Recommendation systems
Week 8
Recommender system can
modeled as a bipartite graph with two node types: users and items.
- Edges connect users and items and indicate user-item interaction
(e.g., click, purchase, review etc.)
- Often edge has timestamp of the interaction.
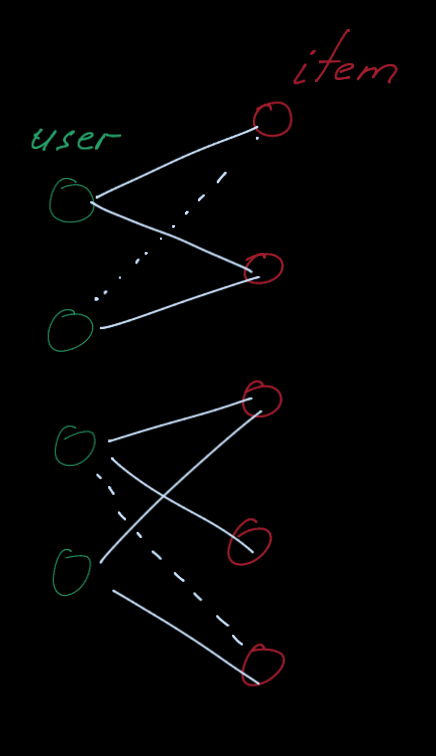
Given past user-item interactions we want to predict new items, the user will
interact in the future
- link prediction task

We need three functions:
- an encoder to generate user embeddings 𝒖
- an encoder to generate item embeddings 𝒗
- Score - a scalar function score(u, v), that returns a real-valued score
link prediction
Evaluation metric
- \( P_u \) is a set of positive items the user will interace in the future.
- \( R_u \) is a set of items recommended by the model.
- In top-K recommendation, \( |R_u| = K \).
- Items that the user has already interacted are excluded.
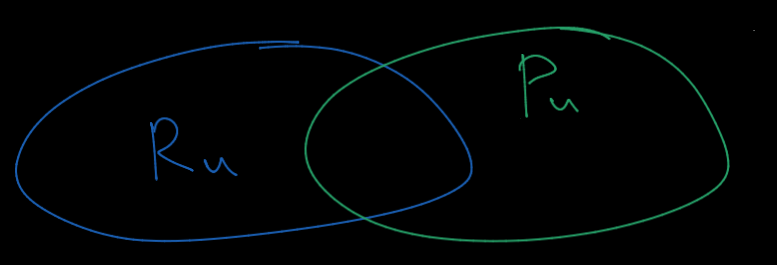
Evaluation metric
The original training objective (recall@K) is not differentiable.
Two surrogate loss functions are widely-used to enable efficient gradient-based optimization.
- Binary loss
- Bayesian personalized Ranking (BPR) loss
Binary Loss
1. Define positive/negative edges
- A set of positive edges \( E \) (i.e., observed/training user-item interactions)
- A set of negative edges \( E_{neg} = {(u,v) | (u,v) \notin E, U \in U, v \in V} \)
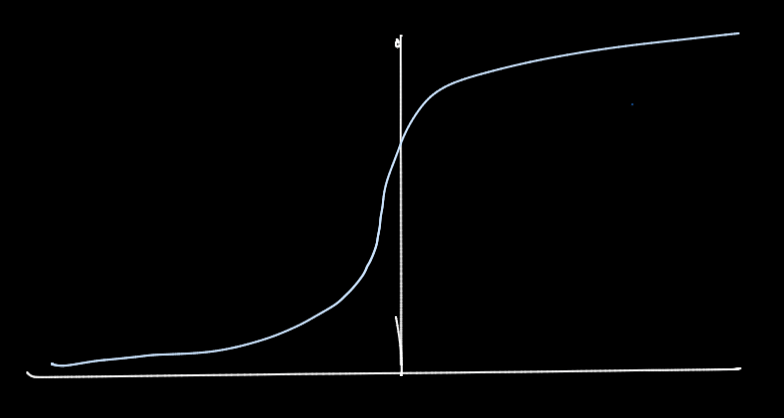
2. Define sigmoid function \( \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1 + exp(-x)} \)
- Maps real-valued scores into binary likelihood scores, i.e., in the range of [0,1].
