Persuasive communication
CMGT 1.3 Communication - Lecture week 6
J. de Boer MSc
Introduction
- Self-persuasion
- Promised land
- Attractiveness
- Decoy effect
- Mere exposure
- Anthropomorphism
- Authority
- Social Proof
- Loss or gain
- God terms
Topics
Follow this presentation live
What to learn?
- Information from the slides
- Syllabus week 6 from Blackboard.
94%
Click, whirr
Automatic, stereotyped behaviour is prevalent in much human action because in many cases, it is the most efficient form of behaving and in other cases, it is simply necessary.
You and I exist in an extraordinarily complicated environment, easily the most rapidly moving and complex that has ever existed on this planet.
To deal with it, we need shortcuts. We can't be expected to recognize and analyze all the aspects in each person, event, and situation we encounter in even one day.
We simply don't have the time, energy, or capacity for it)
Help!
How do I (draw attention/convince others)
and sell/share
my [...]
if 94% of all daily received information
is processed unconsciously?
- Game
- Website
- Product
- Concept
- Idea
- Pitch
- Artwork
- Service
- etc...
- etc...
- etc...
Self-
Persuasion
No one is better than you at persuading yourself to change!
- Holy grail of Persuasion
- No confrontation or resistance
- Generated arguments turn into beliefs
- Relation "sick" & "enjoying life"
- Stimulates choice between two implicit options

Vulcano Insurance
What about you?
'Why smoking is bad' arguments
- Self-argumentation
- External arguments
Promised
land
Buy this product and follow me to the Promised Land!

Basic needs?
Product-irrelevant needs are promised! (social, emotional, sexual)
Seduce to reach desirable goal!

Definition

PL directly aimed at creating strongest reward response in the brain of the perceiver.
Even though claims made are exaggerated or obvious lies
Note: Even unachievable desires are strong motivators!
Why it works
- People want the exaggerated claims to be true
- Presenting these brand with attractive, but unrealistic situations associated them with our dreams and desires
How it works
Just do it
Ever encountered a false prophet?
Attractiveness
also: liking
"It's amazing how complete is the delusion that beauty is goodness." (Leo Tolstoy, The Kreutzer Sonata)
Attractiveness = Averageness

