Concurrency Session - 1
Underlying Hardware
Compute ? Cores ? Threads ?
What's compute ?
- cpu - piece of hardware that executes instructions
Instructions

Quadcore processor
- core - physical processing unit
- one core - handles one thread of execution at a time
- a quadcore processor is physically capable of executing not more than 4 instructions at a time
Disclaimer: To simplify things, we are ignoring hyperthreading for now
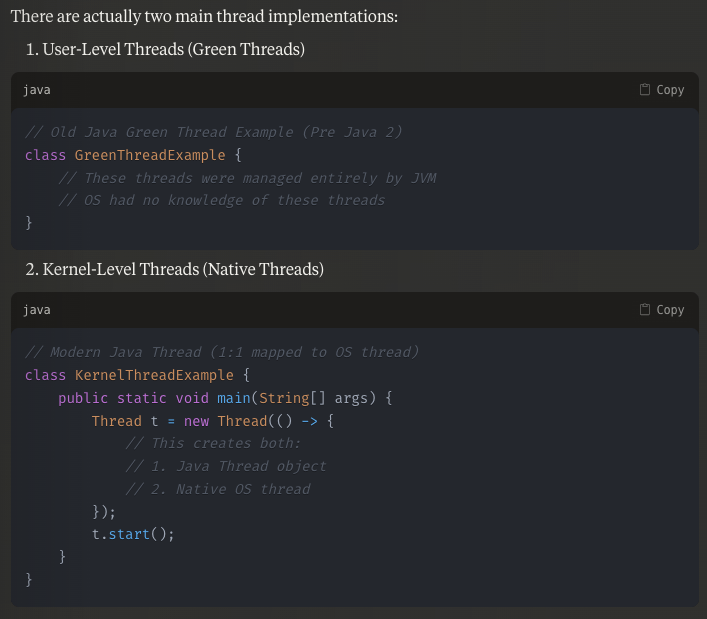
USER THREADS - NOT AN OPERATING SYSTEM LEVEL CONCEPT
BUT MOVING ON JAVA USES KERNEL THREADS 1:1 MAPPING TO OS LEVEL THREAD
https://claude.ai/chat/4683cb85-b412-4691-893a-1b7f9c2b05b7
Concurrency vs Parallelism

Bookish def
Concurrency: managing multiple instruction sequences at the same time
Parallellism: running multiple instruction sequences at the same time
Concurrent: Tasks are making progress during overlapping time periods, but they're taking turns using the CPU
Parallel: Tasks are literally running at the same exact moment on different CPU cores

More
- asyncio is a concurrent programming style and not parallel programming
- nodejs async await is complex, as it uses libuv internally, some parts of the offloaded tasks are run using parallel programming (multiple threads are used).
MULTITHREADING
MODEL

class Main {
public void spawnFourThreads() {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
// operation 1});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
// operation 2});
Thread t3 = new Thread(() -> {
// operation 3});
Thread t4 = new Thread(() -> {
// operation 4});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}CACHE COHERENCY
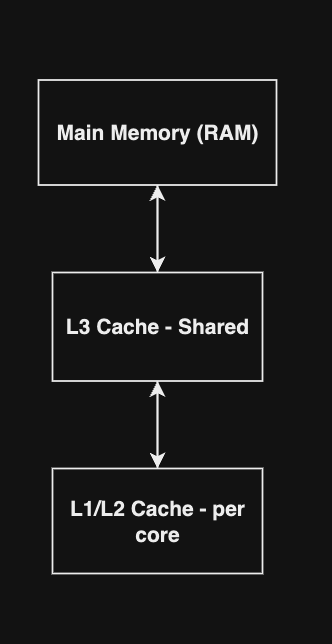
Assumption - 4 core machine, single process, spawns 4 threads
M - Modified
E - Exclusive
S - Shared
I - invalid
Cores maintain cache coherence
By following the MESI protocol
- if only one core reads the cache line - E
- if another core reads - both go to S
- if a core modifies - it goes to M and performs write to RAM and rest all go to I
- If a core has I - it has to read back from RAM
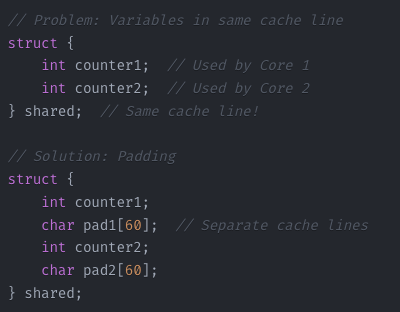
False Sharing
Concurrency Session - 1
By Kaushik Rishi
Concurrency Session - 1
- 58



