CBIOMES e-meeting (Dec 10th, 2025)
Jesse McNichol, St. Francis Xavier University (StFX)
Implications of Prokaryotic Microdiversity for Ecosystem Functional Resilience - an Empirical Approach
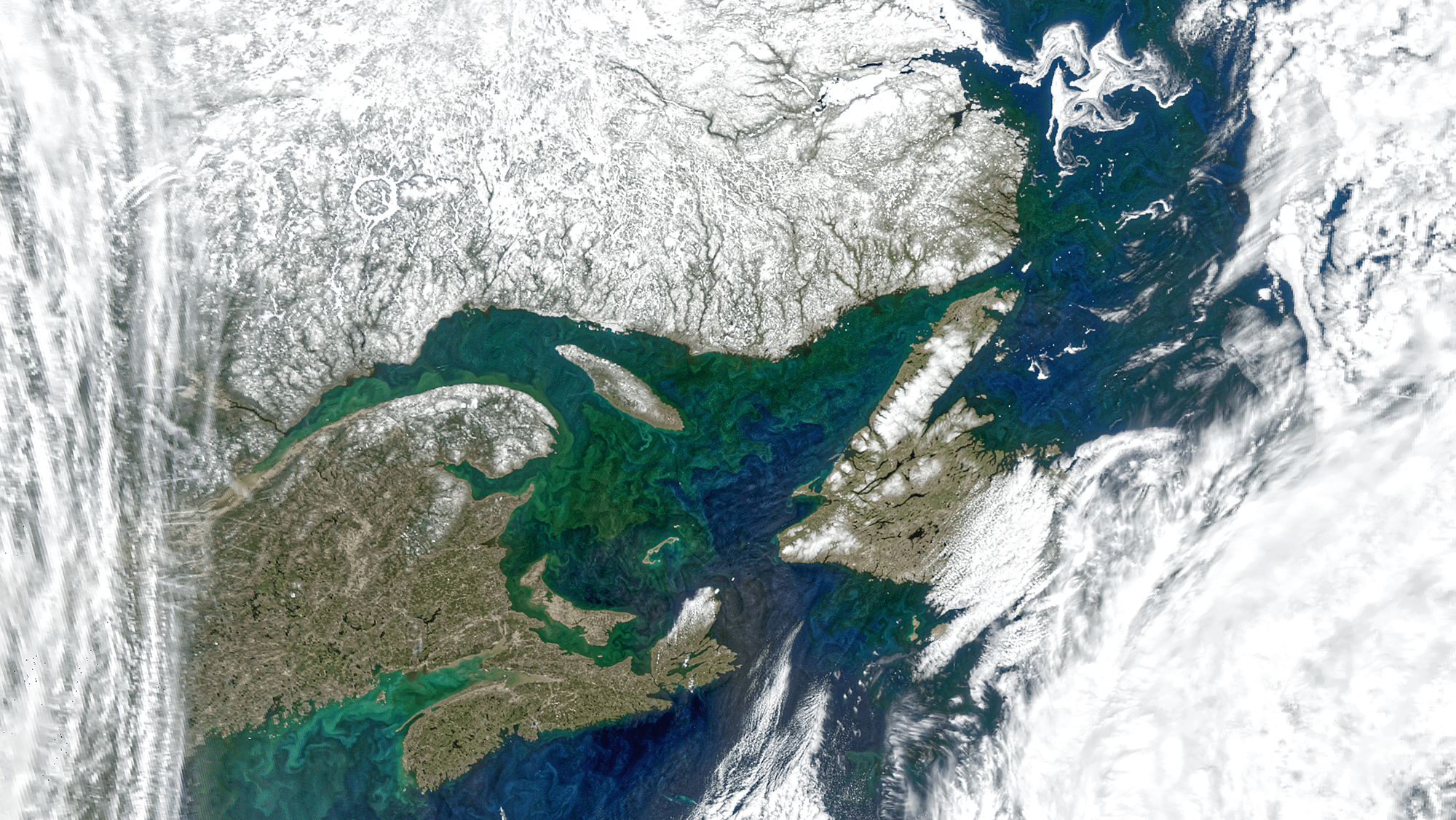
NASA PACE