Curriculum learning
Binary Loss
Binary loss: Binary classification of positive/negative edges using \( 𝜎(𝑓, 𝒖, 𝒗 ) \):
\( -\frac{1}{|E|} \sum_{(u, v) \in E} \log \left(\sigma\left(f_\theta(\boldsymbol{u}, \boldsymbol{v})\right)\right)-\frac{1}{\left|E_{\mathrm{neg}}\right|} \sum_{(u, v) \in E_{\mathrm{neg}}} \log \left(1-\sigma\left(f_\theta(\boldsymbol{u}, \boldsymbol{v})\right)\right) \)
Binary loss pushes the scores of positive edges higher than those of negative edges.
- This aligns with the training recall metric since positive edges need to be recalled.Cae
Binary Loss
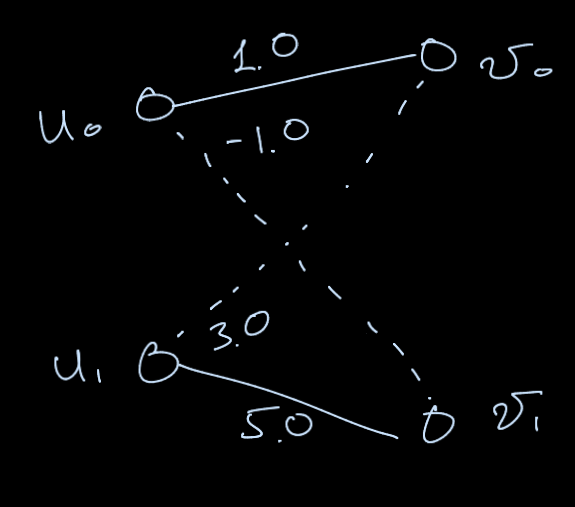
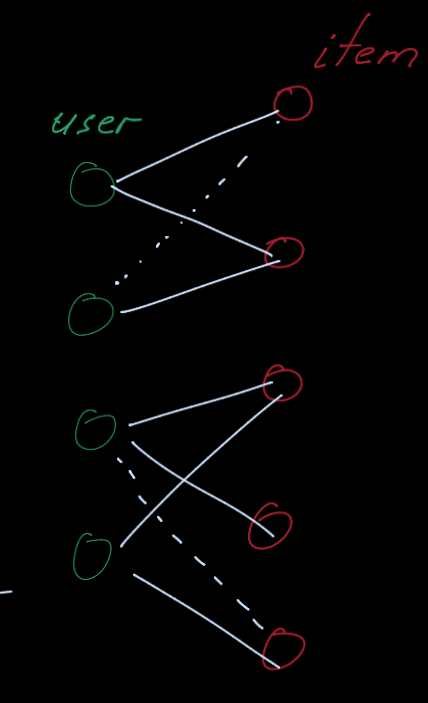
Let’s consider the simplest case:
- Two users, two items
- Metric: Recall@1.
- A model assigns the score for every user-item pair (as shown in the right).
Training Recall@1 is 1.0, because \( v_0 \) is correctly recommended to \( u_0 \)
However, the binary loss would still penalize the model prediction because the negative \( (u_1, v_0) \) edge gets the higher score than \( (u_0, v_0) \)
Bayesian Personalized Ranking
Positive edges for each user \( u^* \in U \)
\( \text { - } \boldsymbol{E}\left(u^*\right) \equiv\left\{\left(u^*, v\right) \mid\left(u^*, v\right) \in \boldsymbol{E}\right\} \)
Negative edges for each user \( u^* \in U \)
\( \boldsymbol{E}_{\text {neg }}\left(u^*\right) \equiv\left\{\left(u^*, v\right) \mid\left(u^*, v\right) \in \boldsymbol{E}_{\text {neg }}\right\} \)

Bayesian Personalized Ranking
For each user \( u^* \), we want the scores of rooted positive edges \( E(u^*) \) to be higher than those of rooted negative edges \( Е_{neg}(u^*) \).
Bayesian Personalized Ranking
For each user \( u^* \), we want the scores of rooted positive edges \( E(u^*) \) to be higher than those of rooted negative edges \( Е_{neg}(u^*) \).
Final BPR Loss: \( L = \frac{1}{|\boldsymbol{U}|} \sum_{u^* \in \boldsymbol{U}} \operatorname{Loss}\left(u^*\right) \)
Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering
Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering (NGCF) explicitly incorporates high-order graph structure when generating user/item embeddings.
