Semi-Supervised Sequence Modeling with Cross-View Training
Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Christopher D. Manning, Quoc V. Le
Outline
- Problem and Motivation
- Cross-View Training
- Cross-View Training Models
- Experiments
- Results
- Takeaways
Focus: sequence modeling tasks attached to a shared Bi-LSTM sentence encoder
Aim: improves the representations of a Bi-LSTM sentence encoder using a mix of labeled and unlabeled data
Problem and Motivation
Semi-supervise learning
Overview
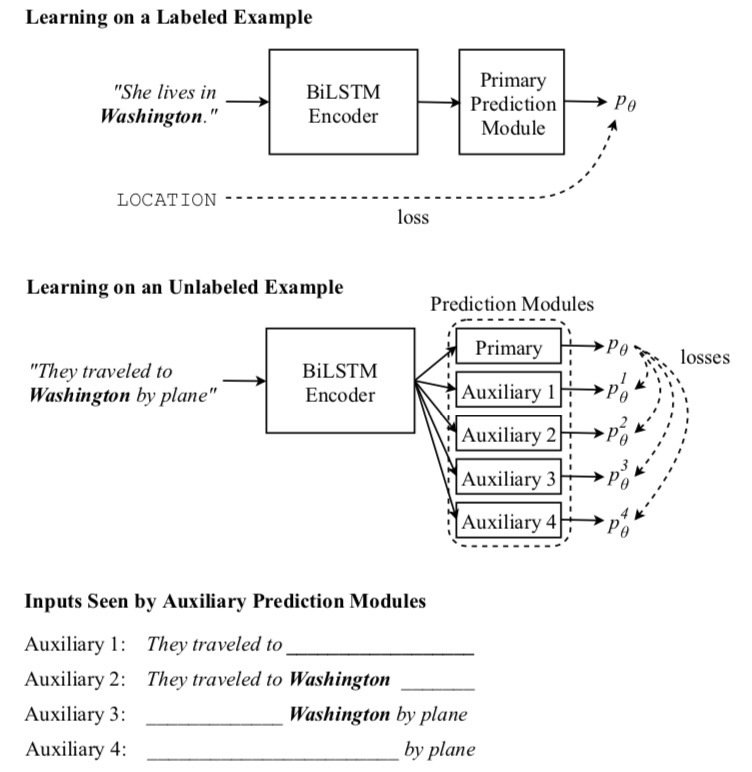
[Labeled examples] standard supervised learning.
[Unlabeled examples] train auxiliary prediction modules with different views of the input to agree with the primary prediction module.
view 1:
view 2:
view 4:
view 3:
Method
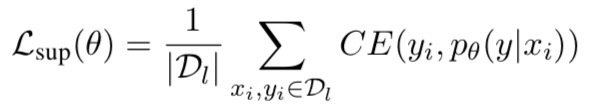
CVT trains the modules to match the primary prediction module on the unlabeled data by minimizing:
The module is trained on labeled examples by minimizing standard cross entropy loss:
primary prediction
auxiliary prediction
Method
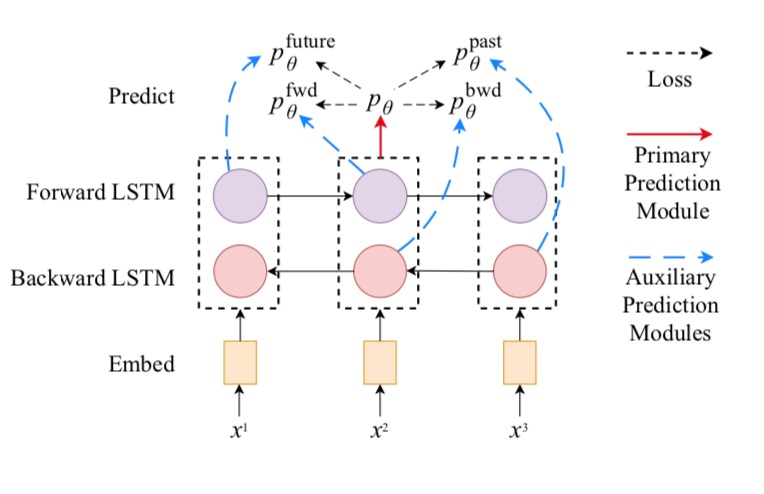
Cross-View Training Models
- Sequence Tagging
- Dependency Parsing
- Sequence-to-sequence learning
Sequence Tagging
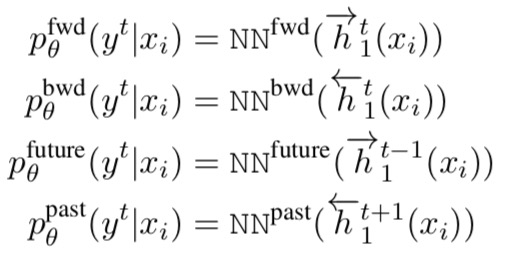

Primary module:
Auxiliary modules
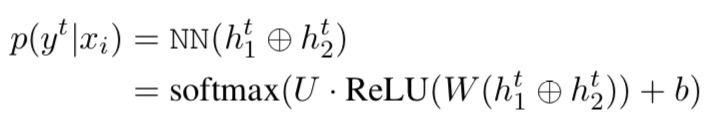
Dependency Parsing
"head"
Words in a sentence are
treated as nodes in a graph.
