Observer &
Basic RxJS
Observer Pattern
The observer pattern is a software design pattern in which an object, called the subject, maintains a list of its dependents, called observers, and notifies them automatically of any state changes, usually by calling one of their methods.
Event Handling
function clickHandler(event) {
console.log('clicked');
}
document.addEventListener('click', clickHandler);
Proxy
function observe(o, callback) {
return new Proxy(o, {
set(target, property, value) {
callback(property, value);
target[property] = value;
},
});
}
const door = { open: false };
const doorObserver = observe(door, (property, value) => {
if (property === 'open') {
// ...
}
});
doorObserver.open = true;
React - useEffect
const [open, setOpen] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
function handler() {
setOpen(false);
}
document.addEventListener('click', handler);
return () => {
document.removeEventListener('click', handler);
};
}, [open]);
Simple Implementation
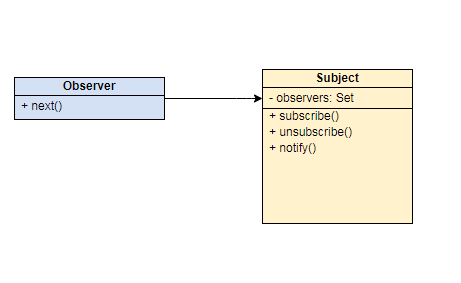
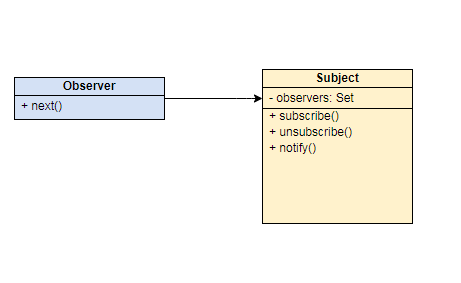
class Subject<P> {
constructor() {
this.observers = new Set<Observer<P>>();
}
subscribe(observer: Observer<P>) {
this.observers.add(observer);
}
unsubscribe(observer: Observer<P>) {
this.observers.remove(observer);
}
notify(payload: P) {
if (this.observers.size > 0) {
this.observers.forEach(observer => observer.next(payload));
}
}
}class Observer<P> {
next(payload: P) {
// ...
}
}
So what ?
Even though we have subject and observers, but what can we do ?
Functional programming
const result = [1, 2, 3, 4]
.filter(num => num % 2 === 0)
.map(num => num * 2)
.flatMap(num => [num, num + 1]);Iterator
function* getNumbers(words) {
for (let word of words) {
if (/^[0-9]+$/.test(word)) {
yield parseInt(word, 10);
}
}
}
const iterator = getNumbers('Rytass 尾牙 1/08 !');
iterator.next();
// { value: 1, done: false }
iterator.next();
// { value: 0, done: false }
iterator.next();
// { value: 8, done: false }
iterator.next();
// { value: undefined, done: true }Description of Observer
It is mainly used to implement distributed event handling systems, in "event driven" software. In those systems, the subject is usually called a "stream of events" or "stream source of events", while the observers are called "sink of events".