Julia Kadel, Unsplash
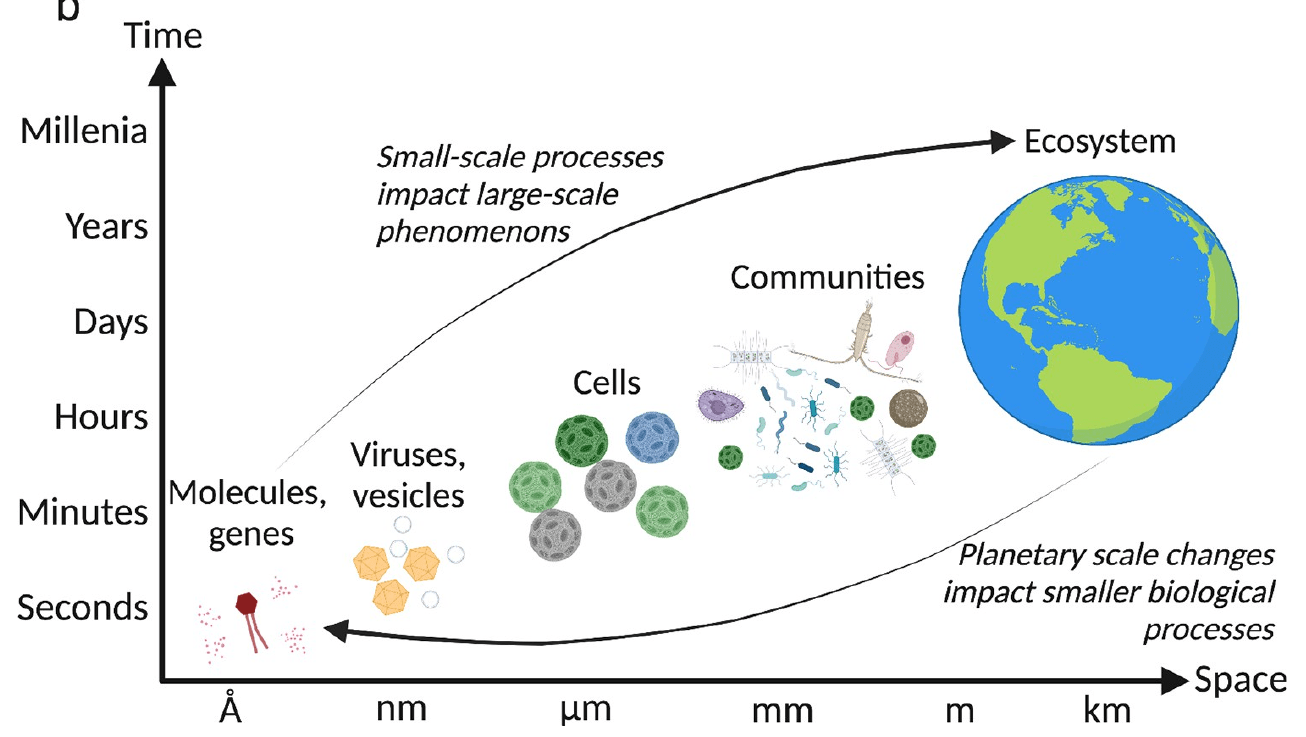
Biological data contains nested diversity
What is the right level for understanding ecosystem function?

Ecologically-relevant annotations aggregate complex ASV data into sensible groupings
- Bacterioplankton
-
Phytoplankton
- Prochlorococcus (ecotype)
Biological data contains nested diversity
What is the right level for understanding ecosystem function?
One strategy: aggregate to broad "guild" level
But what about "microdiversity"?
But what about "microdiversity"?
But what about "microdiversity"?
But what about "microdiversity"?
- A reservoir of diversity that can buffer environmental change, maintaining ecosystem function?
- Neutral genetic variation?
In many cases, we don't know...