Attractiveness
- Western society learn that "beauty is in the eye of the beholder", but use it abundantly in marketing.
- Bodily attractiveness is important, face is first visual object in interactions.
- People believe they are not seduced by beauty in ads.
- In general: your "morning face" is whats counts!
3 physical components
Averageness
How prototypical of representative a face is
Symmetry
The degree to which a face is symmetrical on the vertacial axis
Sexual dimorphism
The hormonal expression of sex-specific features
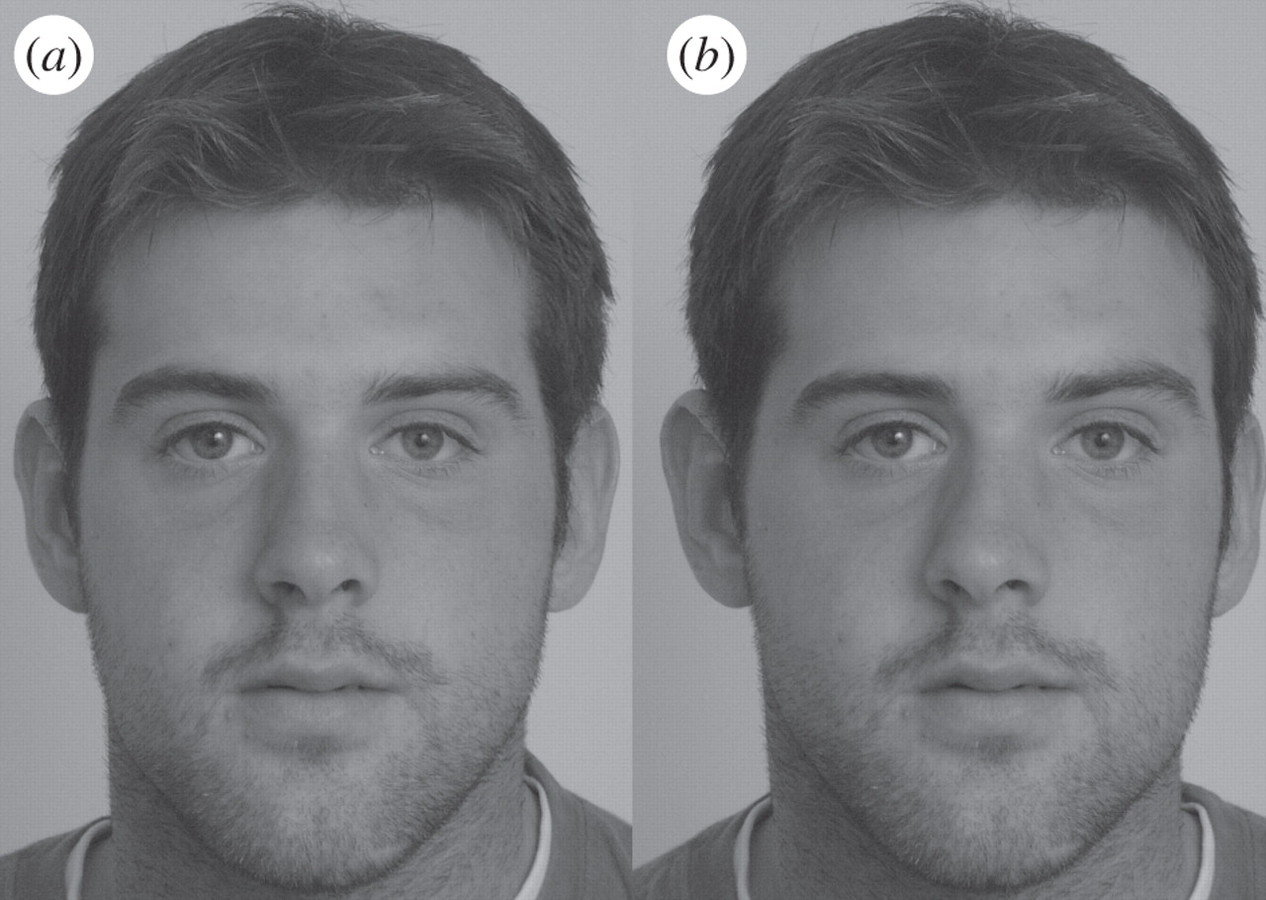
40 faces around the world
Science of Attraction
Decoy
When consumers are choosing between two similar products, introducing a decoy can push people towards the desired direction
The effect explained
Why useful?
It is more difficult to choose between two equally preferred options.
(adding decoy reduces stress reactions by lowering the feeling of conflicting information)
When it works
No matter how well-informed you are about this technique, it is almost undetectable.
Anything ca be advertised as a decoy (even a politician)
How to implement
Always use the decoy as the least-favoured option
Works best in high-quality vs low-quality products.
Interesting read:
The Decoy Effect, or How to Win an Election
by Shankar Vedantam
Take a look at
the canteen or supermarket!
Mere Exposure
The more we see it, the more we like it
- What do you think about Coca Cola?
- Write down 3 associations with this brand.

How it works
- Neutral or positive things are perceived as more positive when repeated.
- Caused by increased feeling of familiarity
- Valid for all visual stimuli (products and people)
- Flood exposure
- Works even if there is no existing connection
Definition
The mere-exposure effect is a psychological phenomenon by which people tend to develop a preference for things merely because they are familiar with them.
The effect has been demonstrated with many kinds of things, including words, Chinese characters, paintings, pictures of faces, geometric figures, and sounds.
In studies of interpersonal attraction, the more often someone sees a person, the more pleasing and likeable they find that person.
Note
- The first 10-20 exposures are most important
- Each additional exposure has a reduced impact
- Each additional exposure has a reduced impact
- Exposures should be brief
- With sufficient delay
- To prevent overexposure
Product Placement
I'm moving to Johannesburg!
Let's try!
You need a pen + paper

