"Paleo ice shelf-ocean interaction:
How we want to derive basal melt estimates
driven by ocean tides"
PhD Candidate: Ole Richter
Supervisory Team: Matt King, Ben Galton-Fenzi, David Gwyther
PhD confirmation presentation
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
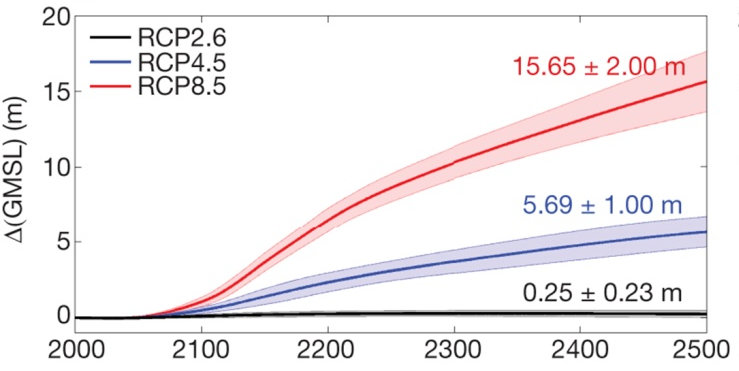
The Antarctic ice sheet is the largest potential source for future sea level rise
Future Antarctic contributions to GMSL
Deconto, R. M., & Pollard, D. (2016). Contribution of Antarctica to past and future sea-level rise. Nature, 531
Changes in glacial melt water flux impact Antarctic Bottom Water formation
Antarctic Bottom Water changes
Purkey, S. G., & Johnson, G. C. (2013). Antarctic bottom water warming and freshening: Contributions to sea level rise, ocean freshwater budgets, and global heat gain. Journal of Climate, 26
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
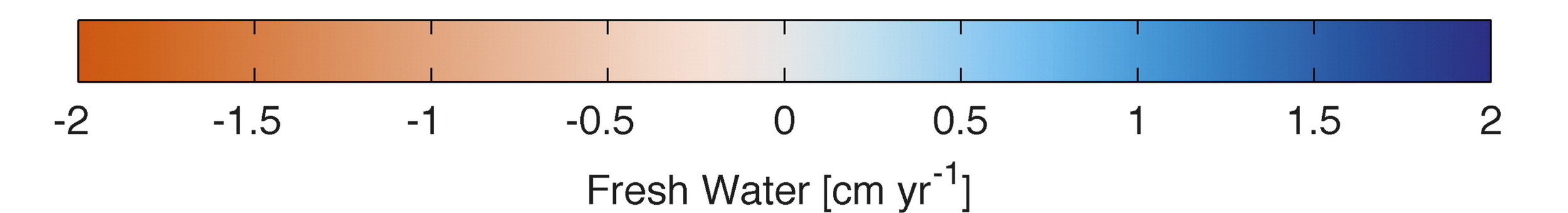
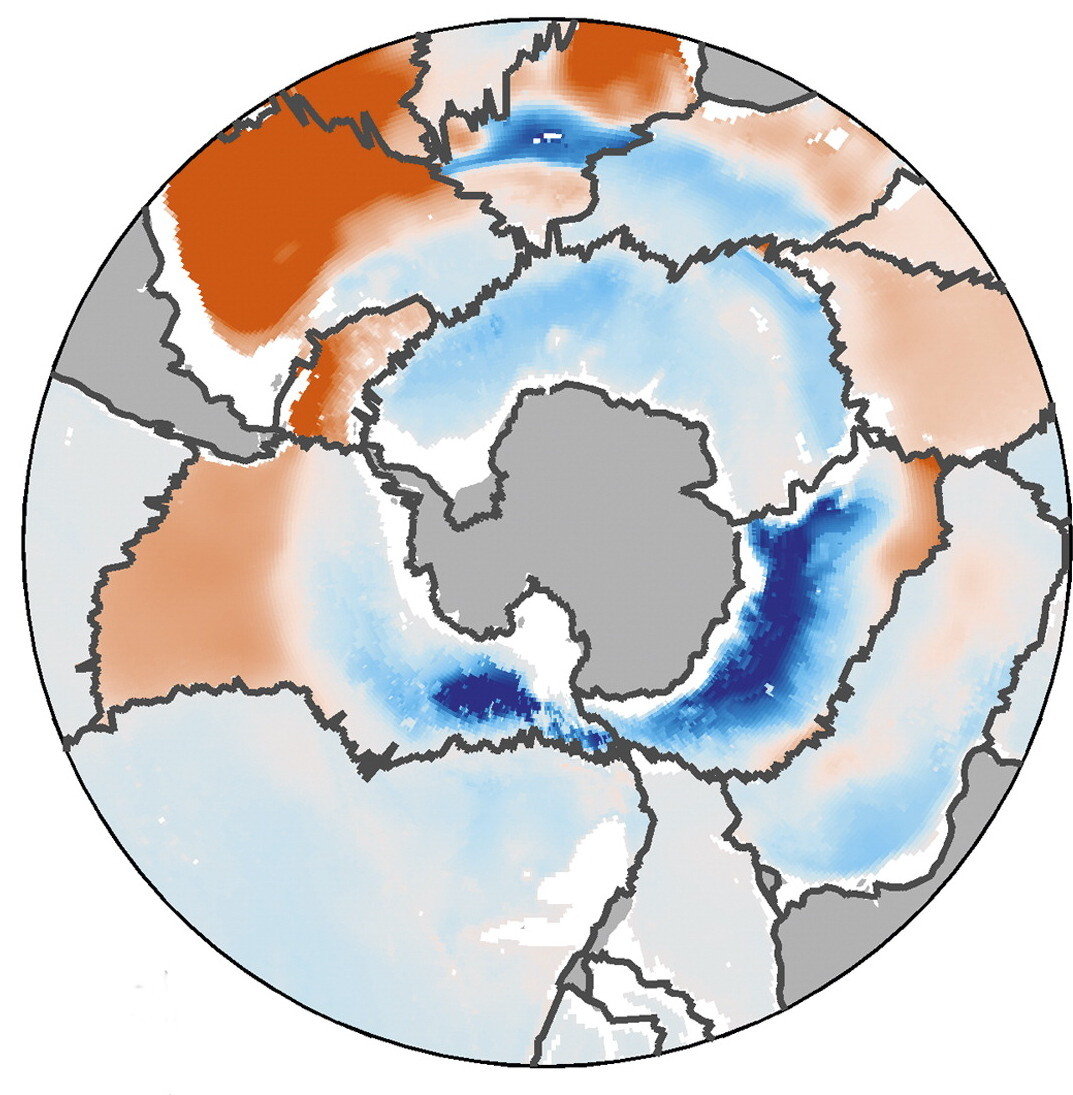
Vertical column freshwater fluxes below 2000 m
Tide-switch "on" at major Antarctic ice shelves:
-
increases net basal melt by 25% - 100%
-
heavily changes basal melt magnitude and distribution
Makinson, K., Holland, P. R., Jenkins, A., Nicholls, K. W., & Holland, D. M. (2011). Influence of tides on melting and freezing beneath Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Geophysical Research Letters, 38
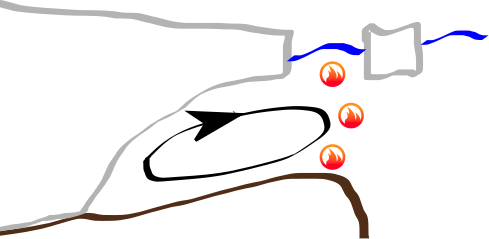
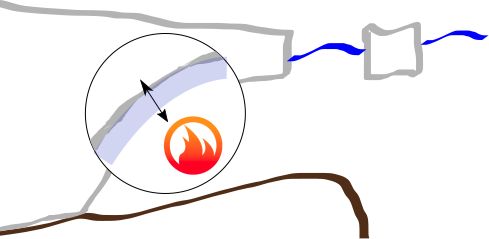
Tidal currents increase ice shelf basal melting
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary



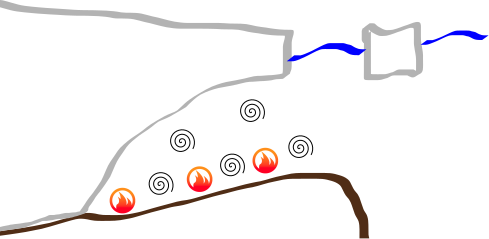
Tidal melting mechanisms
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Tides contribute to:
- mean circulation
- ocean mixing
- turbulent boundary layer transport