Key idea: Use a GNN to generate graph-aware user/item embeddings
Initial shallow embeddings
(not graph-aware)
Use a GNN to propagate
embeddings
NGCF's graph-aware
embeddings


Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering
Forall \( u \in U \) , \( v \in V \), we set
\( \boldsymbol{u} \leftarrow \boldsymbol{h}_u^{(K)}, \boldsymbol{v} \leftarrow \boldsymbol{h}_v^{(K)} \)
Model Venue Year Strategy
| NGCF | SIGIR | 2019 | Pioneer approach in graph CF Inter-dependencies among ego and neighbor nodes |
| DGCF | SIGIR | 2020 | Disentangles users' and items'into intents and weighes their importance Updates graph structure according to those learned intents |
| LightGCF | SIGIR | 2021 | Lightens the graph convolutional layer Removes feature transformation and non-linearities |
| SGL | SIGIR | 2021 | Brings self-supervised and contrastive learning to recommendation Learns multiple node views through node/edge dropout and random walk |
| UltraGCF | CIKM | 2021 | Approximates infinite propagation layers through a constraint loss and negative sampling Explores item-item connections |
| GFCF | CIKM | 2021 | Questions graph convolution in recommendation through graph signal processing Proposes a strong close-form algorithm |
| Datasets | Models | Ours | Original | Performance Shift | |||
| Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | ||
| Gowalla | NGCF | 0.1556 | 0.1320 | 0.1569 | 0.1327 | —1.3*10 -03 | —7*10 -04 |
| DGCF | 0.1736 | 0.1477 | 0.1794 | 0.1521 | —5.8*10 -03 | —4.4*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.1826 | 0.1545 | 0.1830 | 0.1554 | —4*10 -04 | —9*10 -04 | |
| SGL* | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| UltraGCN | 0.1863 | 0.1580 | 0.1862 | 0.1580 | +1*10 -04 | 0 | |
| GPCF | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0 | 0 | |
| Yelp 2018 | NGCF | 0.0556 | 0.0452 | 0.0579 | 0.0477 | —2.3*10 -03 | —2.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0621 | 0.0505 | 0.0640 | 0.0 | —1.9*10 -03 | —1.7*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0629 | 0.0516 | 0.0649 | 0.0 | —2*10 -03 | —1.4*10 -03 | |
| SGL | 0.0669 | 0.0552 | 0.0 675 | 0.0555 | —6*10 -04 | —3*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0672 | 0.0553 | 0.0683 | 0.0561 | —1.1*10 -03 | —8*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0 | 0 | |
| Amazon Book | NGCF | 0.0319 | 0.0246 | 0.0337 | 0.0261 | —1.8*10 -03 | —1.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0384 | 0.0295 | 0.0399 | 0.0308 | —1.5*10 -03 | —1.3*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0419 | 0.0323 | 0.0411 | 0.0315 | +8*10 -04 | +8*10 -04 | |
| SGL | 0.0474 | 0.0372 | 0.0478 | 0.0379 | —4*10 -04 | —7*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0688 | 0.0561 | 0.0681 | 0.0556 | +7*10 -04 | +5*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0 | 0 | |
| *Results are not provided since SGI was not originally trained and tested on Gowalla. | |||||||
The most significant perfomance shift is in the order of 10e-3
| Datasets | Models | Ours | Original | Performance Shift | |||
| Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | ||
| Gowalla | NGCF | 0.1556 | 0.1320 | 0.1569 | 0.1327 | —1.3*10 -03 | —7*10 -04 |
| DGCF | 0.1736 | 0.1477 | 0.1794 | 0.1521 | —5.8*10 -03 | —4.4*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.1826 | 0.1545 | 0.1830 | 0.1554 | —4*10 -04 | —9*10 -04 | |
| SGL* | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| UltraGCN | 0.1863 | 0.1580 | 0.1862 | 0.1580 | +1*10 -04 | 0 | |
| GPCF | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0 | 0 | |
| Yelp 2018 | NGCF | 0.0556 | 0.0452 | 0.0579 | 0.0477 | —2.3*10 -03 | —2.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0621 | 0.0505 | 0.0640 | 0.0 | —1.9*10 -03 | —1.7*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0629 | 0.0516 | 0.0649 | 0.0 | —2*10 -03 | —1.4*10 -03 | |
