Training Overview
Jason M. Coposky
@jason_coposky
Executive Director, iRODS Consortium
Training Overview

January 14-16, 2020
CINES
Montpellier, France




Our Membership
























Consortium
Member
Consortium
Member
Following Along
Today's Training
https://slides.com/jasoncoposky
Other Resources
https://slides.com/irods
https://docs.irods.org
https://irods.org/documentation

What is Data Management
A Definition of Data Management
"The development, execution and supervision of plans, policies, programs and practices that control, protect, deliver and enhance the value of data and information assets."
Organizations need a future-proof solution to managing data and its surrounding infrastructure
What is a Policy
A Definition of Policy
A set of ideas or a plan of what to do in particular situations that has been agreed to officially by a group of people...
So how do we do it?
The iRODS Data Management Stack
Core Competencies
Policy
Capabilities
Patterns
Starting at the bottom :: Core Competencies
The underlying iRODS technology categorized into four areas




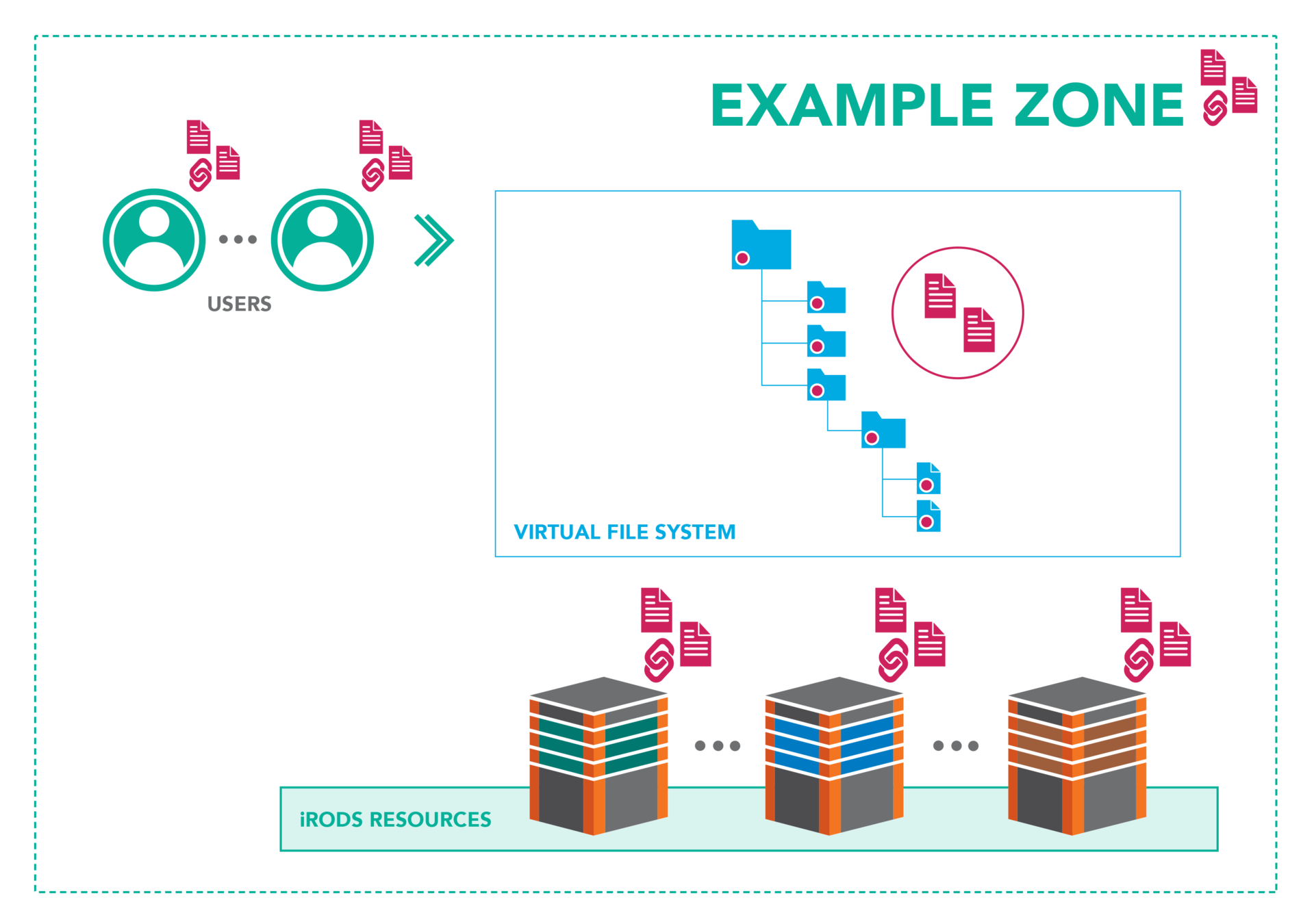
Data Virtualization

Combine various distributed storage technologies into a Unified Namespace
- Existing file systems
- Cloud storage
- On premises object storage
- Archival storage systems
iRODS provides a logical view into the complex physical representation of your data, distributed geographically, and at scale.