"relation"
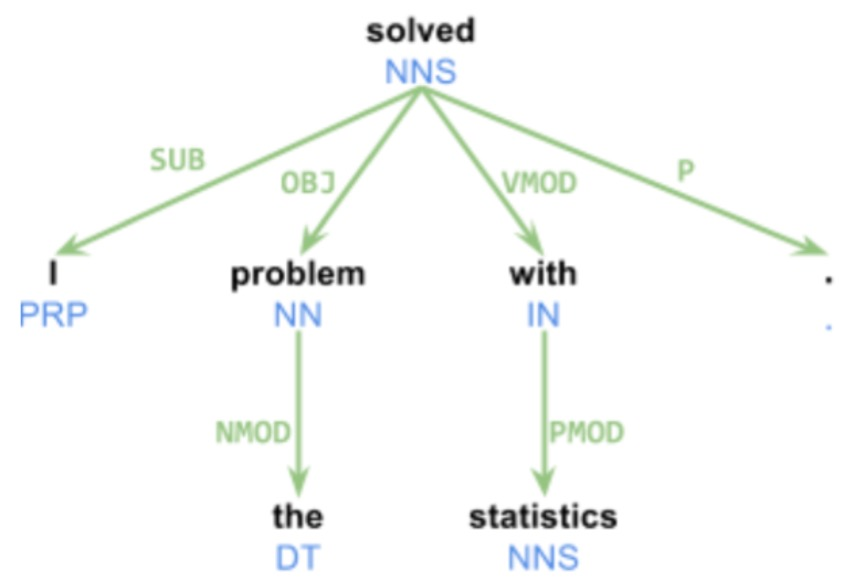
(solved, I, SUB)
Dependency Parsing

Words in a sentence are
treated as nodes in a graph.
The probability of an edge (u,t,r) is given as:
: encoder hidden unit on word
: decoder hidden unit on word
The bilinear classifier uses a weight matrix Wr specific to the candidate relation as well as a weight matrix W shared across all relations.
Dependency Parsing
Words in a sentence are
treated as nodes in a graph.
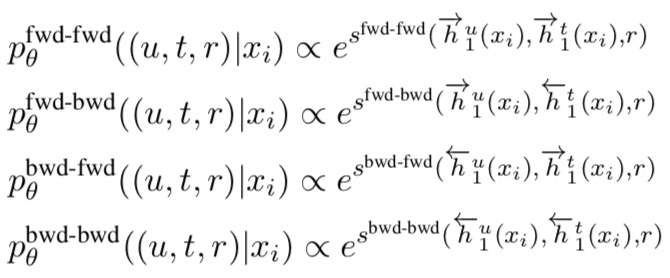
Auxiliary modules:
Sequence to Sequence Learning
Model: encoder-decoder with attention
Attention
context
...
...
encoder
decoder
Sequence to Sequence Learning
Two auxiliary decoders share embedding and LSTM parameters but maintain independent parameters for attention and softmax
auxiliary1:
auxiliary 2:
encoder
decoder
...
...
Sequence to Sequence Learning
encoder
decoder
No target sequence for unlabeled examples.
Teacher forcing to get an output distribution over the vocabulary from the primary decoder at each time step?
...
...
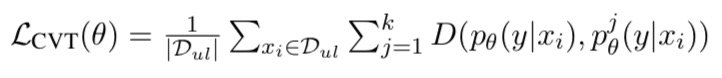
?
Sequence to Sequence Learning
encoder
decoder
produce hard targets for the auxiliary modules by running the primary decoder with beam search on the input sequence.
...
...
