IP SPOOFING
CYBER SECURITY
Presented by - Krsna Chandarana
Index



SPOOFING
means an attempt or attack in your network security without your knowledge pretending to be someone else.
When a scammer disguises themselves as a trusted source to trick users into sharing private data, it’s known as spoofing. This type of scam happens through websites, emails, phone calls, texts, IP addresses and servers.
Generally, scammers make a slight change to a trusted URL or email address to fool users with a simple glance.
SPOOFING

1
ARP Spoofing
happens when the attacker connects his MAC address to the targeted IP address.
2
Email Spoofing
act of sending emails with false sender addresses, designed to steal your information.
3
DNS Spoofing
also known as, DNS cache poisoning, is when false information is entered into a DNS cache. The intent is for DNS queries to return a false response so that users are directed to wrong websites.
5
Website Spoofing
copy the layout, branding of original web pages.
4
Extension Spoofing
used to trick end users into installing executable malware files by disguising the true file type.
6
Caller ID Spoofing display a phone number different than the actual number from which the call was placed.

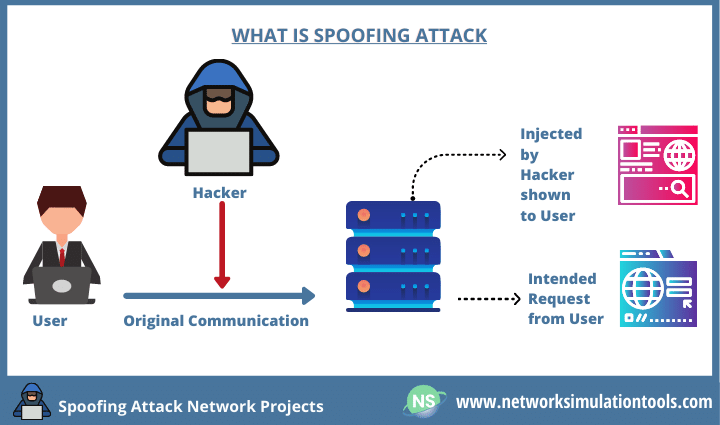
IP Spoofing
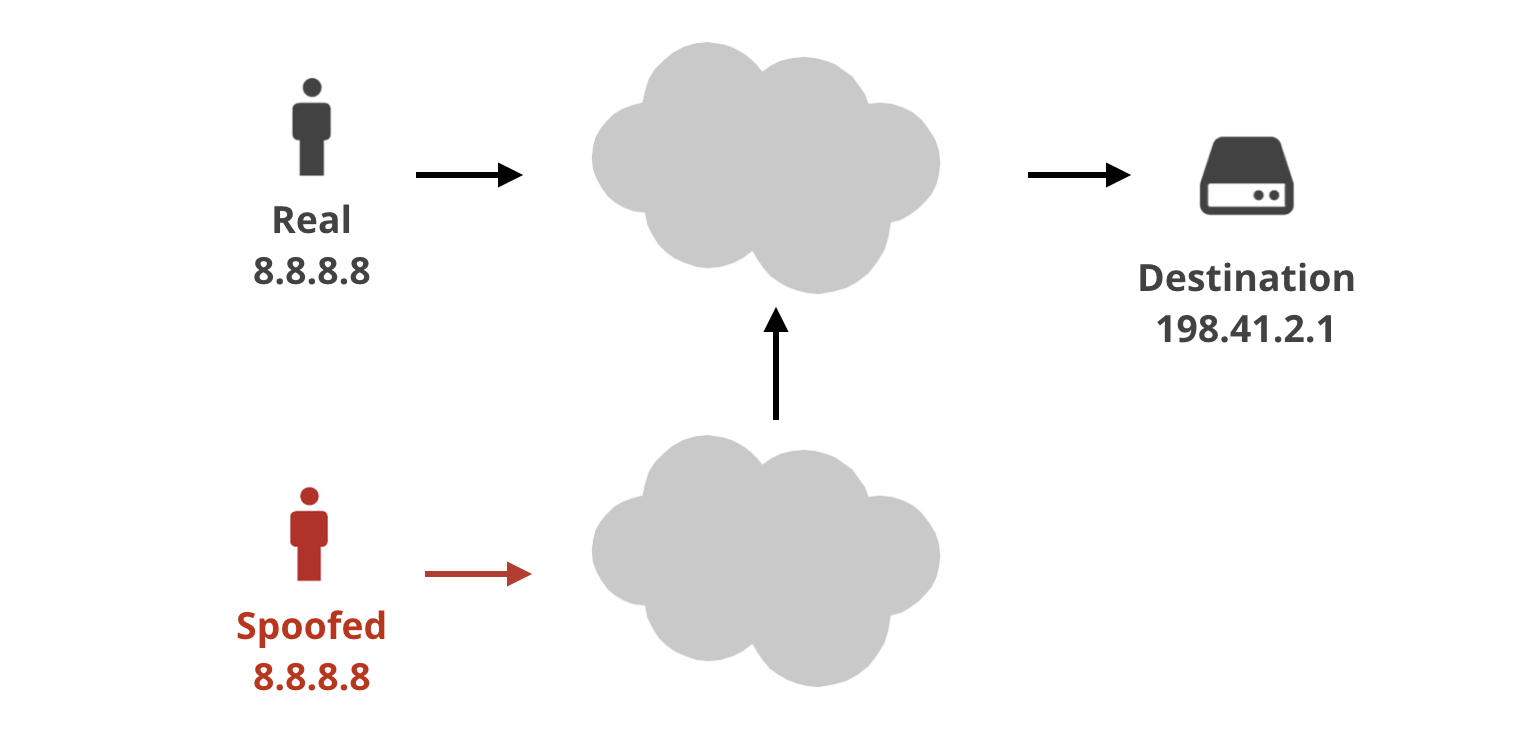
IP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to falsify the source IP address in a packet header to conceal their identity or impersonate another computer system.
