
What is Git?
- Free open source distributed version control system
- Nearly all operations are performed locally
- Every Git working directory is a full-fledged repository with complete history and full version-tracking capabilities
What is version control?
- It's a repository of files, often the files for the source code of computer programs, with monitored access
- Each revision is associated with a timestamp and the person making the change
- Revisions can be compared, restored, and with some types of files, merged
Why use Git?
- Easy to learn
- It's fast which saves time
- You can work offline
- Easy to undo mistakes
- You can group commits
- Losing data is really hard to do
- Generally only adds data
- Has a large community
Git intro
What is a repository
- The root directory of the project
- It contains:
- a set of commit objects
- a set of references to commit objects
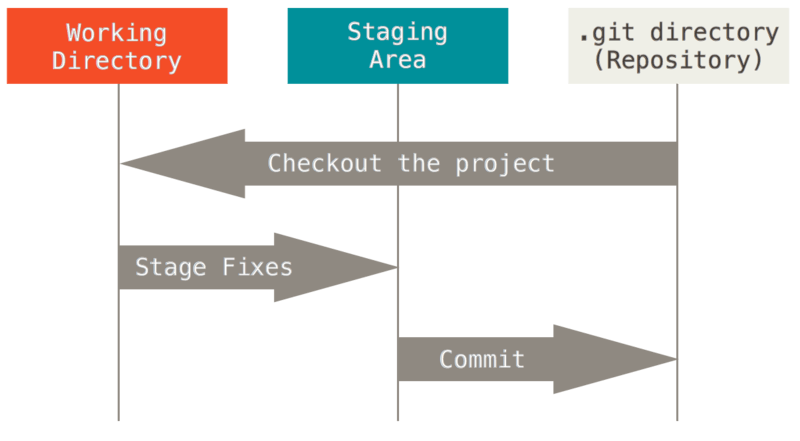
The 3 states
- Repository (remote)
- Staging area
- Working directory (local)
What is a branch?
- Branches are used to develop features isolated from each other
- The master branch is the "default" branch when you create a repository
- Use other branches for development and merge them back upon completion
What is a commit?
- Records a snapshot of the staging area
- Allows you to add messages to your snapshot
What does merging mean?
- Combine another branch context into your current branch
- It automatically figures out how to best combine the different snapshots into a new snapshot with the unique work of both
What is a conflict?
- Where the same block of code is edited in different branches and there is no way for a computer to figure it out how to merge
- Uses conflict markers to point out the conflict
<<<<<<< HEAD
Many Hello World Examples
=======
Hello World Lang Examples
>>>>>>> commit_messageGetting projects
Git clone
- Copy a git repository locally so you can modify it
git clone git://github.com/username/example.gitBasic snapshotting
Git add
- Used when you want to include whatever changes you've made to it in your next commit snapshot
- Anything you've changed that is not added will not be included
// Add a single file
git add filename.html
// Recursively adds all files
git add .
// Recursively adds all files (recurse into subdirectories)
git add *Git status
- See if anything has been modified and/or staged since your last commit so you can decide if you want to commit a new snapshot and what will be recorded in it
// Gives you context and hints about the status
git status
// Gives you a short context of the status
git status -sGit commit
- Records the snapshot of your staged content
- It can then be compared, shared and reverted if needed
// Add a descriptive message to your commit
git commit -m "Place commit message here"
Git rm
- Removes files from the staging area
- It will also remove them from your working directory
// Removes file from staging area and working directory
git rm filename.htmlBranching and merging
Git branch
- Listing branches, creating branches and deleting branches
// Lists all local branches
git branch
// Lists all remote branches
git branch -r
// Creates a new branch called "example" but will not check out the branch immediately
git branch example
// See the last commit on each branch
git branch -v
// Deletes branch called "example" locally
git branch -d example
// Deletes branch called "example" from remote
git push origin :exampleGit checkout
- Switch between branches
// Check out the branch called "example"
git checkout example
// Creates and immediately switches to the branch called "example"
git checkout -b example
Git merge
- Merge a branch into your current one
git merge
// Git merge the branch example in current branch
git merge exampleGit log
- Shows the commit history or list of changes people have made that have lead to the snapshot at the tip of the branch
git logSharing and updating
Git fetch
- Synchronise your repository with a remote repository, fetching all the data it has
git fetch originGit pull
- To update your current branch with the latest changes from the remote server
- Downloads new data and it also directly integrates it into your current working copy files
// Pulls latest version of the branch "example"
git pull origin exampleGit push
- Push your new branches and data to a remote repository to update it with the changes you've made locally
// Pushes your changes to the branch "example"
git push origin exampleGit
By Kim Massaro
Git
The basics of Git version control
- 1,108