Beam search for sequence to sequence learning
[Step 1] select 2 words with max probability, i.e. a, c
Example: beam size = 2, vocab={a,b,c}
[Step 2] all combination {aa,ab,ac,ca,cb,cc}, select 2 sequences with max probability, i.e. aa, ca
[Step 3] repeat, until encounter <END>, output 2 sequences with max probability
Ref: https://www.zhihu.com/question/54356960
Experiments
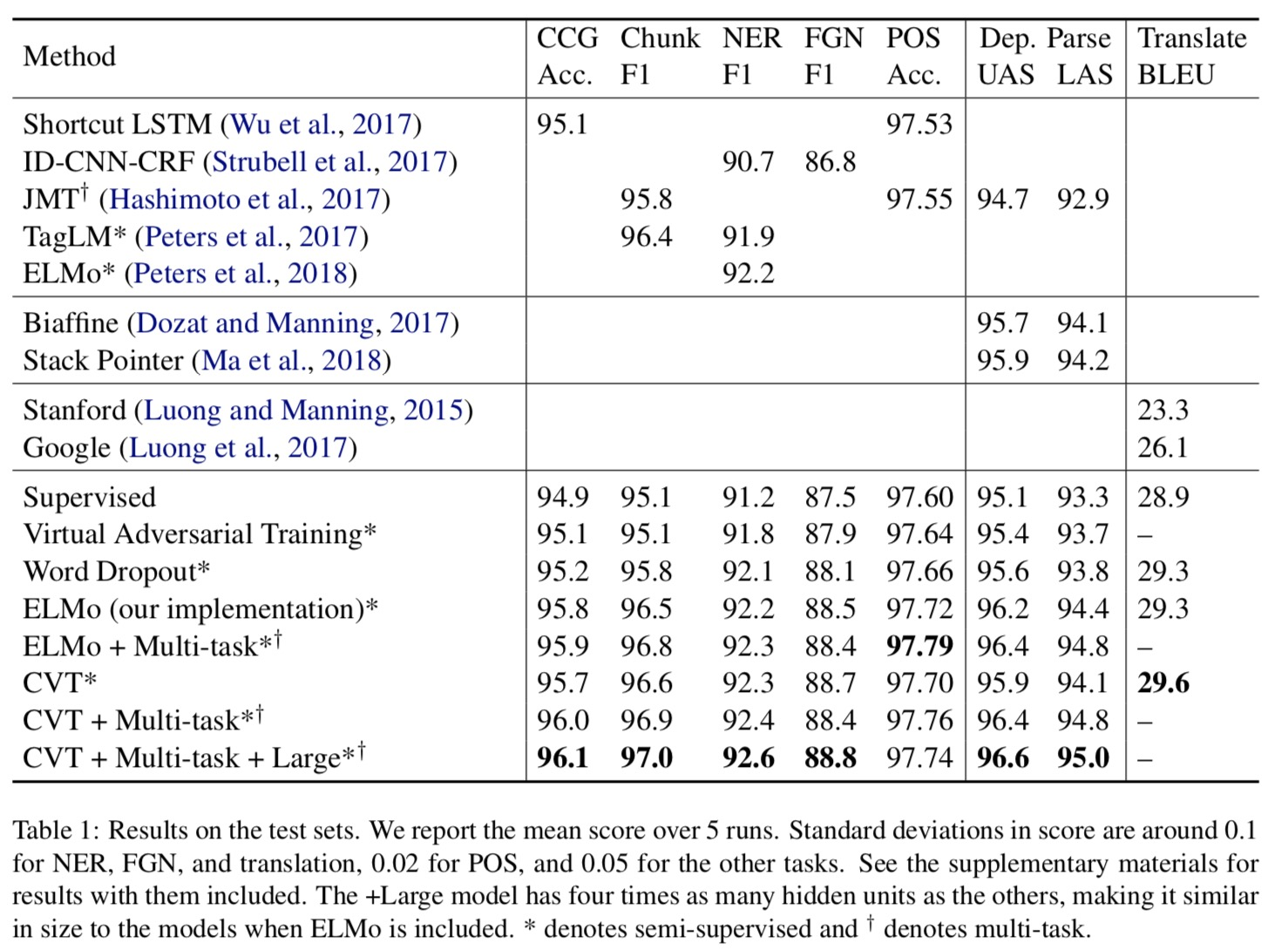
Compare Cross-View Training on 7 tasks:
- CCG: Combinatory Categorical Grammar Supertagging
- Chunk: Text Chunking
- NER: Name Entity Recognition
- FGN: Fine-Grained NER
- POS: Part-of-Speech Tagging
- Dep. Parse: Dependency Parsing
- Translate: Machine Translation
Results
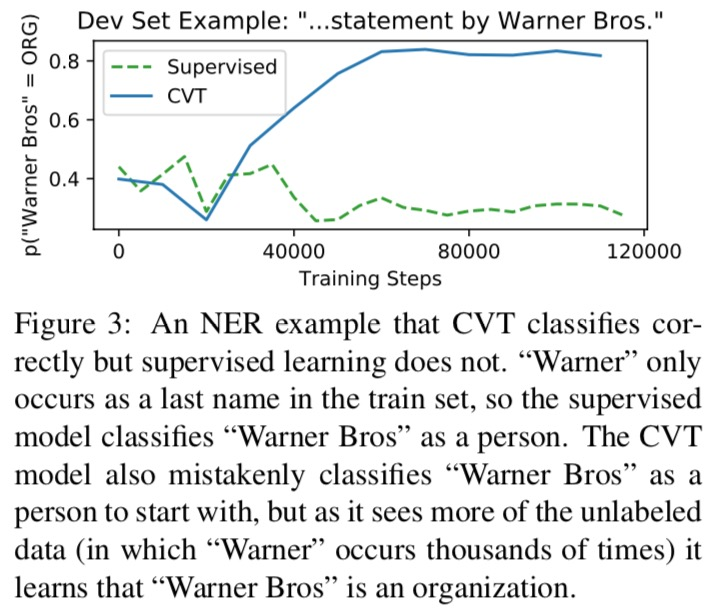
Case study: NER example
Takeways
Semi-supervised learning is an interesting method to address label deficiency in deep learning
About elegance: general to many tasks, succinct mathematical expression
What's more?
Semi-Supervised Sequence Modeling with Cross-View Training
By Jing Liao
Semi-Supervised Sequence Modeling with Cross-View Training
- 129