It is the creation of Internet Protocol (IP) packets which have a modified source address in order to either hide the identity of the sender, to impersonate another computer system, or both.
Sending and receiving IP packets is a primary way in which networked computers and other devices communicate. All IP packets contain a header which precedes the body of the packet and contains important routing information, including the source address. In a normal packet, the source IP address is the address of the sender of the packet. If the packet has been spoofed, the source address will be forged (fake).
IP SPOOFING
PROCESS
With IP spoofing, intruder sends message to a computer system with an IP address indicating message is coming from a different IP address than its actually coming from. If intent is to gain unauthorized access, then Spoof IP address will be that of a system the target considers a trusted host. To Successfully perpetrate an IP Spoofing attack, hacker must find IP address of a machine that the target System Considers a trusted source. Hackers might employ a variety of techniques to find an IP address of a trusted host. After they have obtained trusted IP address they can then modify packet headers of their transmission so its appears that the packet coming from the host.
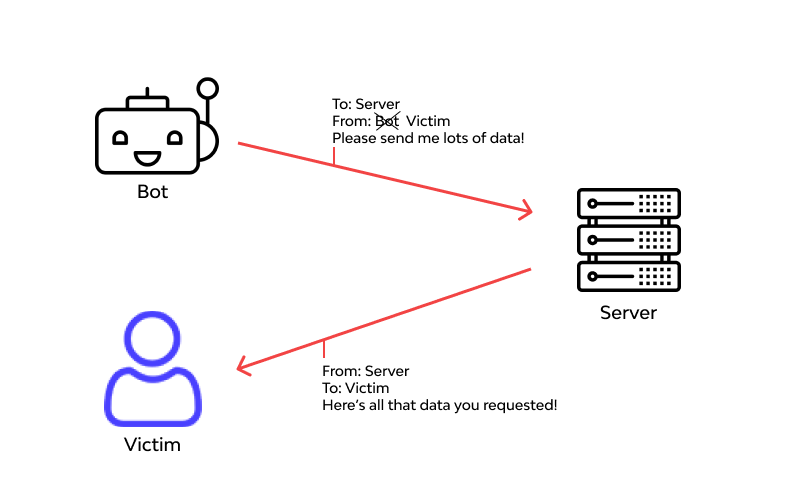
Working
IP Spoofing happens when the attacker sends IP packets with a fake source IP address. It's like forging a return address on a letter and pretending to be someone else.
Spoofing source IP addresses is not technically challenging. Every machine connected to the internet can transmit any bytes of their choosing - including setting arbitrary values in the source IP address field. It's just that such packets can do a great deal of damage when they are permitted onto the wide internet.
