WordPress Multisite
What, Why, and How
JOSH LEE
- Developer since ~2006
- WordPress developer since ~2010
- Have built scores of WordPress websites, plugins, and themes
ONLINE
What
Why
How
What is Multisite?
What is Multisite
Multisite is an option built into every WordPress installation.
It allows multiple websites to be hosted from one installation, as a "network"
What
Why
How
Two Main Ways:
A network of separate blogs/sites
A single site with different user permissions
from section to section
Examples of a Multisite Network
- WordPress.com
- The Rainmaker Platform
- My own blog
Pros of a Multisite Network
- Launching a new site is just a few clicks
- Multiple low-traffic websites in a single hosting environment can save money
- Maintenance and updates for the entire network happen in once place
- New themes and plugins are immediately available to the entire network (or optionally restricted)
- A single user can manage one or many sites with a single sign on
Cons of a Multisite Network
- Single point of failure
- Performance can be more difficult to manage
- All sites must share the same versions of plugins and themes — updates may have adverse effects for untested sites
Multisite for Permission Management
Example: Quarto Knows
Pros of Multisite for Permissions Management
- Each user can have different permissions for any given site.
- Different themes and/or plugins can be activated on each site for department-specific style or functionality
- All of the benefits of a network for creating microsites/landing pages/etc
Cons of Multisite for Permissions Management
- All settings must be set on each site separately, which can be a pain with themes/plugins that require a lot of configuration
- Querying content from across all sites is an added layer of complexity (e.g. for a homepage)
- Some plugins may not work (although some are made specifically for MS too!)
What
Why
How
Installing Multisite
Installing (Enabling) Multisite
<?php
/* inside wp-config.php */
define('WP_ALLOW_MULTISITE', true);Installing Multisite
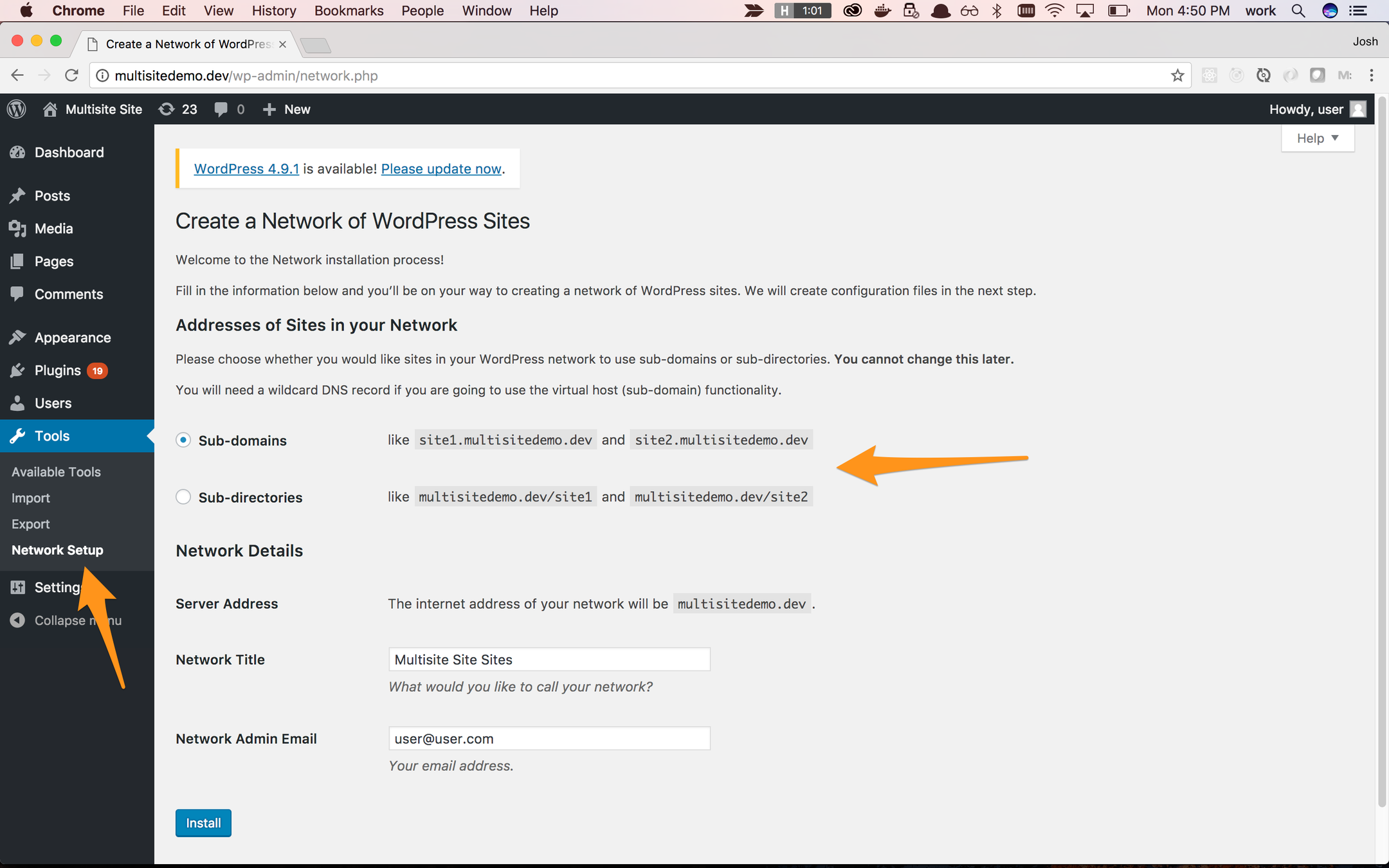
Subdomain Vs Subfolder Install
Subdomain Install
e.g. site1.mynetwork.com, site2.mynetwork.com
Can also be used for full domains since WP 4.5 (or with a plugin on older versions)
Subfolder Install
e.g. mysite.com/site1, mysite.com/site2
Great for the permission segmentation strategy
Super Admins / Site Admins
Super Administrators
- Can access "Network Dashboard"
- Create, edit, and delete sites on the network
- Can change any user's permissions on any site
- Can enable / manage network plugins and themes
- Can manage network-wide settings for WordPress and some plugins
Site Administrators
Site administrators can do all of the things that an administrator of a regular WordPress installation, except:
- Plugin and theme choices are limited to those that have been enabled by a super administrator — new ones cannot be installed