Projection of the Physical into the Logical
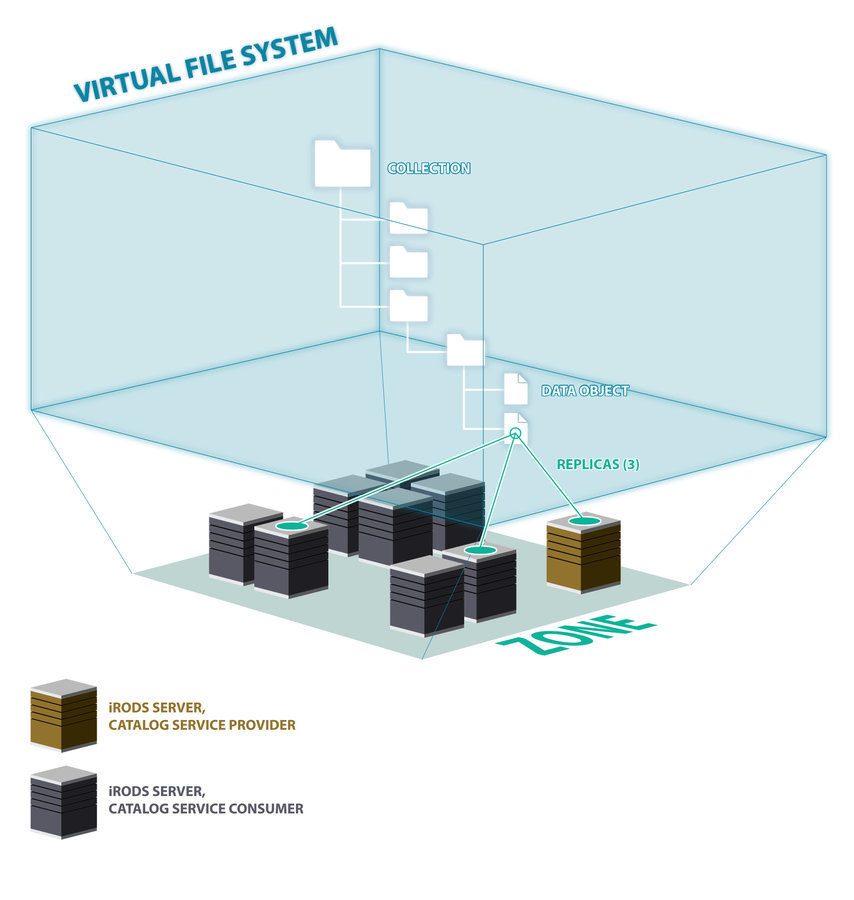
Logical Path
Physical Path(s)

Data Discovery
Attach metadata to any first class entity within the iRODS Zone
- Data Objects
- Collections
- Users
- Storage Resources
- The Namespace
iRODS provides automated and user-provided metadata which makes your data and infrastructure more discoverable, operational and valuable.



Metadata Everywhere

Workflow Automation
Integrated scripting language which is triggered by any operation within the framework
- Authentication
- Storage Access
- Database Interaction
- Network Activity
- Extensible RPC API

The iRODS rule engine provides the ability to capture real world policy as computer actionable rules which may allow, deny, or add context to operations within the system.


Dynamic Policy Enforcement
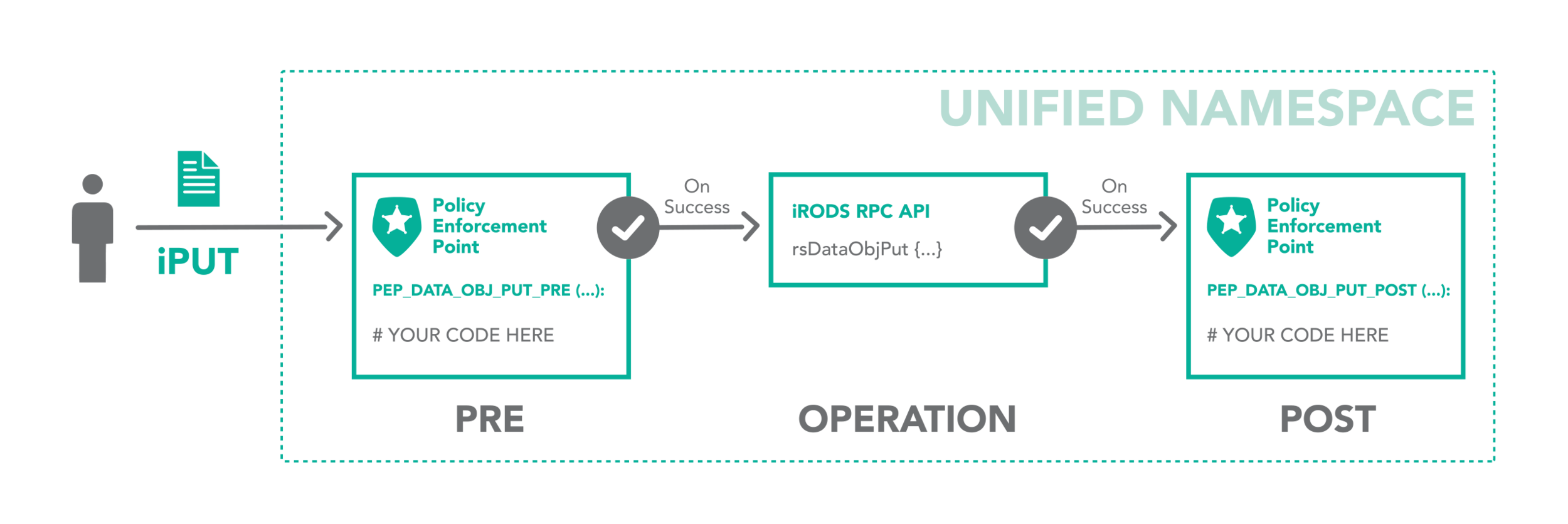
- restrict access
- log for audit and reporting
- provide additional context
- send a notification
The iRODS rule may:

Dynamic Policy Enforcement
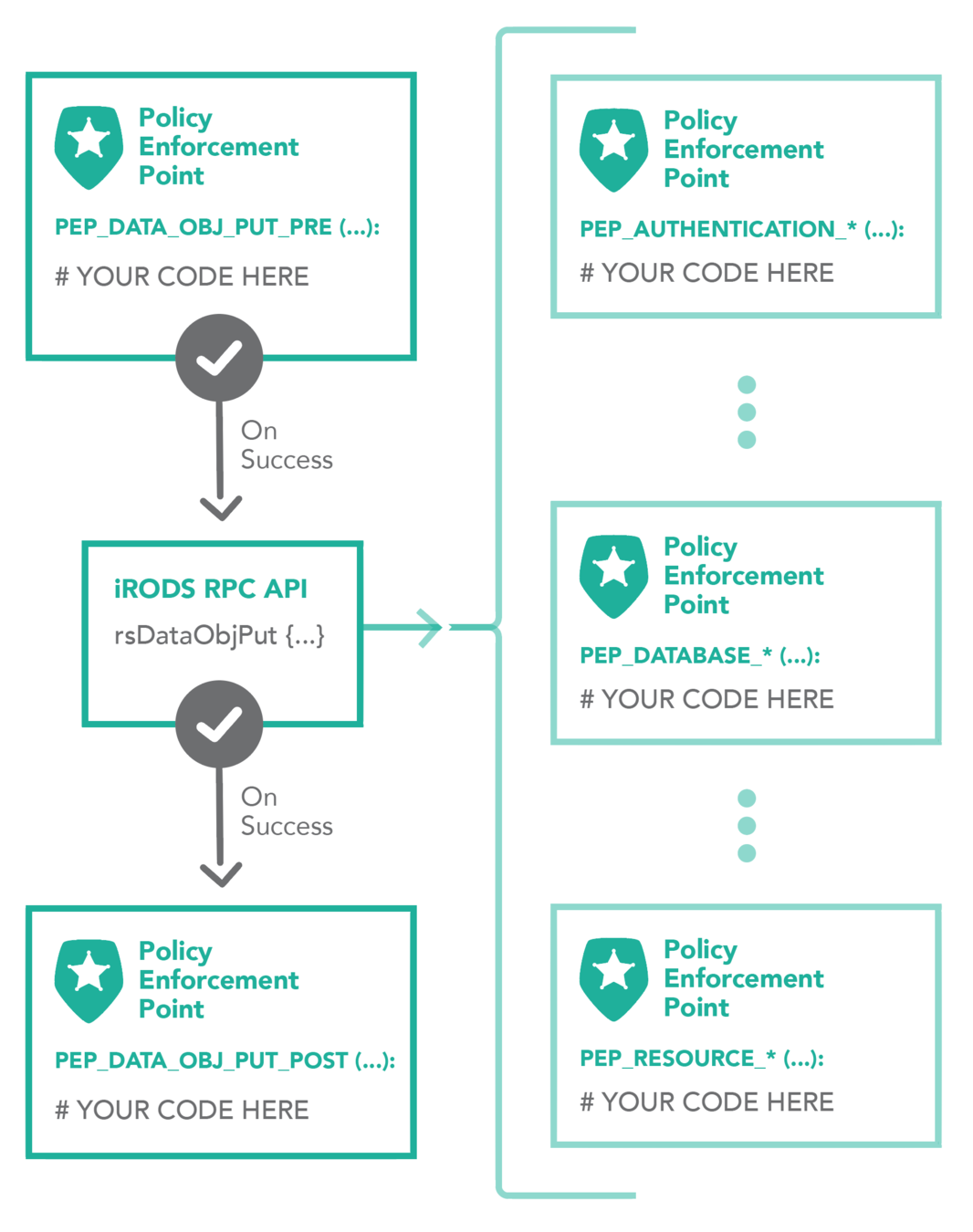
A single API call expands to many plugin operations all of which may invoke policy enforcement
- Authentication
- Database
- Storage
- Network
- Rule Engine
- Microservice
- RPC API
Plugin Interfaces:

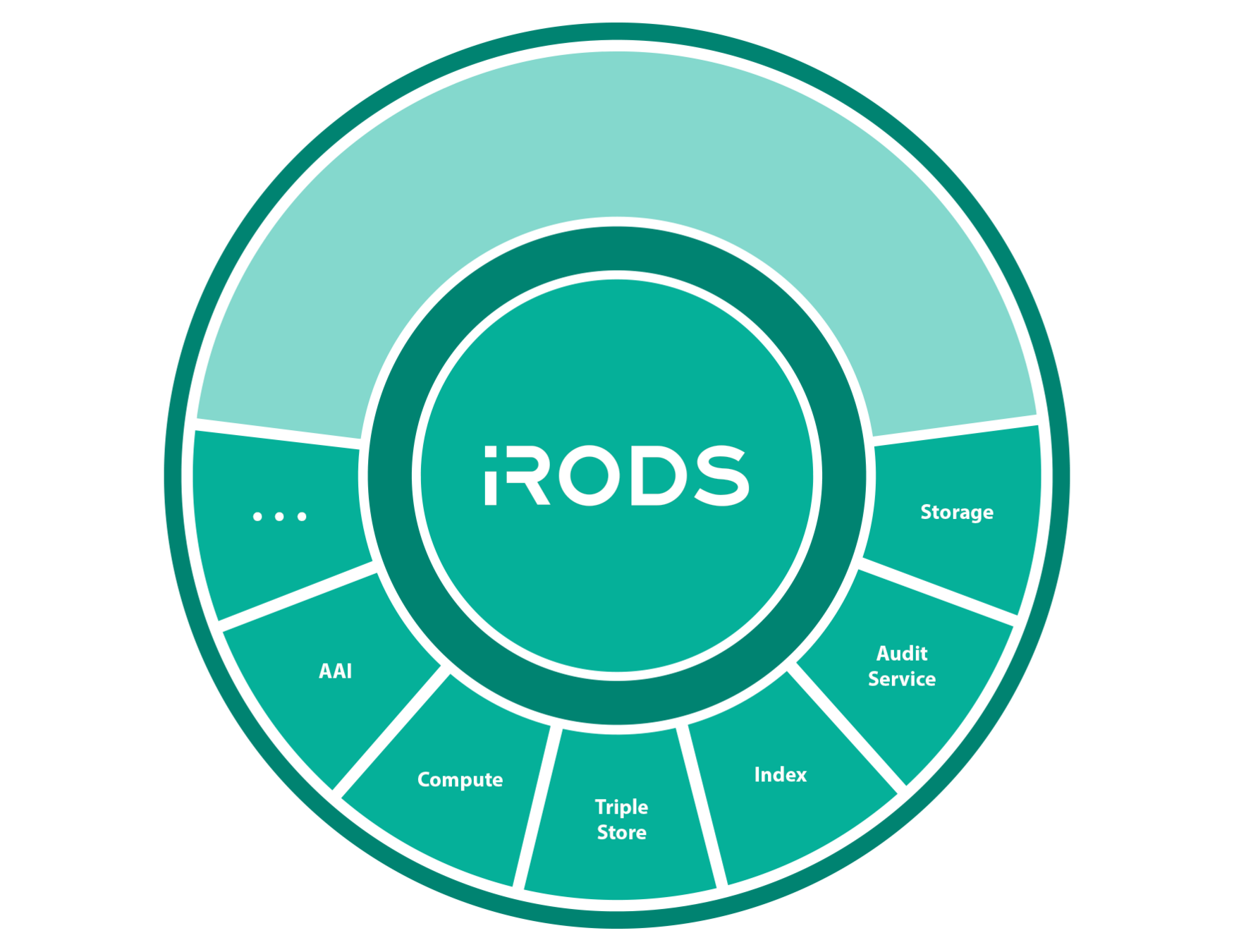
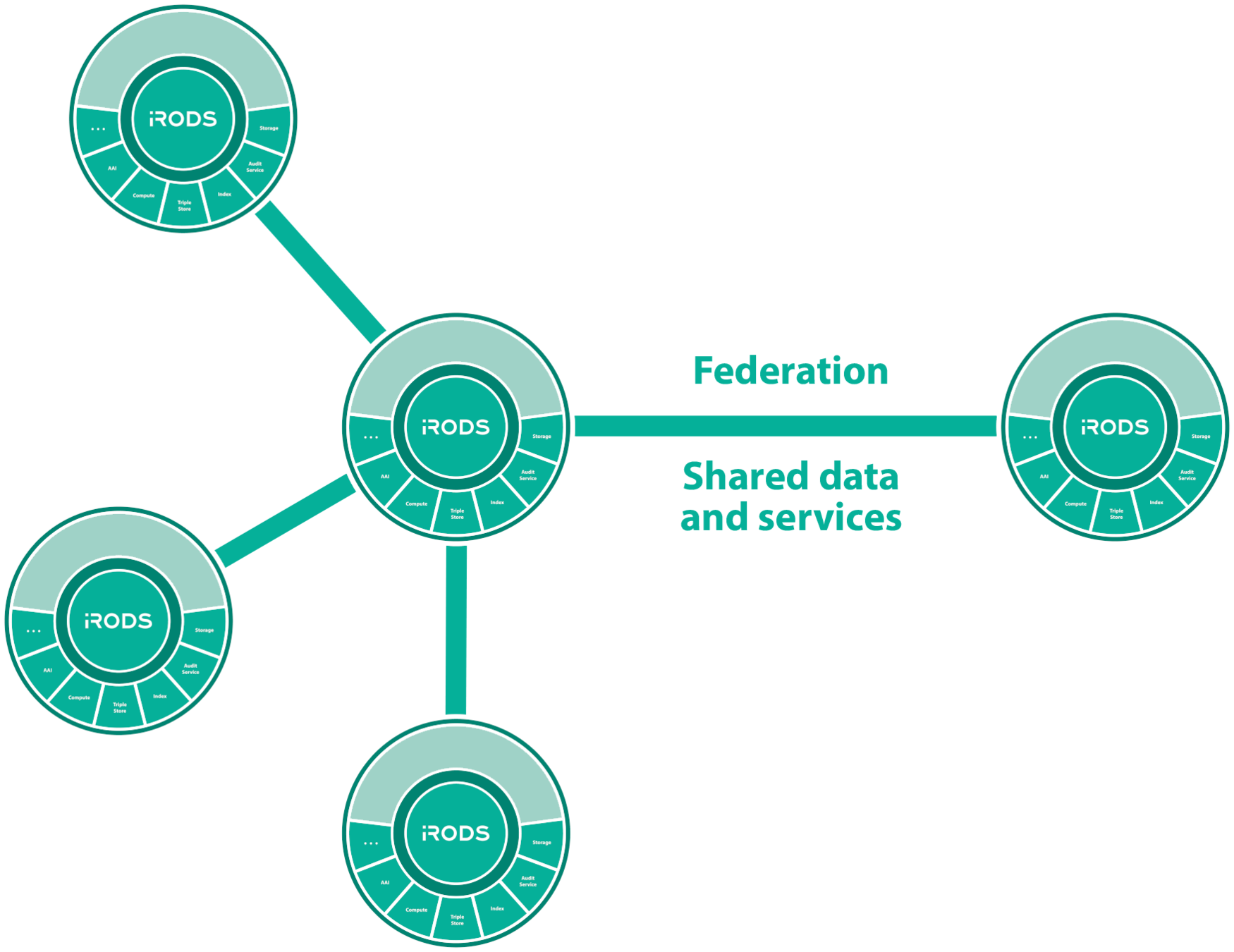
Secure Collaboration
iRODS allows for collaboration across administrative boundaries after deployment
- No need for common infrastructure
- No need for shared funding
- Affords temporary collaborations
iRODS provides the ability to federate namespaces across organizations without pre-coordinated funding or effort.