| SGL | 0.0669 | 0.0552 | 0.0 675 | 0.0555 | —6*10 -04 | —3*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0672 | 0.0553 | 0.0683 | 0.0561 | —1.1*10 -03 | —8*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0 | 0 | |
| Amazon Book | NGCF | 0.0319 | 0.0246 | 0.0337 | 0.0261 | —1.8*10 -03 | —1.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0384 | 0.0295 | 0.0399 | 0.0308 | —1.5*10 -03 | —1.3*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0419 | 0.0323 | 0.0411 | 0.0315 | +8*10 -04 | +8*10 -04 | |
| SGL | 0.0474 | 0.0372 | 0.0478 | 0.0379 | —4*10 -04 | —7*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0688 | 0.0561 | 0.0681 | 0.0556 | +7*10 -04 | +5*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0 | 0 | |
| *Results are not provided since SGI was not originally trained and tested on Gowalla. | |||||||
GFCF is the best replicated model as it does not implement any random initialization of the weights
| Datasets | Models | Ours | Original | Performance Shift | |||
| Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | Recall | nDCG | ||
| Gowalla | NGCF | 0.1556 | 0.1320 | 0.1569 | 0.1327 | —1.3*10 -03 | —7*10 -04 |
| DGCF | 0.1736 | 0.1477 | 0.1794 | 0.1521 | —5.8*10 -03 | —4.4*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.1826 | 0.1545 | 0.1830 | 0.1554 | —4*10 -04 | —9*10 -04 | |
| SGL* | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| UltraGCN | 0.1863 | 0.1580 | 0.1862 | 0.1580 | +1*10 -04 | 0 | |
| GPCF | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0.1849 | 0.1518 | 0 | 0 | |
| Yelp 2018 | NGCF | 0.0556 | 0.0452 | 0.0579 | 0.0477 | —2.3*10 -03 | —2.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0621 | 0.0505 | 0.0640 | 0.0 | —1.9*10 -03 | —1.7*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0629 | 0.0516 | 0.0649 | 0.0 | —2*10 -03 | —1.4*10 -03 | |
| SGL | 0.0669 | 0.0552 | 0.0 675 | 0.0555 | —6*10 -04 | —3*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0672 | 0.0553 | 0.0683 | 0.0561 | —1.1*10 -03 | —8*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0.0697 | 0.0571 | 0 | 0 | |
| Amazon Book | NGCF | 0.0319 | 0.0246 | 0.0337 | 0.0261 | —1.8*10 -03 | —1.5*10 -03 |
| DGCF | 0.0384 | 0.0295 | 0.0399 | 0.0308 | —1.5*10 -03 | —1.3*10 -03 | |
| LightGCN | 0.0419 | 0.0323 | 0.0411 | 0.0315 | +8*10 -04 | +8*10 -04 | |
| SGL | 0.0474 | 0.0372 | 0.0478 | 0.0379 | —4*10 -04 | —7*10 -04 | |
| UltraGCN | 0.0688 | 0.0561 | 0.0681 | 0.0556 | +7*10 -04 | +5*10 -04 | |
| GPCF | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0.0710 | 0.0584 | 0 | 0 | |
| *Results are not provided since SGI was not originally trained and tested on Gowalla. | |||||||
NGCF and DGCF ratele achieve 10e-4 because of the random initializations and stochastic learning processes involved
| Families | Baselines | Models | |||||
| NGCF [71] | DGCF [73] | LightGCN [28] | SGL [78] | UltraGCN [47] | GFCF [59] | ||
| Used as graph CF baseline in (2021 - present) | |||||||
| [10,13,32,62,77,84] | [19,39,46,74,75,92] | [40,54,78,82,88,89] | [22,46,77,82,85,93] | [17,24,42,48,95,96] | [,4,5,41,50,80,96] | ||
| MF-BPR [55] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| NeuMF [29] | ✓ | ||||||
| CMN [18] | ✓ | ||||||
| MacridVAE [38] | ✓ | ||||||
| Classic CF | Mult-VAE [38] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| DNN+SSL [86] | ✓ | ||||||
| ENMF [11] | ✓ | ||||||
| CML [30] | ✓ | ||||||
| DeepWalk [52] | ✓ | ||||||
| LINE [66] | ✓ | ||||||
| Node2Vec [25] | ✓ | ||||||
| NBPO [91] | ✓ | ||||||
Most if the approaches are compared against a small subset of classical CF solutions. However, the recent literature has raised conserns about usually - untested strong CF baselines!
Why comparing traditional recsys?
deck
By karpovilia
deck
- 165