RxJS
document.addEventListener('click', () => console.log('clicked!'));
import { fromEvent } from 'rxjs';
fromEvent(document, 'click')
.subscribe(() => console.log('Clicked!'));
Example
Debounced Resize
fromEvent(window, 'resize')
.pipe(debounceTime(250))
.subscribe(() => console.log('window resized!'));Example
Button Clicked Times
fromEvent(document, 'click')
.pipe(
map(event => 1),
scan((total, now) => total + now, 0)
)
.subscribe(count => console.log(`Clicked ${count} times`));Example
Counter
const plugBtn = document.querySelector('button.plus', 'click');
const minusBtn = document.querySelector('button.minus', 'click');
const plusClickEvent$ = fromEvent(plusBtn, 'click');
const minusClickEvent$ = fromEvent(minusBtn, 'click');
merge(plusClickEvent$.pipe(mapTo(1)), minusClickEvent$.pipe(mapTo(-1)))
.pipe(scan((total, now) => total + now, 0))
.subscribe(count => console.log(`Counter: ${count}`));
RxJS Operator
switchMap
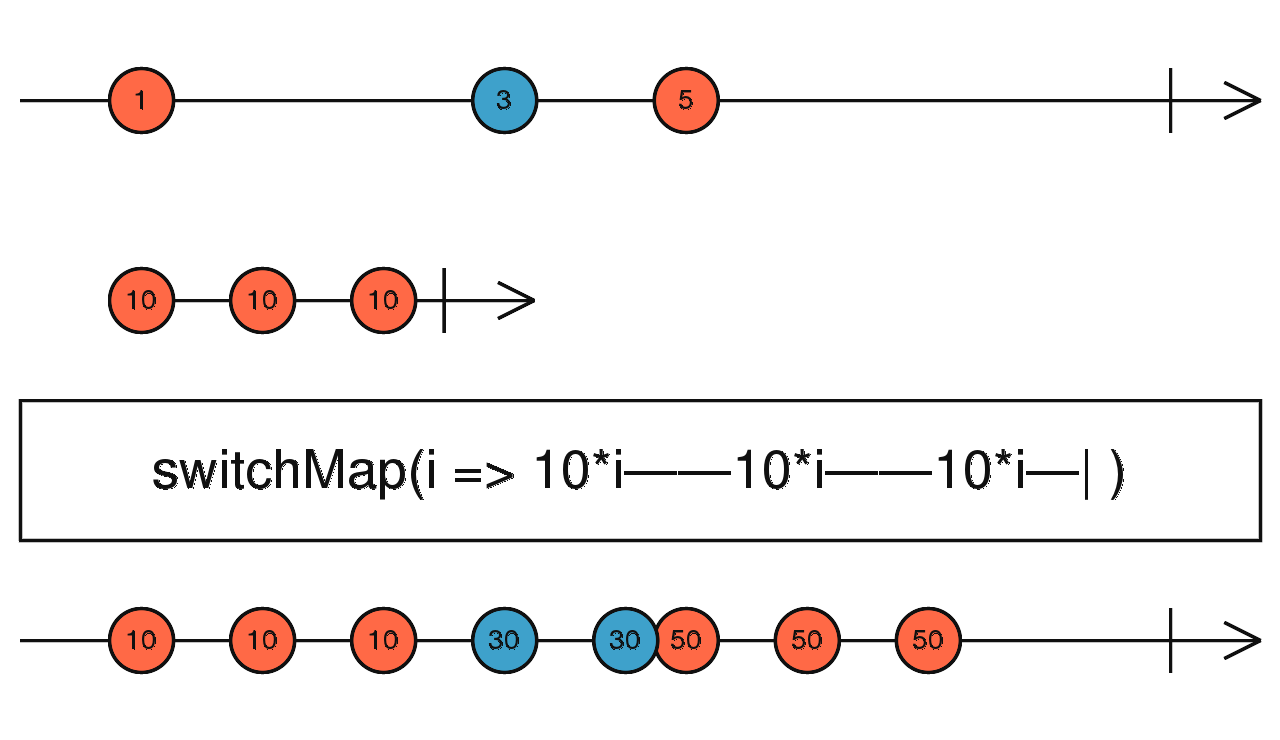
RxJS Operator
switchMap
import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { switchMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const result = clicks.pipe(switchMap((ev) => interval(1000)));
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
// click
// 0