iRODS as a Service Interface

Federation - Shared Data and Services

Ingest to Institutional repository
As data matures and reaches a broader community, data management policy must also evolve to meet these additional requirements.

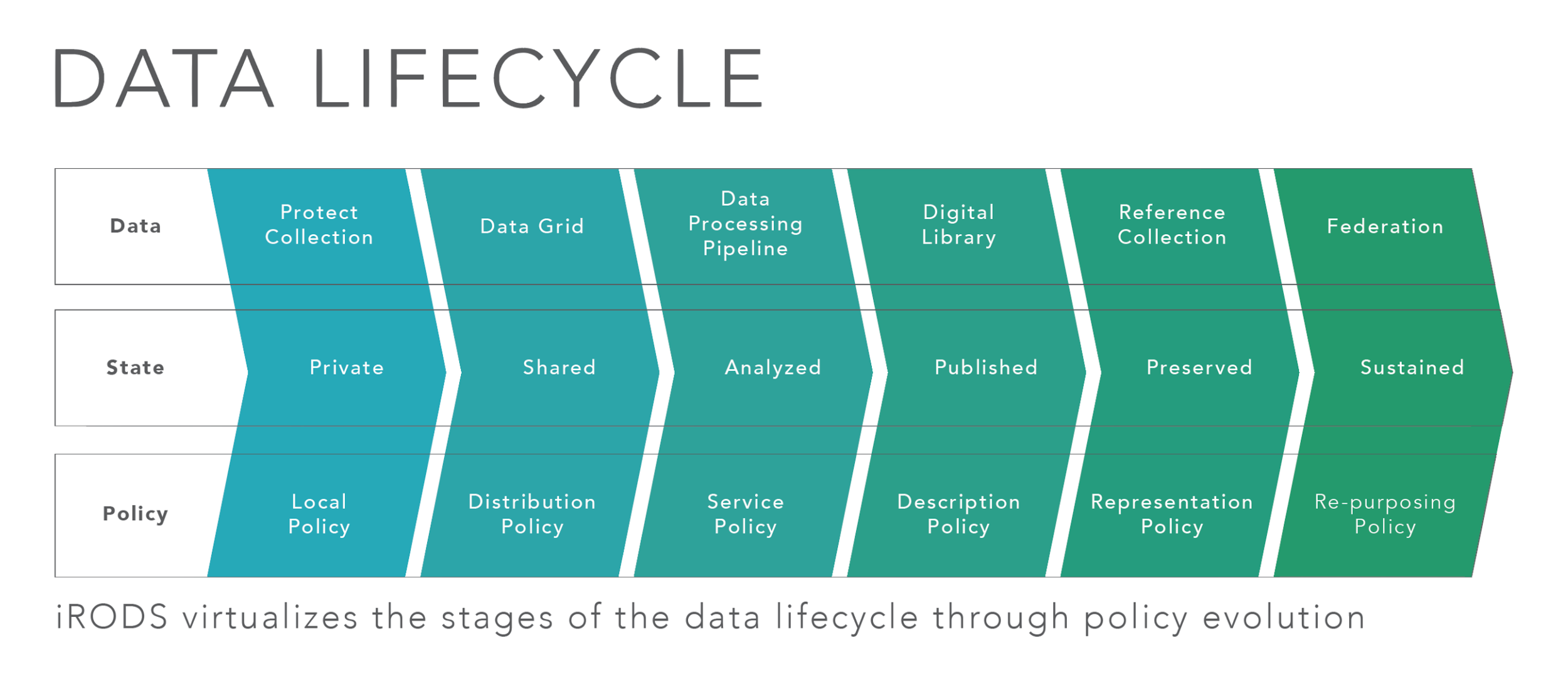
iRODS Policies

The reflection of real world data management decisions in computer actionable code.
(a plan of what to do in particular situations)
Possible Policies


- Data Movement
- Data Verification
- Data Retention
- Data Replication
- Data Placement
- Checksum Computation
- Metadata Extraction
- Metadata Application
- Metadata Conformance
Policy Composition


Consider policy as building blocks towards capabilities
Follow proven software engineering principles:
Favor composition over monolithic implementations
Rules and Dynamic Policy Enforcement Points can be overloaded and fall through
Implement or configure several rule bases or rule engine plugins to achieve complex use cases
Policy Composition across rule bases


For example: pep_data_obj_put_post(...)
- Metadata extraction and application
- Asynchronous Replication
- Initiate Indexing
- Apply access time metadata
- Asynchronous checksum computation
Rather than one monolithic implementation, separate the implementations into individual rule bases, or plugins, and allow the rule(s) to fall through
Policy Composition and Capabilities