Ecosystem
Ecosystem

Metagenomics
Work thus far in literature:
- If metagenomes show different organisms have similar metabolic pathways → ecosystem resilience
- My view: maybe, but this is "potential", not measured resilience
- Ignores other aspects of microbial niches (T optimum, for e.g.)
But what about "microdiversity"?
A "model ecosystem" in Cape Breton
A "model ecosystem" in Cape Breton


Me aboard Dr. Bruce Hatcher's research vessel Exocet in 2024

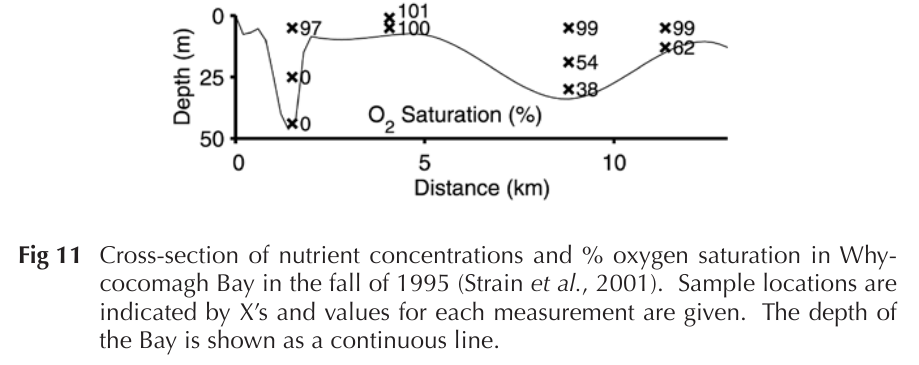
- Stratified basin with anoxic, sulfidic waters ~ 17 m (historically ~1000 μM H2S)
- Temperature and oxygen gradients very steep at redoxcline, system has recently overturned in winter 2024 (?) causing a fish kill
- With Katherine Rutherford (StFX) we are using metabarcoding, metagenomics to understand taxa present, dynamics, functional potential

W. Whycocomagh Bay
A "model ecosystem" in Cape Breton
A "model ecosystem" to ask questions about the link between diversity and function


Lots of genetic diversity, but relationship between diversity & function poorly known (some exceptions, e.g. Prochlorococcus)
A "model ecosystem" to ask questions about the link between diversity and function
...it is unclear and controversial how multiple disturbances affect microbial community stability and what consequences this has for ecosystem functions."

- In this ecosystem, sulfur oxidation is an "ecosystem service"
- "Microbial firewall"
- Prediction: stable stratification means limited functional diversity
- If disturbance (e.g. water overturning) occurs → limited resilience of function
- Goal: experiments to generate empirical data to test this prediction
How resilient are microbial ecosystem services to disturbance?

W. Whycocomagh Bay

Does high genetic "microdiversity" observed in natural microbial ecosystems confer functional resilience of H2S detoxification during deep water mixing, or will rapid changes in environmental conditions slow or stop this critical ecosystem service?"
A simple question
A simple question ... but how to answer it?
Vincent and Vardi, 2023
A "middle way" for understanding microdiversity
Pure cultures
Pros: Highly controlled
Cons: Selects for "lab rats", reduced diversity vs. environment
Environmental 'omics
Pros: Observe everything
Cons: Static measurement, limited functional information
Vincent and Vardi, 2023

A "middle way" for understanding microdiversity
Short-term incubation experiments of seawater
Pro: Generate empirical data for testing hypotheses
Con: The longer you incubate, the less the composition resembles the natural community. Need very short-term incubations, and single-cell activity measurements
A "middle way" for understanding microdiversity


rRNA-FISH & FACS + 14CO2 =
- taxon-specific C-fixation
- response to different chemical conditions in short-term incubations
How we plan to do the work
[H2S]
[O2]
depth
EUX ~3°C
RXL ~10°C
SRF ~22°C
Field sampling
DNA
-3DMB
-MAGs
-FL-16S
Lab processing
OOI
(function,
microdiversity)
OOI-specific measurements:
-Growth rate
-Respiration
-Resilience
Field incubations
FISH probes
(broad group level,
microdiverse subcluster level)