// 1
// 2
// click
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
RxJS Operator
takeUntil
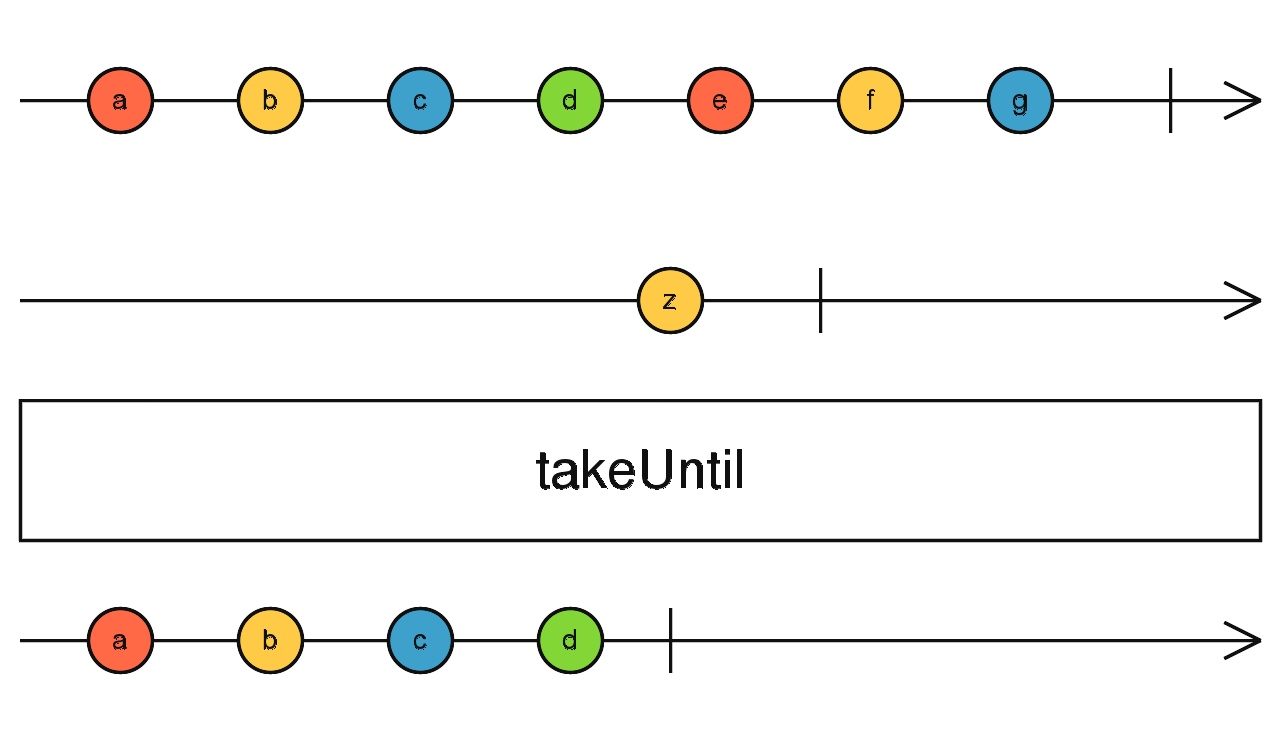
RxJS Operator
takeUntil
import { fromEvent, interval } from 'rxjs';
import { takeUntil } from 'rxjs/operators';
const source = interval(1000);
const clicks = fromEvent(document, 'click');
const result = source.pipe(takeUntil(clicks));
result.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
Example
Autocomplete - fetch
const url =
"https://zh.wikipedia.org/w/api.php?action=opensearch&format=json&limit=5&origin=*";
const getKeywords = keyword =>
fetch(`${url}&search=${keyword}`, { method: "GET", mode: "cors" }).then(res =>
res.json()
);Example
Autocomplete - keyword stream
const keyword$ = new Subject<string>();
keyword$
.pipe(
debounceTime(250),
switchMap(value =>
value
? from(getKeywords(value)).pipe(
map(res => res[1]),
takeUntil(cancel$)
)
: of([])
)
)
.subscribe(setKeywords);
onChange={event => keyword$.next(event.target.value)}
Example
Autocomplete - add cancel stream
const cancel$ = new Subject();
// ...
from(getKeywords(value)).pipe(
map(res => res[1]),
takeUntil(cancel$)
)
// ...
useEffect(() => () => cancel$.next(), []);

Observer & Basic RxJS
By jjaayy
Observer & Basic RxJS
- 549