- Optionally, super administrators may completely disable the "Plugins" admin menu item for site administrators, leaving it up to super administrators only to manage site plugins.
Regular users (the public)
Optionally, registration can be enabled, allowing anybody to sign up and create a site
Be very, very, very, very careful with this if you don't want to end up hosting thousands of websites selling fake watches
Hosting Considerations
Hosting WordPress Multisite
- Pretty similar to regular WordPress: PHP + MySQL are the only requirements
Anatomy of a Multisite
- One folder with WordPress core and wp-content
- Each site has it's own uploads folder within wp-content/uploads
- Each site has it's own set of database tables, with a different prefix
- For multidomain/subdomain installations, all hosts are pointed to the same webroot
Hosting Caveats
- You will need the ability to edit your server's hosts configuration (usually this will be apache or nginx)
- Some hosts offer specific plans designed for Multisite
- Performance can become an issue for large or highly trafficked networks
Managing Performance
- Minimize the amount of PHP and number of SQL queries required to build a front-end page — lean on static assets
- Use a CDN to host static assets
- Use aggressive caching strategies for page content
- I really like Cloudflare as a free, easy band-aid
Plugin and Theme Considerations
Multisite functions
- Get data from other sites (usually done between the "main" site and the subsites, or vice-versa)
- Get network-wide options
Multisite Functions
get_option() becomes get_site_option()
Multisite Functions
get_sites()
* Expensive!
** Actually restores the most recent blog
Database Differences
WP_SITE table
Stores information about the primary site
WP_blogs table
Stores the list of sites ("blogs") and their URLs
WP_Sitemeta table
Stores metadata about the network as a whole
Security Considerations
Security with Multisite
- Every site uses the same database (usually*)
- All sites are using the same plugins and themes
- All sites may have disk write access (e.g. for the uploads folder) which could be left too broadly open
This creates a few vectors for attack...
Security concern mitigation
- Ensure write access is limited to the correct directories, or better yet, use a read-only server and a plugin like WP Offload S3
- Regular administrators should almost never have FTP write access or the ability to install plugins / change code
Deploying Multisite
Deploying Multisite
Just like any other WordPress site: get the wp-content folder onto the server somehow (excepting the uploads folder)
INTERMEDIATE AND ADVANCED SETUPs
Intermediate and Advanced Setups
- Read-only environments (e.g. Heroku)
- Containerization
- Sharded database (e.g. with HyperDB)
- Horizontally scaled servers/containers
Further Reading
Contact Me
Josh Lee
WordPress Multisite
By Josh Lee
WordPress Multisite
- 1,545



