Render chain / render filters / aggregation and cache
This presentation is about Rendering in DX 7.2, explanations about the complete mechanism including the new Aggregation and cache implementation
By JAHANSHAHI Kevan
What is a Render Chain ?
An executions of filters that should generate the fragment html at the end
Render chain facts
- one by fragment
- can call a new sub render chain
- can be start manually from java code:
Resource resource = new Resource("/sites/ACMESPACE/home/list/news/news-1",
currentUserSession, "html", "default", "module");
String htmlContent = RenderService.getInstance().render(resource, renderContext);- The module tag from jsp is in charge of calling new render chains ( but is not the only one )
What is a Render Filter ?
Java class that implement RenderFilter interface, will hook on the rendering of fragments
Render filter facts
- can extends abstract class "AbstractFilter" instead of implementing base interface.
- 3 main methods: prepare, execute, finalize
- have conditions ( filter execution in some specific case )
- have priorities ( order of execution )
- can be provide by modules via Spring ( or OSGI service since 7.2 )
Executions of filters
- First filter
- Filter 2
...
- Filter 80
- Filter 81
- Out filter
- Filter 83
....
prepare()
execute()
finalize()
In real life
- Attribute filter (1)
- Cache filter (3)
- JSP filter (99)
When the fragment is not in cache:
- Attribute filter (1)
- Cache filter (3)
- JSP filter (99)
When the fragment is in cache:
The render chain stop at the first filter that return something on prepare() call.
JSP filter in first case, Cache filter in second case.
prepare()
execute()
finalize()
Summarize :
Prepare():
- called on each filters in ASC order based on priority
- used to store, resolve or calculate things before render execution
- return the original HTML for the fragment ( Prepare phase is finished, execute() will be call next, even if there is filters after the current one. )
Summarize :
Execute():
- called on each filters in DESC order based on priority, starting by the last filter that returned something in the prepare()
- used to modify the HTML directly of the fragment: (rewrite links, inject JS/CSS html tags, resolve macros, etc .)
- return the updated HTML
Finalize():
- called on each filters in ASC order based on priority, until the last filter that returned something in the prepare()
- used to cleanup generated data, variables, and request attributes set by the filter
Summarize :
- we have 35 render filters in core in DX 7.2
some important filters:
- baseAttributesFilter: (resolve and store data) (15)
- aggregateFilter: (???) (16)
- cacheFilter: (cache the HTML for the fragment) (16,5)
- nodeAttributesFilter: (resolve and store data) (16,8)
- templateScriptFilter: (execute the jsp) (99)
Complicate stuffs :
- Want happen when a fragment contains other fragment ?
- How we identify fragments to store/retreive them in cache ?
Aggregation and Cache
The aggregation is responsible of building the page HTML and identifying each fragment by a KEY
The cache is responsible of serving and populating the output cache.
This two operations are linked the cache need the aggregation ( for the keys ), but the aggregation can work alone.
Implems
In DX 7.2 we completly rework the aggregate and cache implementation, to introduce this new mechanism I have to talk about the previous one.
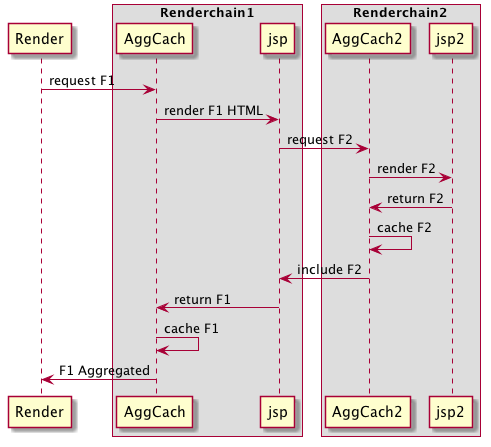
DX 7.1: only one render filter, AggregateCacheFilter
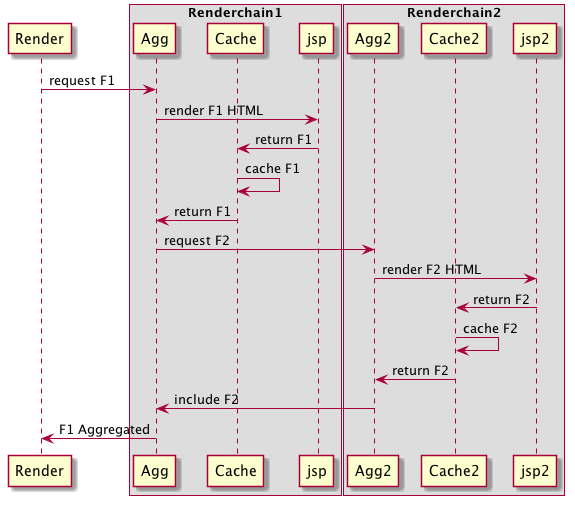
DX 7.2: two differents filters, AggregateFilter and CacheFilter
Fragments
F1
F2
F3
DX 7.1 flow
DX 7.2 flow
DX 7.2 implem
- We now cache the parent fragment before render and aggregate the child fragments. ( this was the topic of the DX 7.2 story )
- We now rely completely on render chain ( the aggregation start new render chain in all the case )
- we simplify the aggregation code.