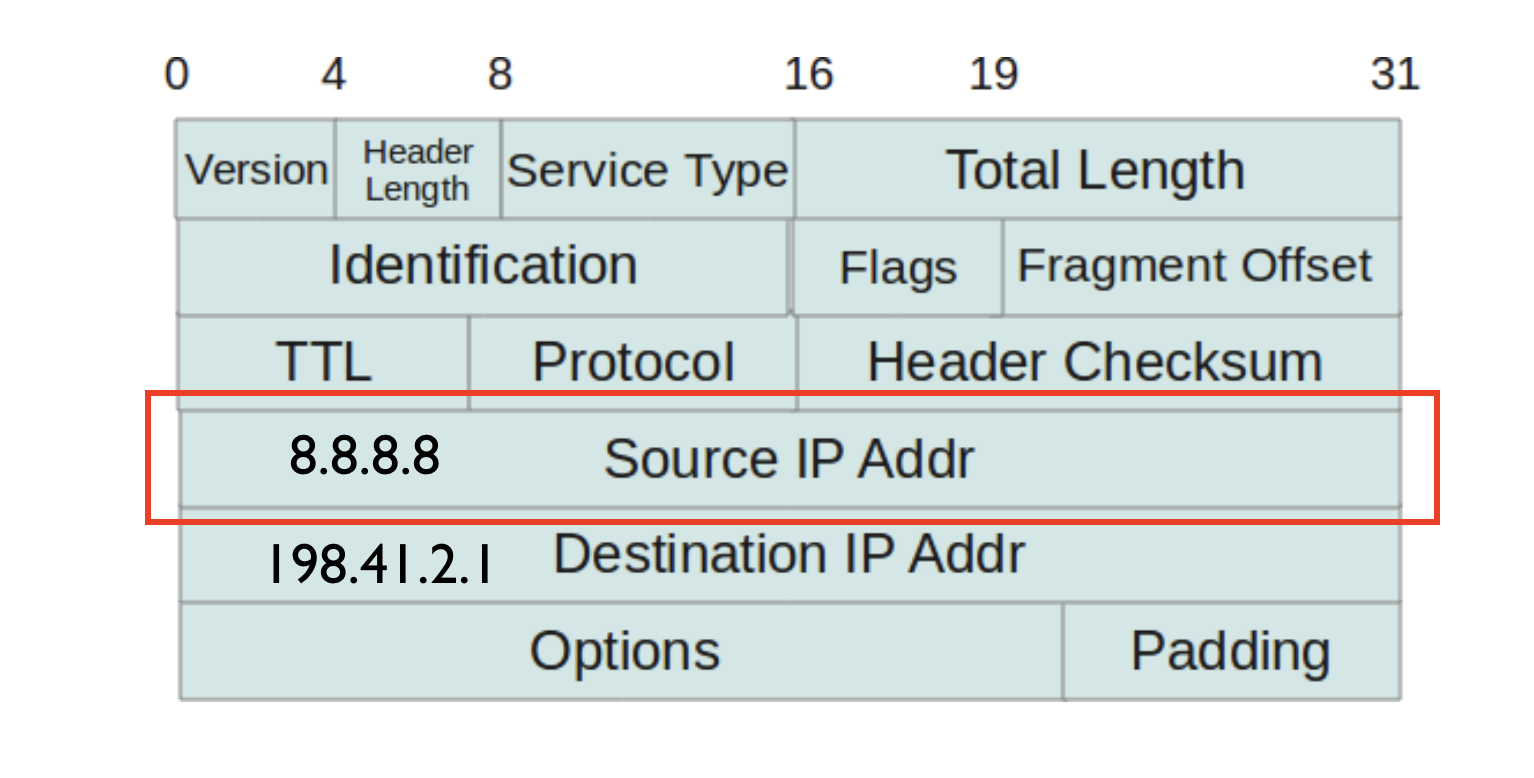
It is done without attracting observation. As it exists in the network layer, rookie users won’t be able to infiltrate so deeply. However, it doesn’t mean that IP spoofing detection is impossible.
For instance, there will be inconsistency in the IP addresses of the target.
Packet filtering is the most preferred IP spoofing detection technique that concerned organizations or individuals can adopt. We have automated and integrated packet-filtering systems that analyze endpoint traffic and figure out any inconsistencies in the IP addresses.
how to DETEct ip spoofing
two types of packet filtering
The first kind is ingress filtering which examines the received packets and tries to find out whether the IP header of the request source is legitimate. It takes the help of access control lists to find out this. If the source IP header doesn’t match the list, it will be discarded immediately.
Egress filtering is the second type and helps in IP spoofing by making sure whether or not the source IP addresses of the outgoing packets match with the aimed organization’s network system. This way, it stops insiders from carrying out the attack.
The main measures that minimize the possibility of such attacks include:
- Router filtering
- Encryption and authentication(will reduce the likelihood of spoofing.)
- Robust verification methods
- Network monitoring
- Firewall (protects your network, filters traffic with fake IP addresses, blocks access of unauthorized strangers)
how to Protect against ip spoofing
- Turn on spam filter.
- Confirm information with the source.
- Set up two-factor authentication.
- Download cybersecurity software.
DO's
- Click on unfamiliar downloads.
- Answer calls or emails from unrecognized senders.
- Give out your personal information to unfamiliar sources.
- Use the same password across multiple logins.
DONT's
-
Denial of Service (DOS) Attack
-
Man in the Middle Attack
-
Blind Spoofing Attack
-
Non-Blind Spoofing Attack
TYPES OF IP SPOOFING

〞
IP spoofs are dangerous for networks, databases, computers and users. It is a must that any one – in one way or the other – is informed about it. It is also important that each person takes responsibility and protects themselves from these sorts of attacks; our data is the future, let’s keep it safe.
THANK YOU !
IP SPOOFING
By Krsna C
IP SPOOFING
- 31