Katherine Rutherford (StFX)

Bruce Hatcher (CBU)
3DMB=3-domain metabarcoding, FL-16S=full-length 16S (PacBio)
SRF=surface, RXL=redoxcline, EUX=Euxinic (sulfide-rich waters)

- Street map = meta'omics data from Whycocomagh (which organisms are involved in sulfur cycling)
- Allows us to design FISH probes for particular organisms (including microdiversity within clade)
- FISH probes allows us to derive:
- Cell size, biovolume, morphological variability
- In situ growth rates
- Metabolic rates during incubations
How we plan to do the work
How we plan to do the work: in situ growth rates

FISH probes + FODC method → OOI growth rate (including microdiverse subclusters)
Could be compared with MAG estimates (gRodon)
How we plan to do the work: incubations
[H2S]
[O2]
depth
EUX ~3°C
RXL ~10°C
SRF ~22°C
Simulate upwelling to surface by subjecting RXL or SRF communities to increased [H2S], temp, [O2] (or combinations of all) by mixing at different ratios and incubating at controlled temperatures for ~6-12 h. Response (compared to control) measured by:
- Single-cell respiration rates
- Bulk H2S oxidation
- Bulk community respiration w/ spot optodes

in situ conditions (control)

"disturbance" conditions
How we plan to do the work: organism-specific respiration
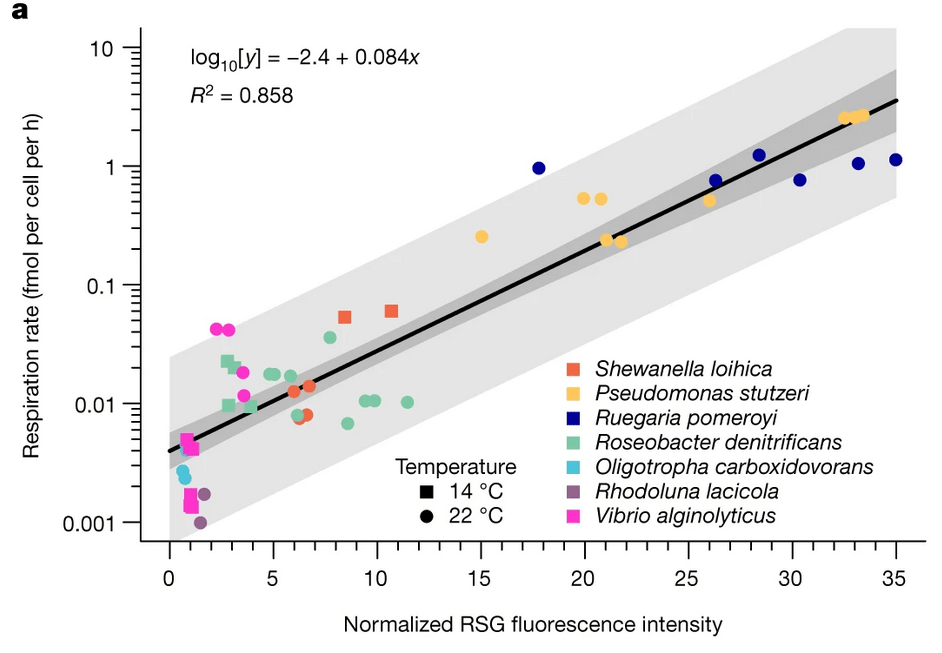
FISH probes + Redox Sensor Green → OOI respiration rate changes after short-term incubations
Possible outcomes (null)
Cell-specific respiration rate (RSG)
Killed
NIC
RXL @ RXL
NIC=No incubation control + RSG | RXL @ RXL=redoxcline water incubated at in situ conditions
RXL @ SRF=redoxcline water incubated at surface conditions (increased O2, temp)
RXL @ SRF
Possible outcomes (limited resilience)
Cell-specific respiration rate (RSG)
Killed
NIC
RXL @ RXL
NIC=No incubation control + RSG | RXL @ RXL=redoxcline water incubated at in situ conditions
RXL @ SRF=redoxcline water incubated at surface conditions (increased O2, temp)
RXL @ SRF
Possible outcomes (more activity with upwelling)
Cell-specific respiration rate (RSG)
Killed
NIC
RXL @ RXL
NIC=No incubation control + RSG | RXL @ RXL=redoxcline water incubated at in situ conditions
RXL @ SRF=redoxcline water incubated at surface conditions (increased O2, temp)
RXL @ SRF
Possible outcomes (incubations not working)
Cell-specific respiration rate (RSG)
Killed
NIC
RXL @ RXL
NIC=No incubation control + RSG | RXL @ RXL=redoxcline water incubated at in situ conditions
RXL @ SRF=redoxcline water incubated at surface conditions (increased O2, temp)
RXL @ SRF
Next steps
[H2S]
[O2]
depth
EUX ~3°C
RXL ~10°C
SRF ~22°C

