The terminal
The basics
change the current directory
cd ~/code/ruby/ror/my_project
The long way
The short way
cd ~/c/r/ro/my_pro + tab
Thanks Zsh
Create a folder
mkdir -p project1/code project2/presentationmkdir : create a folder
-p : create also the subfolders
it create:
current folder -> project1 -> code
current folder -> project2 -> presentation
Create and edit a file
create a file: touch
touch my_fileEdit the file: nano
nano my_fileSave with CTRL + O and exit with CTRL + X
See the content of a file
cat my_file.txt
The owners
The super user : root
Try:
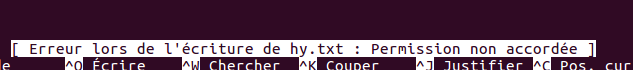
apt-get updatePermission non accordée / Permission denied
Result:
Now do it with a sudo
sudo apt-get update=> if you don't have the permission to do something , you can do it with the root permissions
Create a folder with the root permissions
sudo nano a_file.txt
exit and open this file with a simple nano
=> you don't have the permission , if the root user create something, the simple user don't have any permissions to this file
List the files
ls -llist all the files with the permissions
The file is owned by the root user (and the root group)
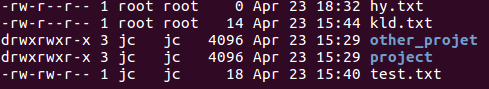
Change the owner
sudo chown jc:jc hy.txt
now , the owner of the file hy.txt is jc and the group jc
you can find your user name with the command
whoamiyou can change the owner of a directory with the argument : -R
sudo chown -R jc:jc a_folderif you will change the owner of a file , you NEED to be the owner of the file
Manage the users
Add a user
Delete a user
passwd JohDoeChange the password of a user
adduser JohnDoedeluser JohDoePermissions
Read-Write-Execute

d = directory
(- = file )
Read
Write
Execute
The owner
Read
Write
Execute
The group
Execute
Other
Change the permissions
| Permission | number | sum |
|---|---|---|
| --- | 0 | 0+0+0 |
| r-- | 4 | 4+0+0 |
| -w- | 2 | 0+2+0 |
| --x | 1 | 0+0+1 |
| rw- | 6 | 4+2+0 |
| -wx | 3 | 0+2+1 |
| r-x | 5 | 4+0+1 |
| rwx | 7 | 4+2+1 |
example: 7 3 0
owner-group-other
Change the permissions
(sudo) chmod 777 my_file.txtFor a file
For a directory (and his files)
(sudo) chmod 777 *
For a everything in a file
(sudo) chmod -R 777 my_direcotoryFor a everything in a file and in his directory
(sudo) chmod -R 777 *
Some usefull commands
Remove files and directorys
rm a_file
DELETE A DIRECTORY
rm -r a_directory
DELETE EVERYTHING
rm *
FORCE DELETING
rm -f a_file
Never run this command
sudo rm -rf /*=> it delete everything (your OS, your files)
Ping a website
ping google.be=> it give the ip of a website, and it say if you are connected to the network
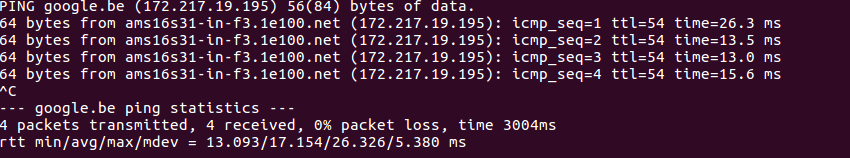
Stop the command with CTRL+C
Your network status
ifconfig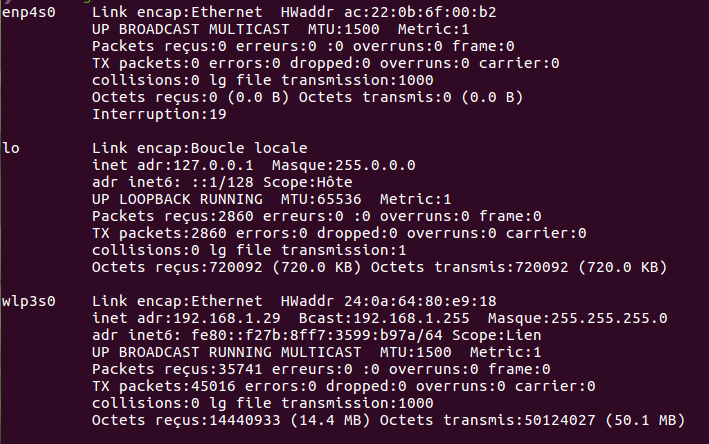
Ethernet connexion
= eth0
Wifi connexion
= wlan0
My local ip (ipv4) address
My local ip (ipv6) address
My mac addres (not real)
My local connexion (useless)
Change your macaddress
Your mac address is uniq so it isn't very good for your Privacy Policy but you can very easy change your mac address, it's usefull
for your privacy , free wifi hotspot with time and for some problems with internet connexion
examples of mac address:
09-74-A3-D4-D1-43
ED-40-74-9F-EA-8A
BA-89-E7-1E-92-F4
.......
Change your macaddress on ubuntu
sudo nmcli connection modify --temporary the_wifi_name 802-11-wireless.cloned-mac-address mac_addr
#then you do :
nmcli connection up wifi_name
Change your macaddress on apple
sudo ifconfig en0 xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
Enjoy your terminal (and your privacy)
deck
By jchr
deck
- 841