For example - Storage Tiering
- Data Access Time
- Identifying Violating Objects
- Data Replication
- Data Verification
- Data Retention
The storage tiering capability - implemented as a composite which delegates each requirement out to separate policies.
Policy Composition and Capabilities


Policies composed into a Capability framework delegate by naming convention:
- irods_policy_access_time
- irods_policy_data_movement
- irods_policy_data_replication
- irods_policy_data_verification
Each policy may be overridden by another rule engine, or rule base to customize to future use cases or technologies
Each policy may now be reused and combined into new Capabilities
iRODS Capabilities









Deployment Patterns

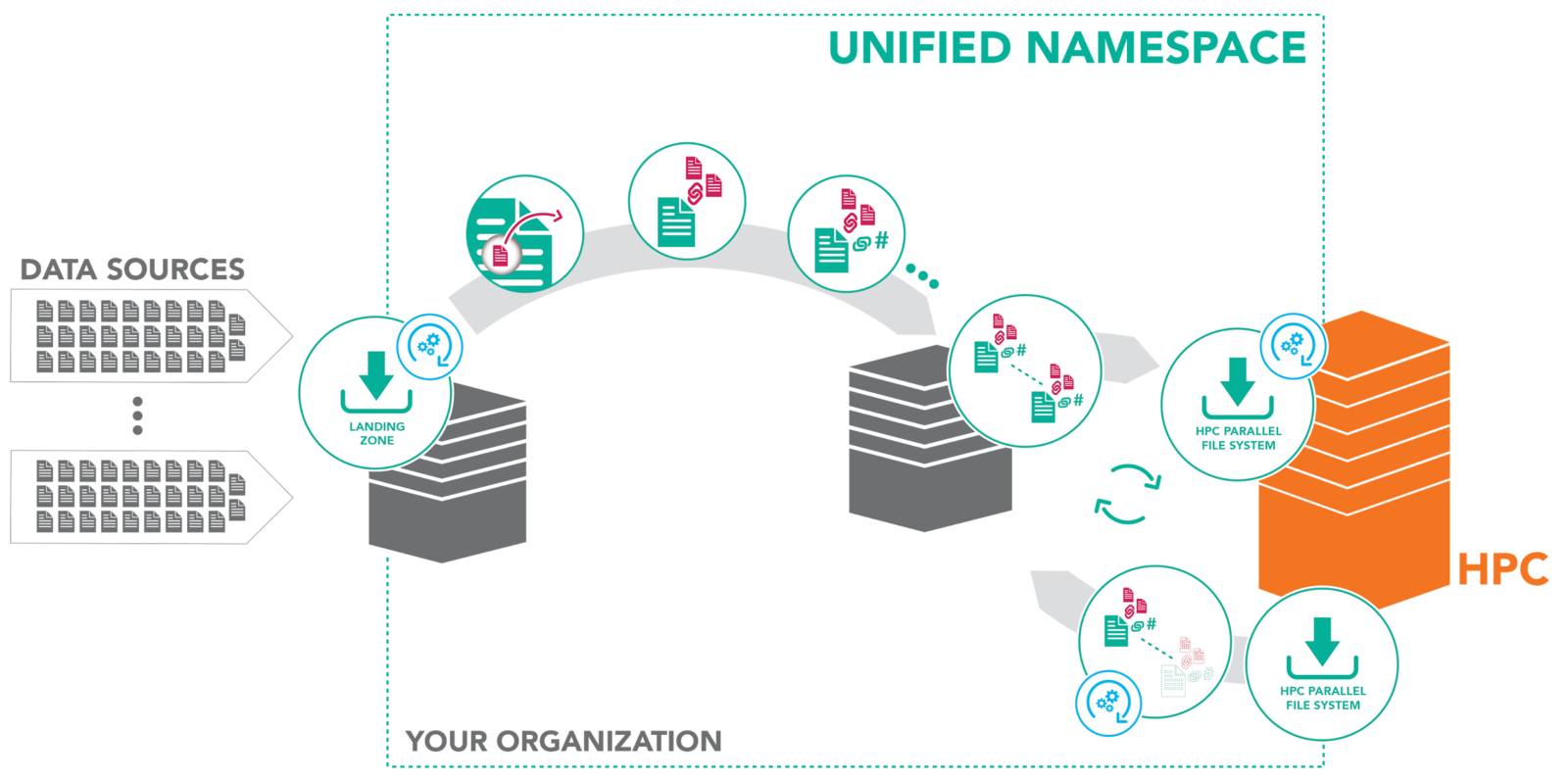