- the Aggregate and cache is now separate in two filters
Not possible in 7.2
- Read the node before the cache filter !!!! ( be careful of filters conditions that could be apply on nodes )
- Storing data in request from a parent jsp, use this data in a child fragment and clean the request at the end of the parent jsp won't work anymore. the child fragment will not see the data because the parent jsp is fully executed before the rendering of child.
Detailed flow of Aggregation
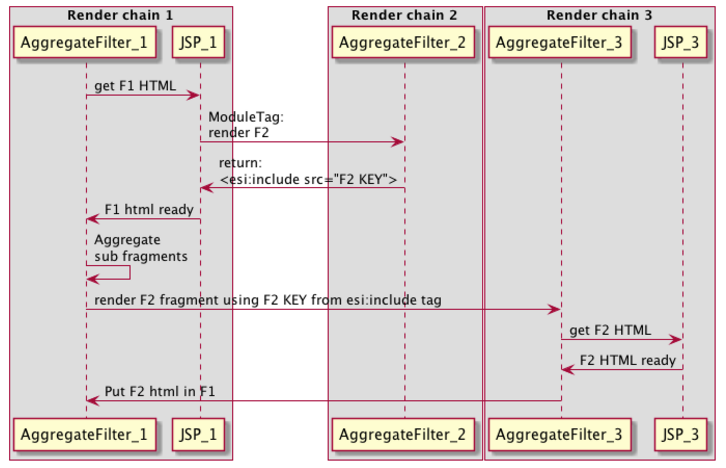
Esi_tags in 7.2
The sub fragments are replace by jahia_esi:include tags when the parent fragment jsp is rendered.
So, each manual call to a new render chain from the jsp or filters under the AggregateFilter will now return:
"<jahia_esi:include src=\"" + FRAGMENT KEY + "\"></jahia_esi:include>" This esi tags will be replace during aggregation phase only when the parent fragment html is fully rendered.
The ModuleTag.render() will now return this esi tags instead of sub fragment html.
Summarize:
The new implementation is different than the old one, and implementations of custom render filters from module since 7.2 should be controlled.
But not only...
- data stored in memory during rendering
- custom calls to new render chain
- filter priority compare to cache filter
Complicate stuffs
- how fragment key are generate ?
- how can we store/restore data from parent to childs fragments now ?
- how can we bypass the aggregation ?
Fragment key
Originally called cache keys, they are more fragment keys now.
Every body should already know the CacheKeyPartGenerator.
But do you know exactly the purpose of each methods available on this interface ?
getValue() ?
replacePlaceHolders() ?
Fragment keys
fragment key: This is the identity of the fragment without the context.
fragment final key: The complete identity of a fragment, the final key is the result of (fragment key + the current context of rendering). For exemple the same fragment key can result in multiple different final keys depending of the context of the render request. ( users logged or not, parameters, etc .)
Key Part Generator
This Classes are use to add new entries to fragment keys, and fragment final keys. For that you can implement
CacheKeyPartGenerator.
They can be provide by modules using spring beans.
They contains three methods:
getKey() : just the id for this generator
getValue(): ???
replacePlaceholders(): ???
Key Part Generator
getValue(): use to generate the key only when the fragment is not found in cache. Remember the esi tags ?
esi tags are holding the keys build by the getValue().
( F1 html contain the esi tag for F2, and this esi tag is the fragment key for F2. If F1 is in cache we have F2 fragment key )
Summarize:
- build the fragment key
- only when parent fragment is not in cache (because esi tags not available)
- support heavy operations like reading nodes from JCR
Key Part Generator
replacePlaceHolders(): use to build the final key. When the fragment key is retrieved from parent fragment esi tag or have been construct. This method is called just after to identify the fragment based on the current context of execution.
This method is used to replace the previous value in the key, by something that could potentially differentiate the fragment based on the context, even if the initial fragment key is the same.
Summarize:
- Build the fragment final key
- Always called in all the case
- Do not support heavy operations, avoid JCR read here.