in situ conditions (control)

"disturbance" conditions
Winter 2026:
Identify targets from bioinformatics, optimize FISH probes
Spring / summer 2026:
Apply incubation approach with FISH probes targeting organisms of interest
What knowledge we can gain?


- An inventory of sulfur oxidation potential in system from metagenomics (Illumina + Nanopore)
- Spatiotemporal diversity patterns (stochastic? predictable?)
- In situ growth and respiration rates (FODC, RSG)
- Resilience to realistic disturbances across diversity
- "Traits" we can use to model future disturbance
STAY TUNED over the next 2-3 years!
Does high genetic "microdiversity" observed in natural microbial ecosystems confer functional resilience of H2S detoxification during deep water mixing, or will rapid changes in environmental conditions slow or stop this critical ecosystem service?"



Much to learn!
Questions?
Thanks to:
- Current and former CBIOMES collaborators (Fuhrman, Follows, Levine, Zakem labs)
- Dr. Bruce Hatcher (CBU)
- Katherine Rutherford (StFX)
- All of you for listening!

stfxmicroeco.ca | jmcnicho@stfx.ca
https://slides.com/jcmcnch/cbiomes-e-seminar-2025/



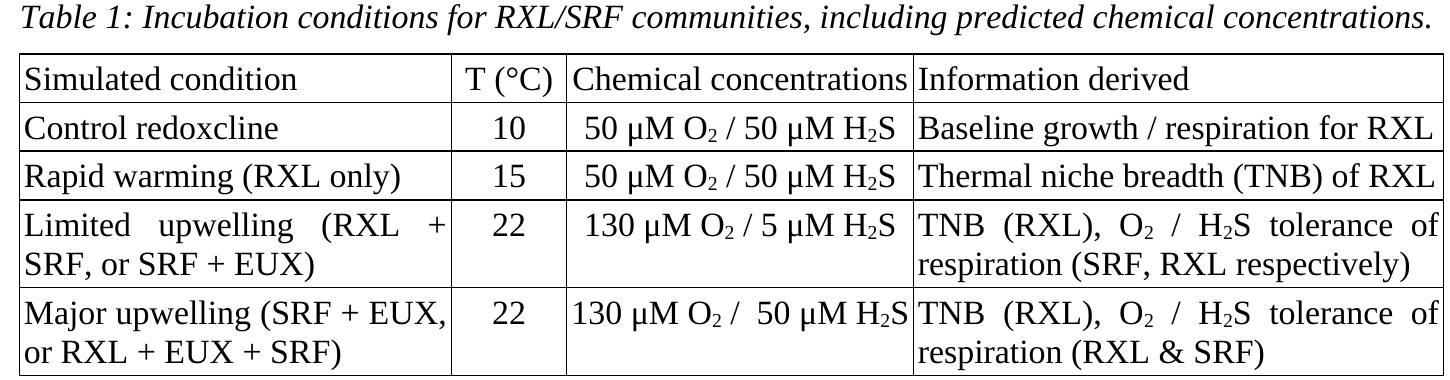
Summary of incubation conditions


Ecosystem maps from eDNA

Ecosystem DNA
A Map


Metabarcoding
Vincent and Vardi, 2023
Ecosystem maps from eDNA → tackling big questions
Ecosystem maps can be cheaply generated from a "quiver" of DIY methods that I like to use
- Kit-free, non-toxic DNA extraction with linear acrylamide as co-precipitant, allows for recovery of very small amounts of DNA for PCR (~10 mL seawater*)
- Cheap, simple protocol for removal of PCR inhibitors with linear acrylamide (for difficult samples, Zymo 1-step is cheap & works)
- Protocols for decontamination of reusable plasticware for molecular protocols (reduce waste, guarantee quality)
- 1-step PCR reaction for library prep in lab (advantages = speed, lower cost, flexibility)
*Other methods for as little as 1 µL exist
A story about ecosystem maps + meta'omics + models





Figure 1: Overview of sampling and data processing workflow. Oxygen and sulfide depth profiles shown in blue and orange, respectively. SRF=surface, RXL=redoxcline, EUX=euxinic. 3DMB=3-domain metabarcoding, MAGs = metagenome assembled genomes, FL-16S = full-length 16S. OOI = organism of interest. FISH = fluorescence in-situ hybridzation.
[H2S]
[O2]
depth
EUX ~3°C
RXL ~10°C
SRF ~22°C
DNA
-3DMB
-MAGs
-FL-16S
OOI
(function,
microdiversity)
(broad group level,
microdiverse subcluster level)
FISH probes
OOI-specific measurements:
-Growth rate
-Respiration
-Resilience
Field sampling
Lab processing
Field incubations