Data to Compute
Compute to Data
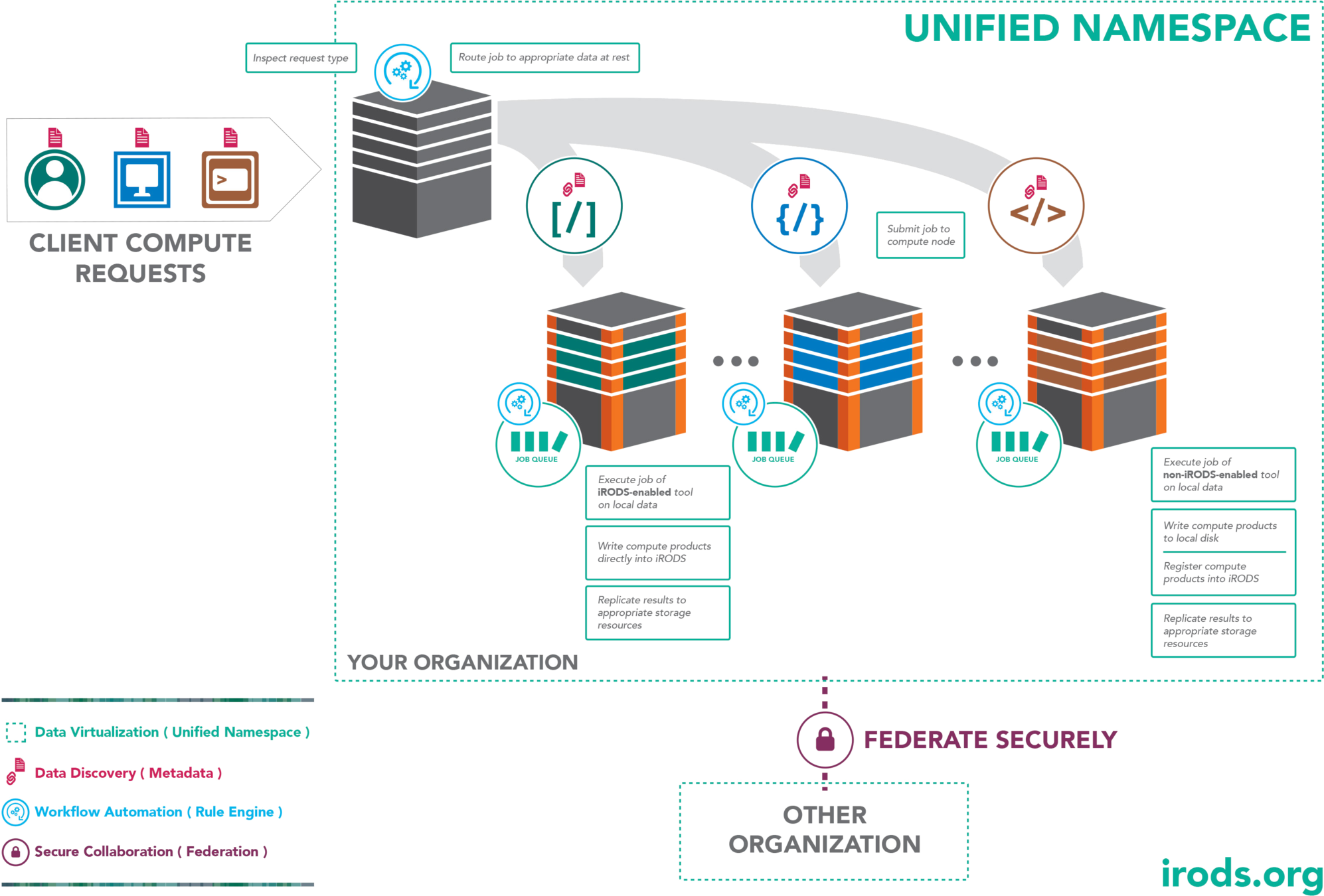
Data Transfer Nodes
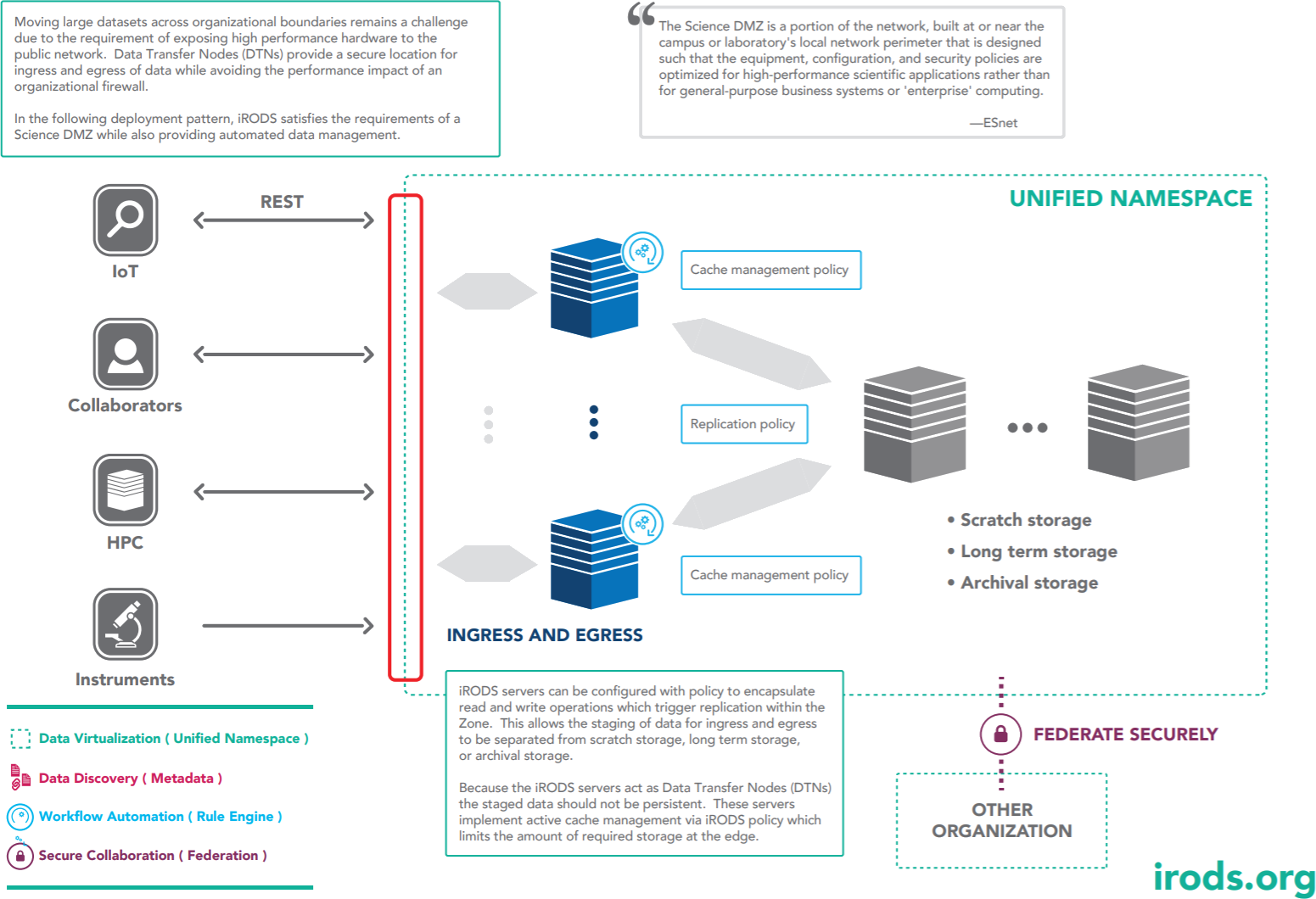
Filesystem Synchronization
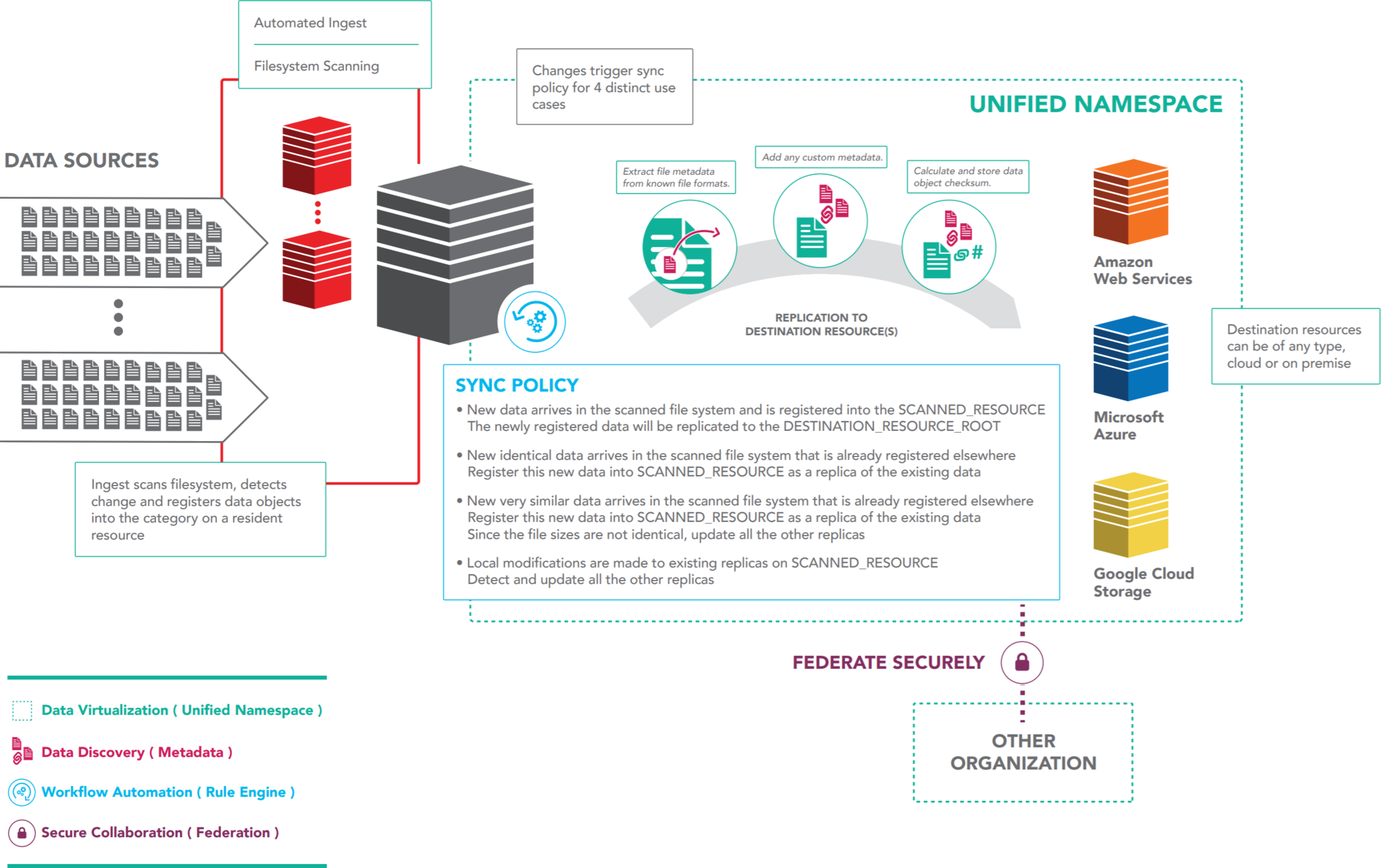
The Data Management Model



Questions?
CINES 2020 - Training Overview
By jason coposky
CINES 2020 - Training Overview
iRODS User Group Meeting 2019 - Policy Training Module
- 1,319