Key Part Generator
public class ContextCacheKeyPartGenerator implements CacheKeyPartGenerator {
@Override
public String getKey() {
return "context";
}
@Override
public String getValue(Resource resource, RenderContext renderContext, Properties properties) {
// read the node to detect if the resource need to be contextual
// will be call only one time
if (resource.getNode().isNodeType("jnt:contextualizedNode")) {
return "contextual";
}
return "notContextual";
}
@Override
public String replacePlaceholders(RenderContext renderContext, String keyPart) {
// apply the contextual changes in the final key to differentiate the fragments
if("contextual".equals(keyPart)) {
return renderContext.isLoggedIn() ? "logged" : "notLogged";
}
return keyPart;
}
}Key Part Generator
In the previous exemple the node of type "jnt:contextualizedNode" will have 2 possible differents final key depending on the context (user logged or not)
This is the best usage of a CacheKeyPartGenrator.
- avoid JCR read in replacePlaceHolders (because call every time)
- use this two methods to decouple the logic of your cache key part generators ( what is contextual ? what is not contextual ? do you need to read nodes ? )
Key Part Generator
When do you need this part generator ?
- when you want to add custom logic on fragment identity in cache
- But not only !!!
RenderContextTuner
New interface available for DX 7.2, allow you to empower CacheKeyPartGenerator implementation.
But what is the purpose ?
It allow you to store data in the fragment key to be able to re-inject this data when a new render chain is started for this fragment.
By doing this you can pass data from parent to childs fragment even in all the case ( fragments in cache or not, one in cache and not the other, etc .)
RenderContextTuner
Two methods available:
Object prepareContextForContentGeneration(String value, Resource resource,
RenderContext renderContext);
void restoreContextAfterContentGeneration(String value, Resource resource,
RenderContext renderContext, Object original);prepareContextForContentGeneration(): this method is called just before the render chain start for the current fragment key, you can inject data in the request from there using key part value (value)
restoreContextAfterContentGeneration(): this method is called just after the render chain finished for the current fragment key, you can clean up the injected data for next fragment rendering.
RenderContextTuner
Why ?
Because this operations was already done before, but hardcoded in the AggregateCacheFilter, we just export this operations in the dedicated generators.
And make this kind of operations open to the integrators if it's needed.
Most of the time this operations are not needed, but sometime it can save you when you want to make object transit between render chains.
public class InAreaCacheKeyPartGenerator implements CacheKeyPartGenerator, RenderContextTuner {
@Override
public String getKey() { return "inArea"; }
@Override
public String getValue(Resource resource, RenderContext renderContext, Properties properties) {
HttpServletRequest request = renderContext.getRequest();
Object inArea = request.getAttribute("inArea");
return inArea != null ? inArea.toString() : "";
}
@Override
public String replacePlaceholders(RenderContext renderContext, String keyPart) {}
@Override
public Object prepareContextForContentGeneration(String value, Resource resource, RenderContext renderContext) {
Object original = renderContext.getRequest().getAttribute("inArea");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
renderContext.getRequest().removeAttribute("inArea");
} else {
renderContext.getRequest().setAttribute("inArea", Boolean.valueOf(value));
}
return original;
}
@Override
public void restoreContextAfterContentGeneration(String value, Resource resource, RenderContext renderContext, Object original) {
if (original != null) {
renderContext.getRequest().setAttribute("inArea", original);
} else {
renderContext.getRequest().removeAttribute("inArea");
}
}
}If you don't like ?
Because we know that sometime people don't like the changes.
We introduce a way to skip the aggregation on a dedicated fragment:
- set the request attribute: aggregateFilter.skip (don't forget the remove the attribute after your fragment is rendered)
- use the new skipAggregation module tag jsp attribute
- use the new skip.aggregation view property
If you don't like ?
What happen to fragment rendered without aggregation ?
They will be only one entry in cache for this fragment, and this fragment HTML will directly contain his sub fragments.
If you skip the aggregation for a list, this list will contains all his elements in cache directly.
If you don't like ?
Why ?
For the reason said before:
- Store data in request from parent fragment, use this data in childs fragments, remove this data at the end of parent fragment. Will not work anymore, because of the order of JSPs execution
This can be solve by RenderContextTuner new interface or by skipping the aggregation at parent fragment level.
Questions ?

Render chain / render filters / aggregation and cache
By Kevan Jahanshahi
Render chain / render filters / aggregation and cache
This deck is about Rendering in DX 7.2, explanations about the complete mechanism including the the new Aggregation and cache implementation
- 1,047
