COMP2511 Week 8
Adgenda
- Admin Stuff
- Generics
- Singleton Pattern
Admin Stuff
- Ass 1 marks released
- Ass 2 is due this Friday 5pm
- Ass 3 released Today
- Please let me know if you are doing it solo or in pairs.
- Please also make sure to make your pair blog post private on Confluence so that only you, your partner and cs2511-22t3-staff can access it.
Generics
Generics
What is this?
- Generics enable types to be passed when defining classes, interfaces or methods
Benefits
- Remove casting and offer stronger type checks at compile time
- Allow implementations of generic algorithms, that work on a collection of different types


Generics
public class Box<T> {
private T value;
public Box(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
}
public class Box<T, S> {
private T value1;
private S value2;
public Box(T value1, S value2) {
this.value1 = value1;
this.value2 = value2;
}
public void setValue(T value1, S value2) {
this.value1 = value1;
this.value2 = value2;
}
public T getValue1() {
return value1;
}
public S getValue2() {
return value2;
}
}
Generics
Inside src/stack, there are a series of stubs for a Stack class which takes in a generic type. There are a series of tests inside StackTest.java which currently fail.
Implement the methods so that the tests pass, using an ArrayList to store the internal data structure.
Generics
Answer the following questions:
-
What is
E?- A generic type
-
What is the Iterable interface? Why does it have an
Eas well? What methods does it force us to implement?- Iterable: Something that can be iterated over
- Forces us to implement the .iterator() method
-
When completing
toArrayList, why do we need to make a copy rather than just returning our internalArrayList?- So we don't return a pointer and don't break encapsulation
-
What does the
.iterator()method allow us to do? Discuss the test insideStackTest.java.- Allows us to loop through it like a normal collection in a standardized way
Generics
public static Integer sumStack(Stack<? extends Integer> stack);
- What does the
<? extends Type>and<? super Type>mean?- extends: the parameterized type must be a class or subclass of the given type
- super: the parameterised type must be a class or super class of the given type
- What is the difference between
?andE?- ? can't be referred to as a type (Type erasure)
- E can
Singleton Pattern
Singleton Pattern
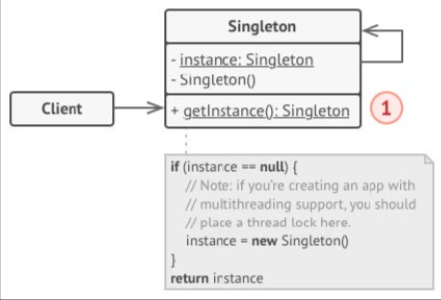
What is this?
Singleton is a creational design pattern that lets you ensure that a class has only one instance, while providing a global access point to this instance.
Benefits
It helps avoid initialisation overhead when only 1 copy of an instance is needed.
Singleton Pattern
Consider the Bank Account class from Lab 04. What if multiple people try to access the bank account at the same time? Inside src/unsw/heist are three classes:
-
BankAccount, from Lab 04. -
BankAccountAccessor. Objects of this type are an instance of an access to a bank account to withdraw money a given number of times by given amounts. -
BankAccountThreadedAccessor, which extendsThread, and overrides the method run to create a new instance ofBankAccountAccessorand access the bank.
Singleton Pattern
Currently, when you run the code, you will find that each thread accesses the bank at the same time (which doesn't make sense). In some cases some strange behaviour is produced by this race condition:
Denver is accessing the bank.
Tokyo is accessing the bank.
The final balance is: $100
Rio is accessing the bank.
Rio successfully withdrew $20
Tokyo successfully withdrew $6
Denver successfully withdrew $49
Tokyo successfully withdrew $6
Denver failed to withdraw $49.
Rio successfully withdrew $20
Rio failed to withdraw $20.
Denver is leaving the bank, the balance is -1
Tokyo failed to withdraw $6.
Rio failed to withdraw $20.
Tokyo failed to withdraw $6.
Rio failed to withdraw $20.
Tokyo failed to withdraw $6.
Tokyo failed to withdraw $6.
Rio is leaving the bank, the balance is -1
Tokyo is leaving the bank, the balance is -1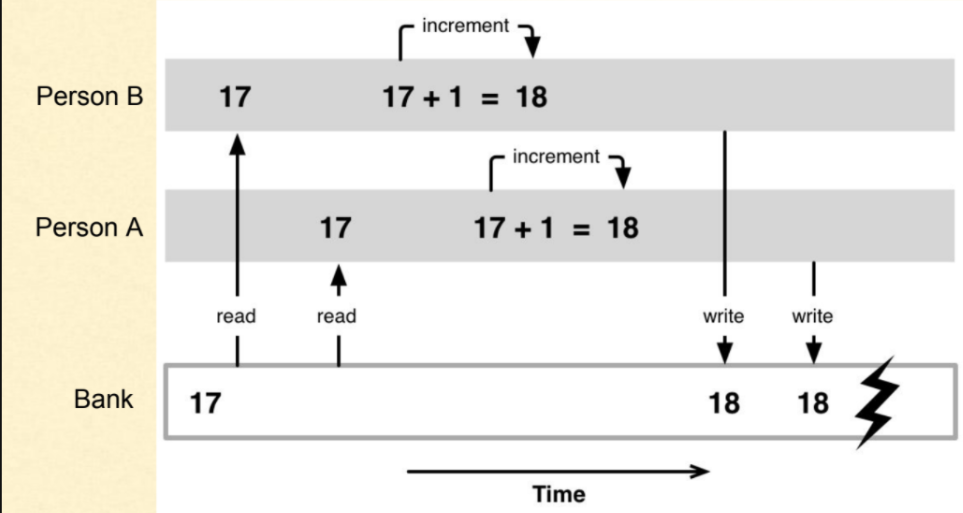
Use the Singleton Pattern to ensure that only one person can access the bank at a time. You can assume for simplicity's sake that only one access to any bank account can ever be made at a given time.
COMP2511 22T3 Week 8
By Jayden Leung
COMP2511 22T3 Week 8
- 231