Mueller, R. D., Padman, L., Dinniman, M. S., Erofeeva, S. Y., Fricker, H. A., & King, M. A. (2012). Impact of tide-topography interactions on basal melting of Larsen C Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117
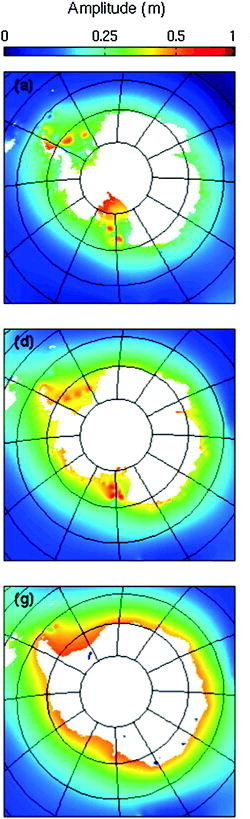
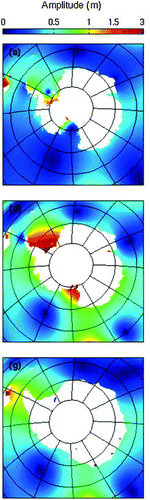
Griffiths, S. D., & Peltier, W. R. (2009). Modeling of polar ocean tides at the Last Glacial Maximum: Amplification sensitivity, and climatological implications. Journal of Climate, 22
M2
K1
PD
LGM
LGM GL+
Antartic paleo tides:
-
have been amplified at LGM (K1 up to 70%; M2 up to 200%)
-
inconsistently changed during the last deglaciation
-
are sensitive to grounding line position
Antarctic MEGA tides at LGM
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
M2
M2
PD
LGM
LGM GL+
K1
K1
Background summary:
-
Antarctic ice shelf basal melting is strongly dependent on tides
-
Antarctic tides changed from MEGA at LGM to moderate at PD
Research scope:
-
Quantification of changes in tidal melting between LGM and PD
-
Identification of governing mechanisms that drive these changes
-
Quantification of changes in dense shelf water export at Pliocene, the Last Interglacial and future scenarios
The missions
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS):
-
3D
-
free surface
-
terrain following
-
ice shelf hydrostatic pressure
-
ice-ocean thermodynamics (TEOS-10)
-
Frazil formation (Ben)
-
varying drag coefficient (Dave)
Fancy ROMS
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Domain
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Idea behind:
- captures important ocean currents
- resourceful
- FAST !
Resolution
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary

St-Laurent, P., J. M. Klinck, and M. S. Dinniman (2015), Impact of local winter cooling on the melt of Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica, J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 120
Velocity at 350 m
- 1 km resolution needed to resolve critical small eddies on continental shelf
- 10 km development -> 4 km, 1 year initial conditions -> 1 km, 1 month production runs
Sub ice shelf cavity
Southern ocean
Peltier (2014) global earth system model ICE-6G_C (VM5a)
Pollard (2016) dynamic ice sheet-shelf model
Small scale features
Schaffer (2016) Global high resolution present day topography map R-Topo
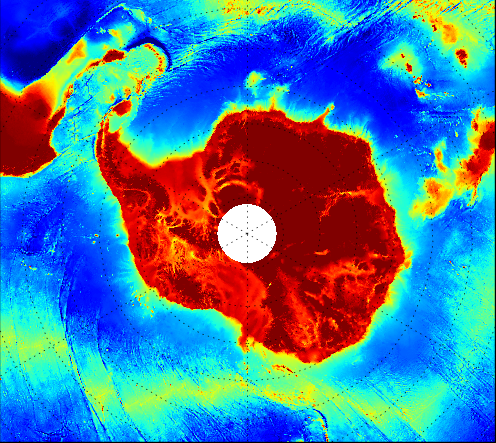
Paleo Topography
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Local tidal potential
Global ocean tides
Wilmes (2014) global paleo tide model
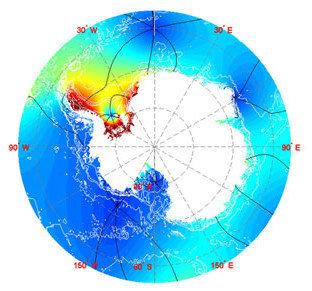
Paleo Tides
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Kate Hedstrom POT_Tides algorithm
Experiments |
|---|
PD realistic |
PD consistent |
LGM |
LGM to PD |
| Pliocene, LIG, Future |
Outputs/Outcomes |
|---|
3D Antarctic tidal dynamics |
Changes in basal melting |
Changes in dense shelf water export |
Paper |
|---|
"High Resolution Antarctic Tidal Dynamics today and at LGM" |
"Tidal melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves since LGM" |
"Potential future shut down of AABW formation" |
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Current status
The strategy

paleo Antarctic tide-topo
ocean-ice shelf model ROMS
fate of AABW formation
ice sheet models
reduce uncertainties in
sea level rise projections
basal melt rates (LGM to PD)
dense shelf water export (PD, Pliocene, LIG, Future)
ice-ocean interaction
Knowledge
CPU POWER
PhD time


?
1. Background 2. Research scope 3.Methodology 4. Experiments, Outcomes 5. Summary
Summary
Thank you!
PhD Confirmation
By konsole
PhD Confirmation
- 149