REMEMBER
Which face correspondents with which name
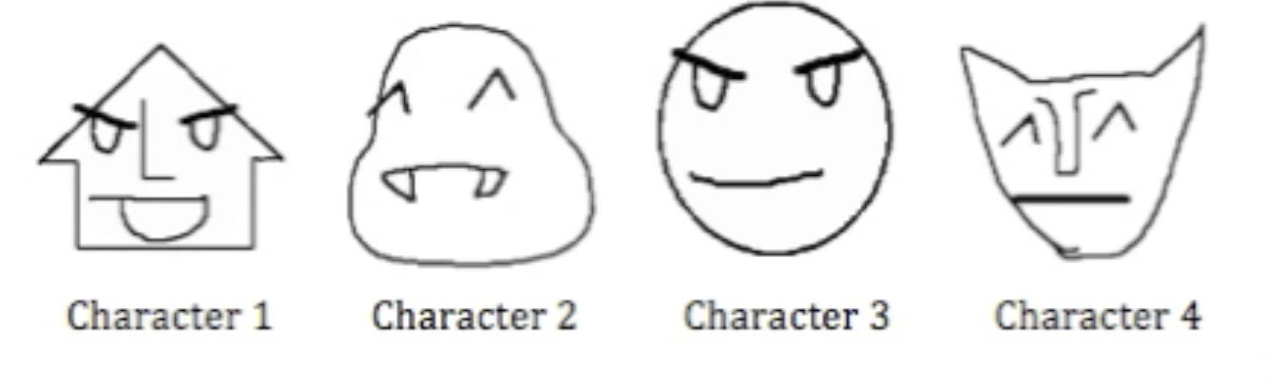
RECALL
Write down the name of each character

How many correct?

Draw your preferred characters
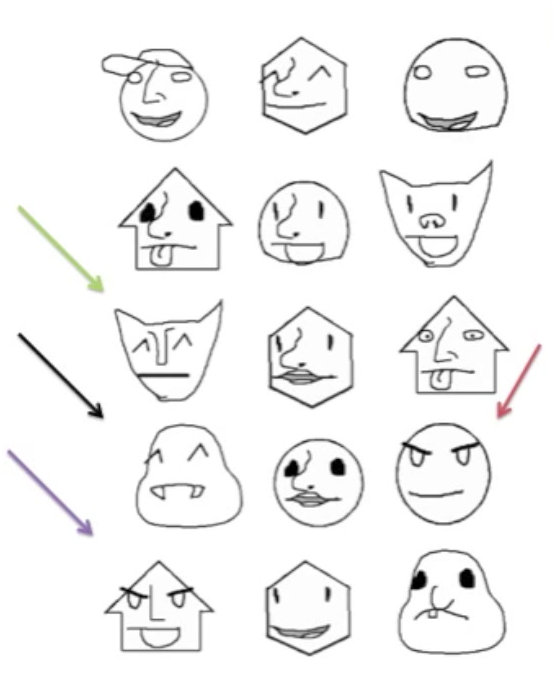
How many of these do you prefer?
Anthropomorphism
When a brand or product is seen as human-like,
people will like it more and feel closer to it.
What do you see?
- Scenario
- Characters
- Emotions

Definition
The tendency to describe and visualise animals or non-living things using human characteristics.
Humans try to explain many events with Anthropo-morphism (forces of nature, behaviour of animals) by ascribing thoughts, needs, or intentionality to these events as if they were human.
Kids
We use it when we're little: stuffed animal, pets.
Feeling pity for Nemo
History

We keep using it.
Our brain continues to try to see things as human-like.
It makes us bond with objects. It makes it see more like us!
Growing old
Futuristic Anthropomorphism?
When did you use it
in your work?
Authority
People or symbols that signify legitimate authority trigger compliance and obedience
Authority works:
Academic titles
Impressive clothing
Expensive material goods