Vincent and Vardi, 2023
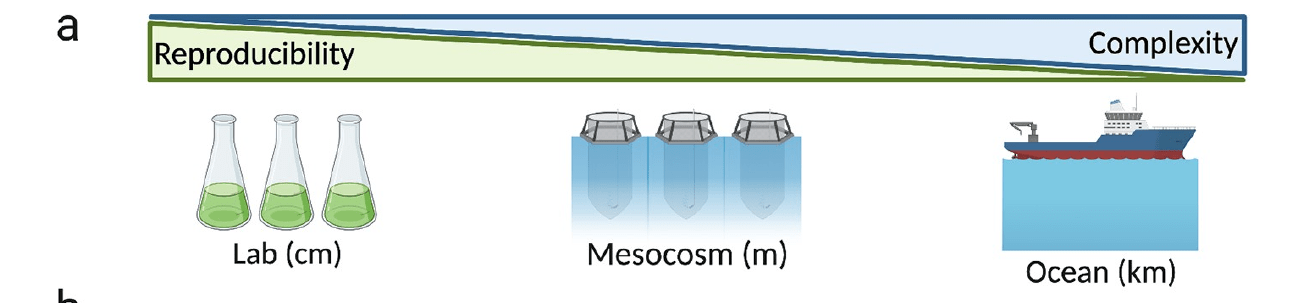
Coastal systems are flexible: experiment across scales, depending on question
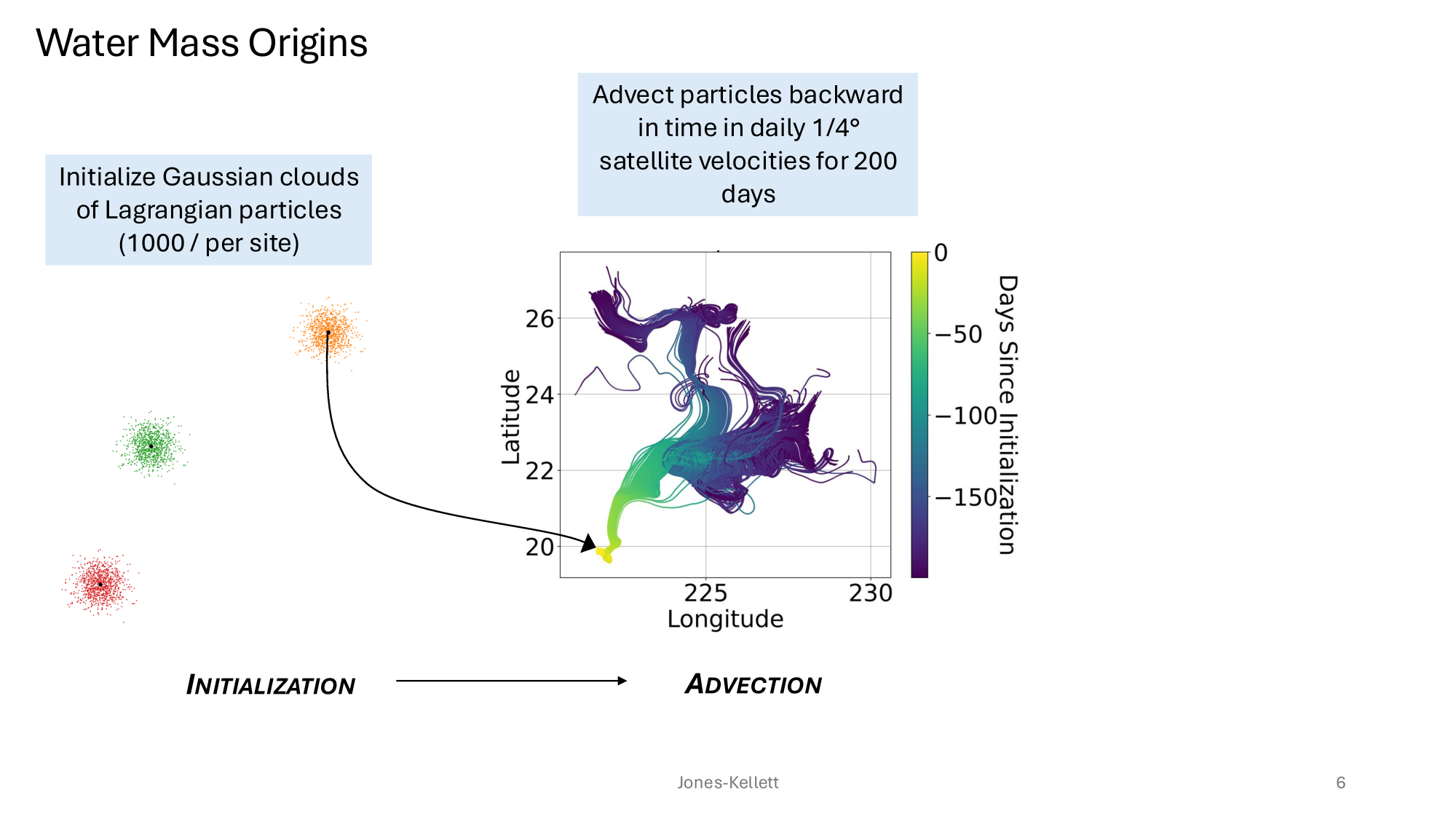
