onClick = this._onClick.bind(this);
}
_onClick() {
this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>You clicked {this.state.count} times.</div>
<button type="submit" onClick={this._onClick}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
}React.js - component lifecycle
class CustomButton extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// initialisation
}
componentDidMount() {} // before component is attached to DOM
componentDidMount() {
// after component is attached to DOM
findDOMNode(this) // <div> element
}
// return true/false if component should be updated
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) {}
componentWillUpdate() {} // before component is updated
componentDidUpdate() {} // after component is updated
componentWillUnmount() {} // before element is detached from tree
render() {
return (<div></div>);
}
}React.js - how NOT to deal with state
class Comments extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {items: []};
}
componentDidUpdate() {
$.get('http://example.com/comments').then(function(data) {
this.setState({items: JSON.parse(data)});
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.state.items.map((comment) => <p>{comment}</p>)}
</div>
);
}
}React.js - how to deal with state

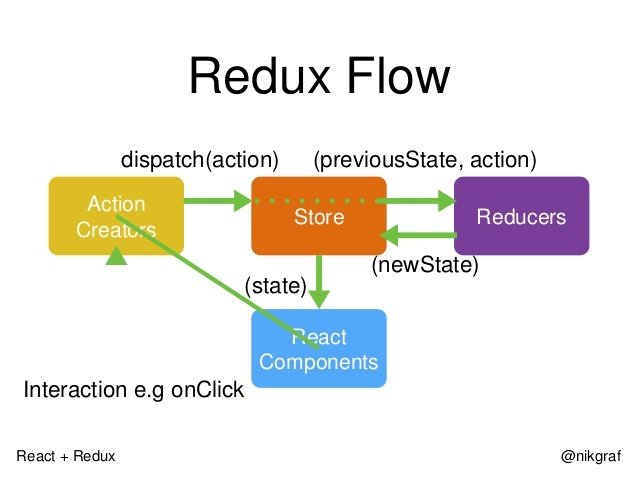
Demo time!

Thanks!
-
React.js: https://facebook.github.io
-
ES2015: http://exploringjs.com/es6/
React.js basics
By Jaroslav Kubíček
React.js basics
- 364