Rank, stature, age, position, experience, gender, abilities
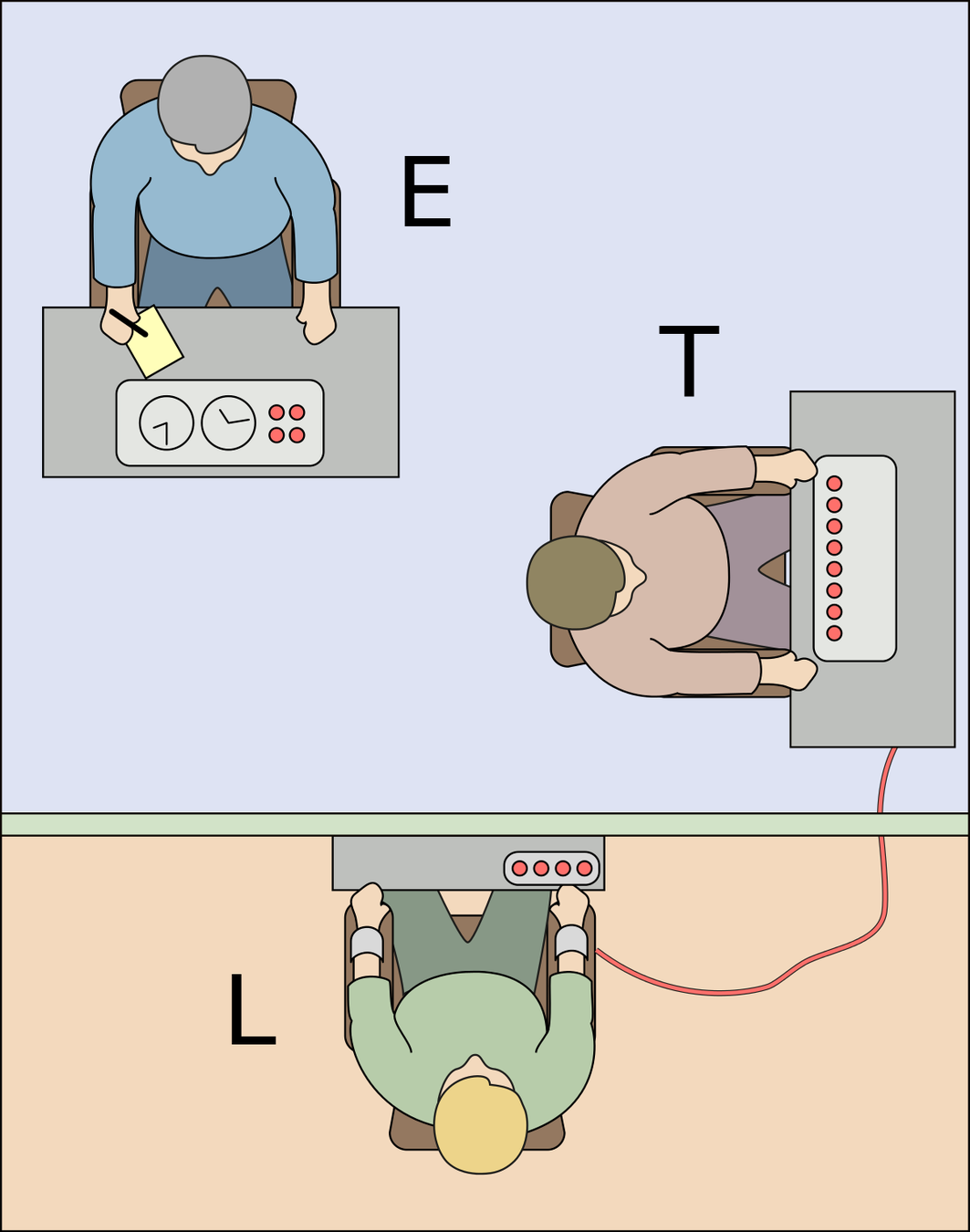
Milgram's experiment
Milgram (1963) was interested in researching how far people would go in obeying an instruction if it involved harming another person.
How easily could ordinary people be influenced into committing atrocities, for example, Germans in WWII.

Social
Proof
People have an innate drive to
copy others' decisions and behaviour
Social Proof on the web

