Stacking context
Stacking order
Every element in an HTML document can be either in front of or behind every other element in the document
1 Without z-index
Stacking order is the same as the order of appearance in the HTML
2 When introduce position
Any positioned elements (and their children) are displayed in front of any non-positioned elements.
3 When introduce z-index
things get a little trickier
z-index creates stacking context
Stacking Context
A three-dimensional conceptualization of HTML elements along imaginary z-axis relative to the user,
Stacking Context
Groups of elements with a common parent that move forward or backward together in the stacking order
Example
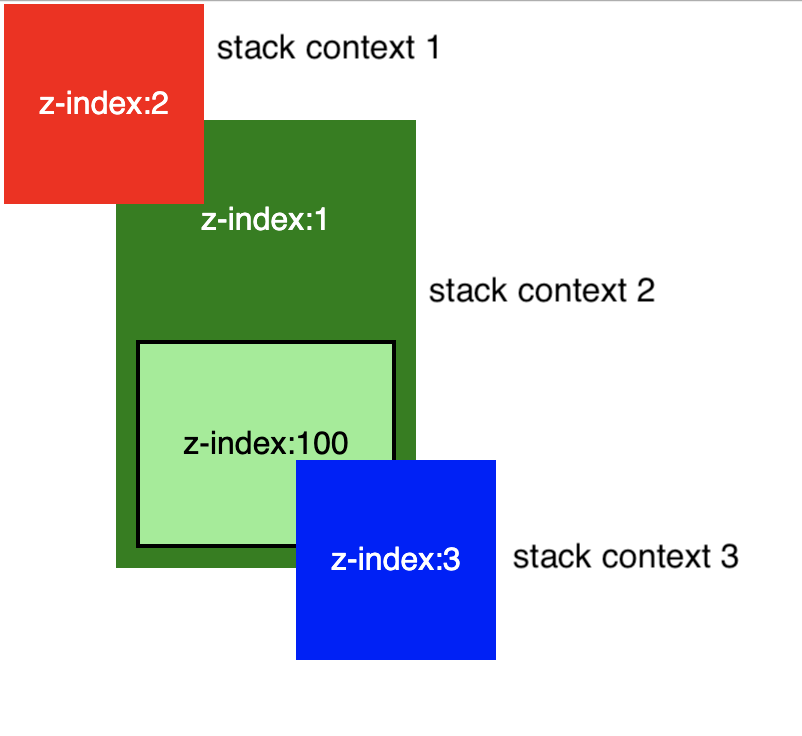
What forms stack context
- Element is the root element of a document
- Element has a position value other than static and a z-index value other than auto
- Element has an opacity value less than 1
- Element with properties: transform, filter, clip-path, will-change etc
Stacking order within stacking context
- The stacking context’s root element
- Positioned elements (and their children) with negative z-index values
- Non-positioned elements
- Positioned elements (and their children) with a z-index value of auto
- Positioned elements (and their children) with positive z-index values
original css
<div><!-- 1 -->
<span class="red"><!-- 6 --></span>
</div>
<div><!-- 2 -->
<span class="green"><!-- 4 --><span>
</div>
<div><!-- 3 -->
<span class="blue"><!-- 5 --></span>
</div>After apply tranform
<div><!-- 1 -->
<span class="red"><!-- 1.1 --></span>
</div>
<div><!-- 2 -->
<span class="green"><!-- 4 --><span>
</div>
<div><!-- 3 -->
<span class="blue"><!-- 5 --></span>
</div>Quiz
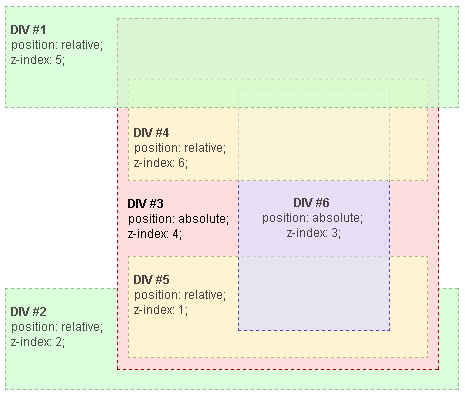
My Finance Example
Stacking context
By jingliu
Stacking context
- 313



