Python Programming
Class 1
Author: Jose Miguel Arrieta R.
¿What is a Computer program?
-
A computer program is a collection of instructions that performs a specific task when executed by a computer
¿What is Python?
Designed by Guido van Rossum
Python is a high-level programming language, and its core design philosophy is all about code readability and a syntax which allows programmers to express concepts in a few lines of code.”

Python Advantages
- Readable: Intuitive and strict syntax
- Productive: saves a lot of code.
- Portable: For every operating system.
- Reloaded: It comes with many libraries.
¿What is Python used for?
-
Web Development
- Frameworks such as Django, Flask
-
Data Analysis
- Libraries such as NumPy and Pandas
- Data visualisation libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn
-
Internet Of Things
- Raspberry Pi + python
-
Web Scraping
- Example: https://scrapy.org/
-
Computer Vision
-
OpenCV library
-
-
Machine Learning
- Libraries such as Scikit-Learn, NLTK and TensorFlow.
-
Game Development
- PyGame
Programming tools

Download: https://www.anaconda.com/download/.

-
Anaconda is the world’s most popular Python data science platform (Everything you need 'out of the box').
-
Includes:
- Spyder (IDE/editor - like pycharm) and Jupyter
-
Includes:
Spyder
Spyder is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
Console

Spyder is the Scientific PYthon Development EnviRonment
Sublime is an text editor
Notes:
-
When to use?
- Reports with code
- Reproducible


The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text.
Python Code
Data Types
- Conversions
- type command
-
Integer <int>
-
Float <float>
-
String <str>
-
Boolean <bool>
- etc.
- Example
>>> type(5)
<type 'int'>
>>> type('str')
<type 'str'>
>>> type(4.6)
<type 'float'>
Variables
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program.
- Example
a = 5.0
b = 'Hola'
c = 5+6Math operators
- + plus
- - minus
- /
- * multiply
- < less-than
- < greater-than
- <= less-than-equal
- >= greater-than-equal
- and
- or
- not
Logic operators
Input/Output operators
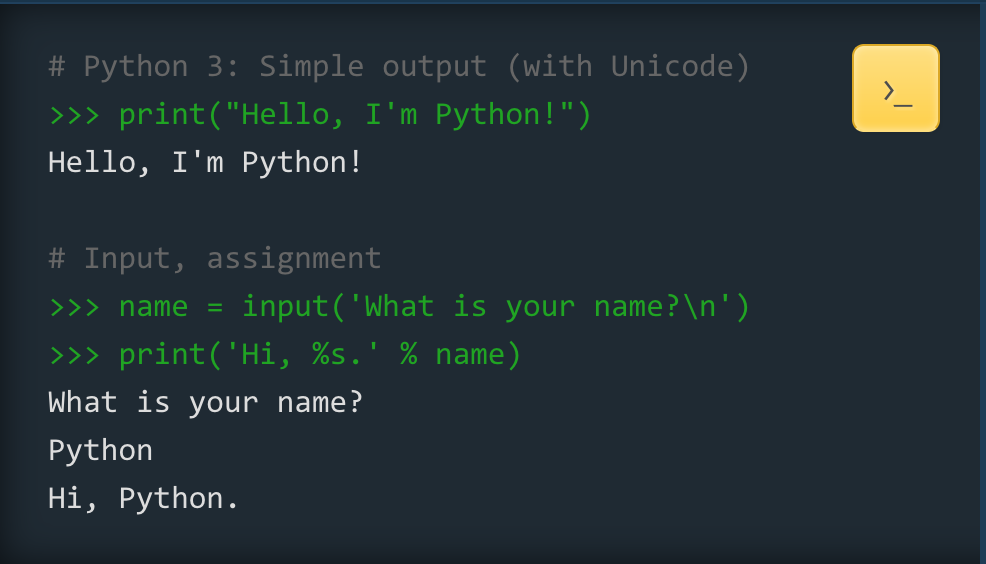
Input and output (I/O) operators are used to take input and display output.
>>> a = input('Inserte un número: ')
Inserte un número: 3
>>> a
3
>>> print(a)
3
>>> print('Hola')
HolaComments
Single-line comments
Comments that span multiple lines
# This is a comment"""
a = input('Inserte un número: ')
a
print(a)
print('Hola')
"""
print('This is not commented')Exercise 1
- Write a script that request two number from user
- Make a sum with the two numbers and save result in a variable.
- Finally print result variable
- Note: Write script in Spyder, save, open console and run with python in console.
Answer 1
#Sum Two numbers.
# Request first number from user.
a = float(input("Ingrese un numero: "))
# Request second number to user.
b = float(input("Ingrese otro numero: "))
# Make the sum.
c = a + b
# Show result in screen.
print("\nLa suma de los numeros es: " +str(c))Exercise 2
- Create an algorithm to calculate perimeter and area of a circle
- Create a variable with pi value
- Request radio to the user
- Calculate perimeter and save in variable
- Calculate area and save in variable
- Print in screen perimeter and area variables
Answer 2
# Variables:
PI = 3.141592
# Request the radio to the user
r = float(input("Ingrese el radio del circulo: "))
# Calculate perimeter
p = 2 * PI * r
# Calculate area
a = PI * r ** 2
# Muestra los resultados en pantalla
print "El perímetro del circulo es: ", p
print "El área del circulo es: ", aExercise 3
Algorithm to transform Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Request Fahrenheit to user
- Make transformation
- Show result in screen
Answer 3
# Request Fahrenheit degrees to transform into Celsius
f = float(input("Ingrese los grados Fahrenheit:"));
# Make conversion
c = (f - 32.0) * (5.0 / 9.0);
# Show result in screen
print f, " grados Fahrenheit corresponden a ", c, " grados Centígrados"Python-Programming [Class 1]
By Jose Arrieta
Python-Programming [Class 1]
Python Advantages, Anaconda, Spyder, Jupyter, Python Data Types, Variables, Math operators, Logic operators, Input/Output operators, Comments
- 8,547



