(does anyone know)
What is Digital Humanities?
Humanities Computing? Digital Humanities? Digital History? A field? A practice? A discipline? A waste of time?
Humanities Computing
Digital Humanities
But first, how did we get here?
Blending of math, humanities, and state power.*
*this is still true.
Both share a similar mission:
"using information technology to illuminate the human record, and bringing an understanding of the human record to bear on the development and use of information technology."
|
From, "The Digital Humanities and Humanities Computing: An Introduction" Susan Schreibman, Ray Siemens, and John Unsworth, http://digitalhumanities.org:3030/companion/view?docId=blackwell/9781405103213/9781405103213.xml&doc.view=print&chunk.id=ss1-1-3&toc.depth=1&toc.id=0. |
What is technology?



“There is no such thing as a new idea. It is impossible. We simply take a lot of old ideas and put them into a sort of mental kaleidoscope. We give them a turn and they make new and curious combinations. We keep on turning and making new combinations indefinitely; but they are the same old pieces of colored glass that have been in use through all the ages.” -- Mark Twain,
Codex --> Printed Book --> Ebook

The Codex Gigas, 13th century, Bohemia.

The Gutenberg Bible, 15th century, Germany.
Project Gutenberg, 2019, World Wide Web.
Punch Cards
- IBM is rescued by the Social Security Act. The punch card becomes the official computing device for the New Deal.



1940s:
-
Jorge Luis Borges (author) publishes "Garden of Forking Paths." Suggests ideas of a multiverse, or multiple pathways.
-
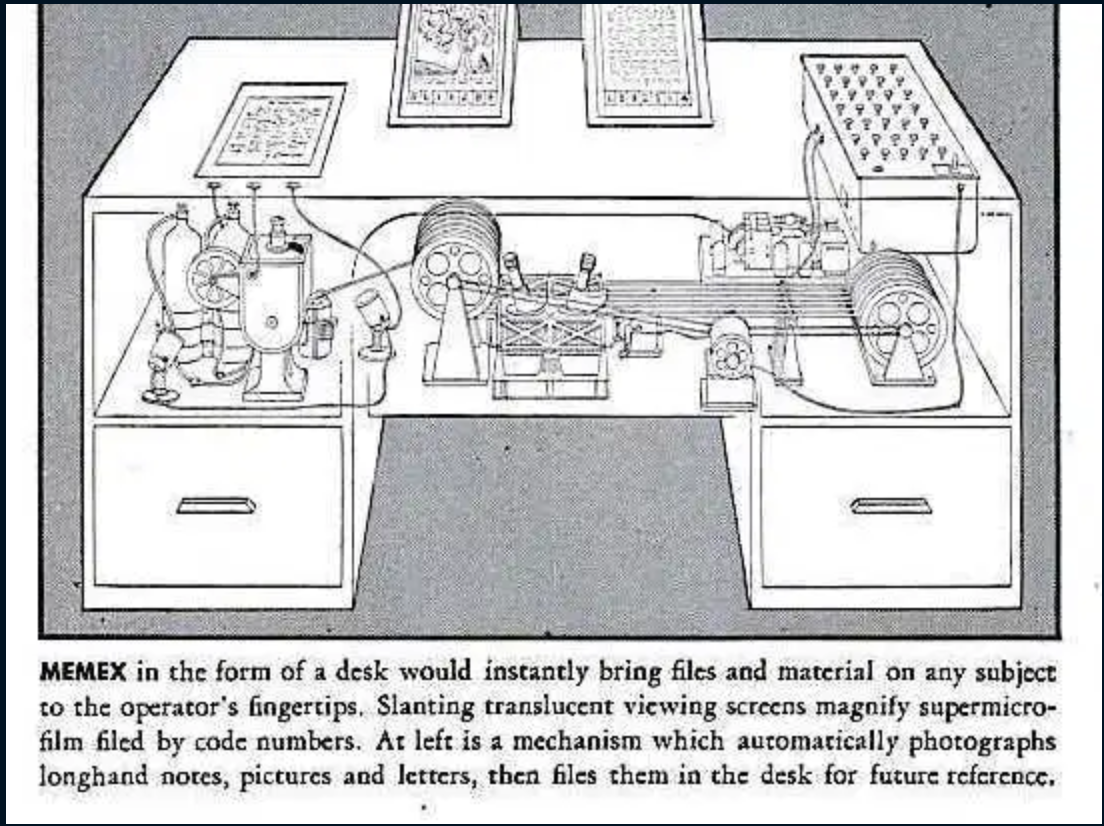
Vannevar Bush (scientist on Manhattan project) publishes "As We May Think." Hypothesizes the Memex, which would tie information together through free association.
- Jesuit priest Father Busa attempts to index the writings of St. Thomas Aquinas with the help of IBM computing. (completed 1970s)


1950s-1960s
- Alan Turing cracks the Enigma code and designs the Turing Test.
- ELIZA one of the first AI programs to pass the Turing Test.
- Ted Nelson conceives of Project Xanadu and invents the term "hypertext."

The Internet
1980s-1990s
- The graphical user interface replaces the command line by 1980s, leading to the personal computing revolution.
- Hypercard creates possibility for user-guided explorations of virtual worlds.
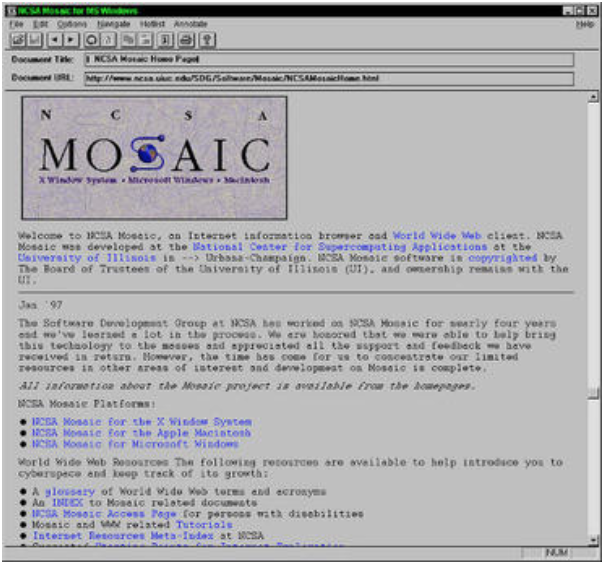
- World Wide Web and Electronic Mail gain popularity.


21st Century
- The Internet continues to expand (RIP Floppy Disk and CD-ROM; hello Cloud).
- Web 2.0: the web becomes participatory. Enter Myspace, Livejournal, Facebook and other social media websites.
- Content management systems (CMS) like Omeka and Wordpress are built for people to publish online.






What do Digital Humanists make?
Brennan: "approach to researching and interpreting the past that relies on computer and communication technologies to help gather, quantify, interpret, and share historical materials and narratives."
-
Digital Collections
-
Teaching and Learning
-
Digital Exhibits and Publications
-
Collaborative Digital Public History
-
Computational Analysis
What do Digital Humanists Value?
Open source/Open access
Collaboration
New scales of analysis/publication
Open source = code freely available
Open access = content freely available
DH teams are often interdisciplinary and interinstitutional: scholars, web developers, librarians, students, the public
Use computational methods to analzye sources in new ways
Use web publishing tools to reach larger audiences

What is Digital Humanities?
By jdauteri
What is Digital Humanities?
- 688