Loss or gain
Should the glass be half full or half empty? Fearing loss increases risk-taking: expecting gains increases safety behaviour
Loss vs Gain Framing
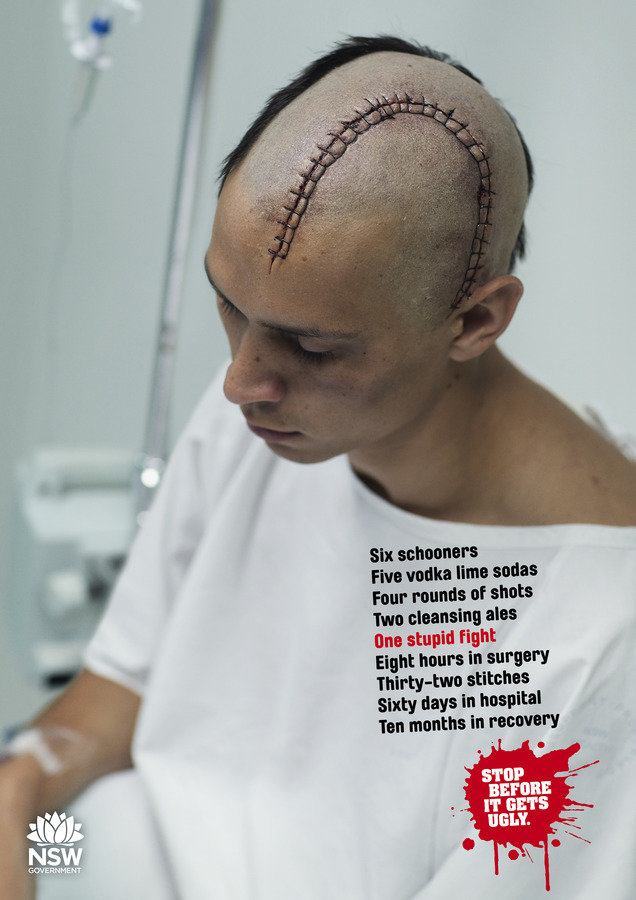
"Healthy lifestyles" campaigns are often framed negative.
The effect is dependent on conscious processing of the image.
Everything else being equal: People opt for certainty.
Certainty effect
the certainty effect happens when people overweight outcomes that are considered certain relative to outcomes that are merely possible
- Li & Chapman (2009)
A
The FIRST Gamble is 61% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 39% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 63% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 37% chance of winning 0.
A
The FIRST Gamble is 98% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 2% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 100% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 0% chance of winning 0.

A
The FIRST Gamble is 61% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 39% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 63% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 37% chance of winning 0.

A
The FIRST Gamble is 98% chance of winning 65.000 Euros and 2% chance of winning 0.
B
The SECOND Gamble is 100% chance of winning 60.000 Euros and 0% chance of winning 0.

Both changes increased 37%
Certainty effect
happened
Situation 1 : both gambles risky
Most people prefer higher outcome
Situation 2 : Smaller outcome becomes certain
Most people prefer sure thing over risky option
Certainty effect
People are drawn to certainty, giving higher preference to options that have high levels of certainty.
Often leads to risk/loss aversion
Loss aversion
Loss aversion
People are 2x more sensitive for feelings of los, than to feelings of gain.
Once in a loss situation, we do everything to avoid it.
A loss or gain frame needs to be followed up by a clear "how-to" to move someone to act.
God terms
Some words are to intrinsically good,
it is hard to say 'no' to them
Terms people value
Equality
Freedom
Justice
Love
Wonderful
Happiness
Progress
Democracy
Terms people avoid association with
Terrorist
Inequality
Deterioration
Rivalry
Hypocrite
Sadness
Weakness
Incompetent
Let's try!
Note all God terms
(words with positive meaning)
in the speech by MLK.
God Terms Examples
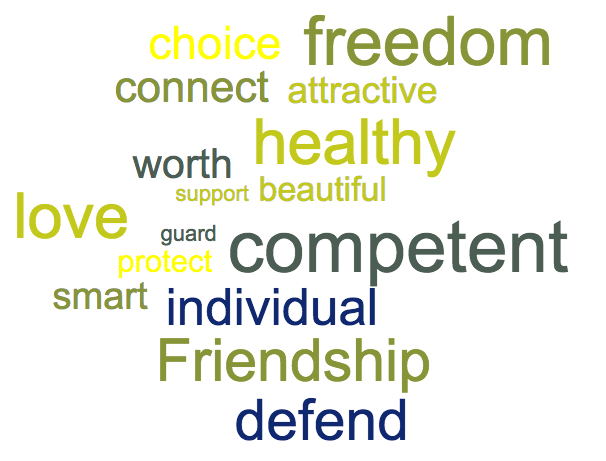
Many words have inherent positive or negative connotations.
They refer to desires,
needs, and fears.


Remarks
God terms & Devil terms play into our needs. Using these words triggers the respective needs in the target.
When God terms are popular for a while, the powers of their use deteriorates
(they can even turn into Devil terms!)
Applicability
Differences
Gender
- In ads, women describe their physical attractiveness
- Men showcase their material wealth
(Buss & Kenrick, 1998)
Culture
healthcare commercial
- Northern America: doctor in a white coat
- Europe: Testimonials other users
Thank you
Good luck - Prepare well!
CMGT 1.3 Communication 2021 - Persuasive communication
By Johannes de Boer
CMGT 1.3 Communication 2021 - Persuasive communication
- 308