GRUMP 2.0 = a story about absolute units
Slide credits: Dr. Lexi Jones-Kellett (aejk@alum.mit.edu)
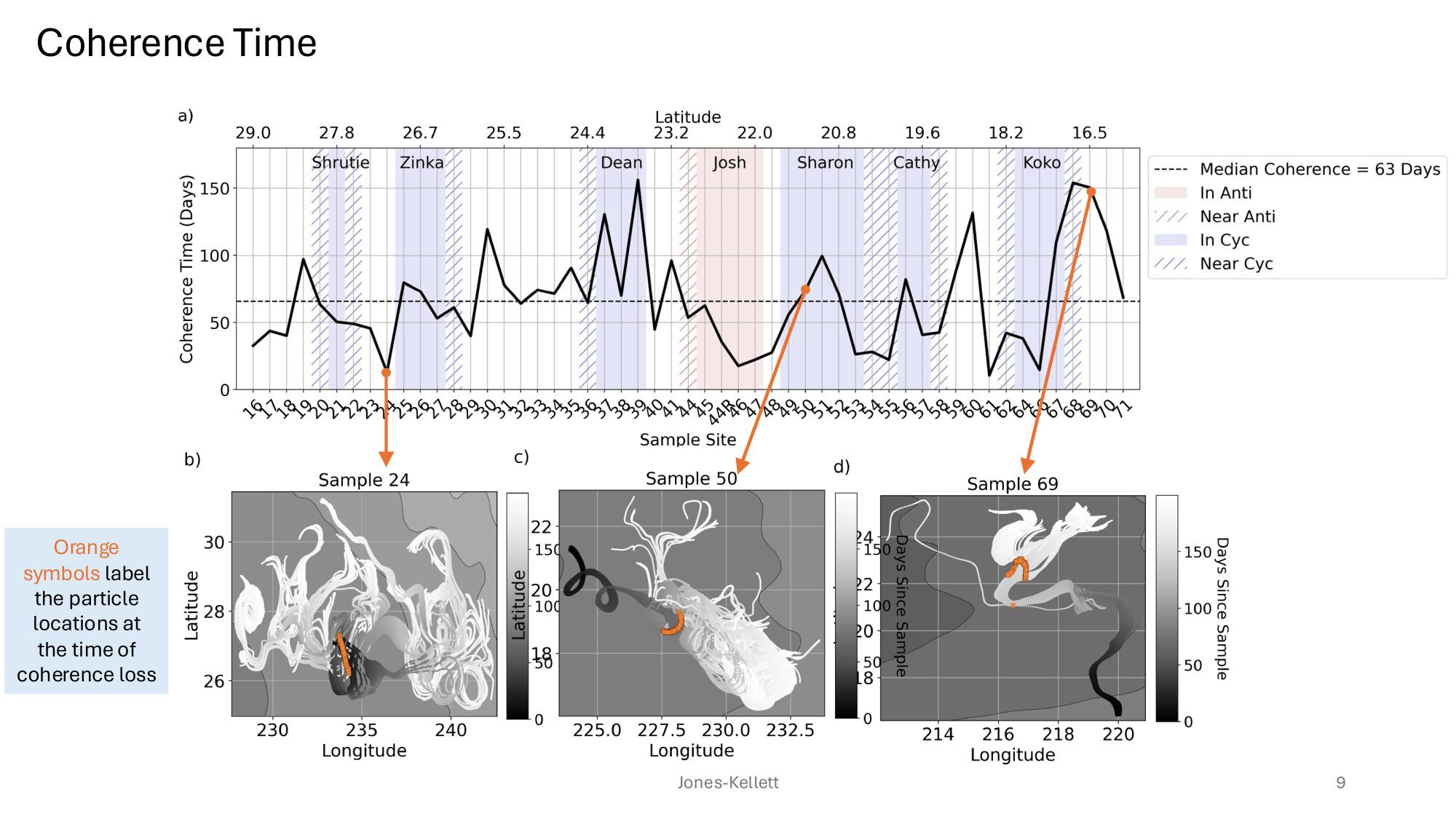
GRUMP 2.0 = a story about absolute units
Slide credits: Dr. Lexi Jones-Kellett (aejk@alum.mit.edu)
CBIOMES e-seminar 2025
By jcmcnch
CBIOMES e-seminar 2025
CBIOMES scholars project overview
- 27



