Synthetic polarization maps around embedded protostars &
ionization as a regulator of disk size
Michael Küffmeier




S. Reißl, S. Wolf, I. Stephens, H. Calcutt, B. Zhao, P. Caselli

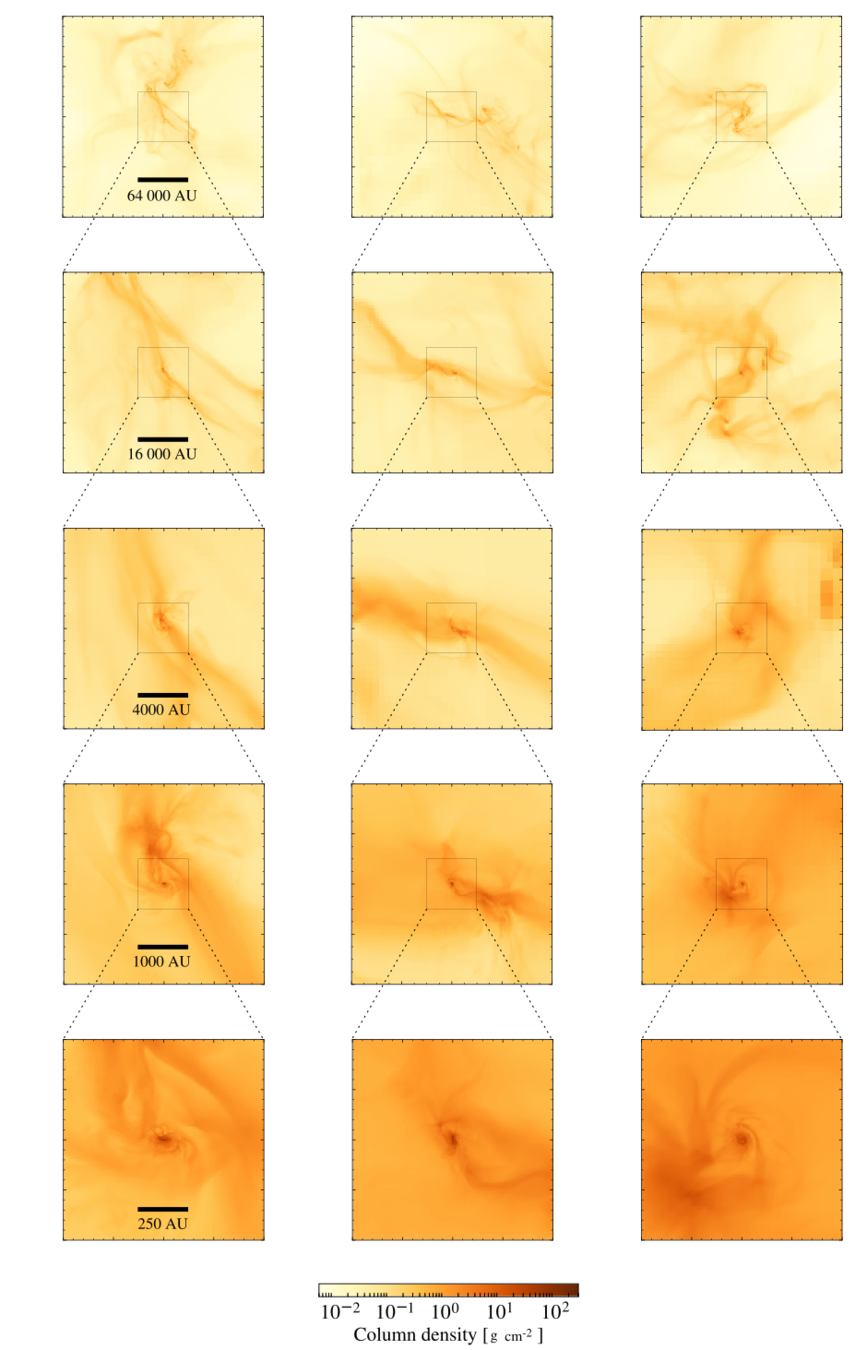
Zoom-in on embedded protostellar multiple
Küffmeier et al.
2019

Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
~1500 AU
bridge structure similar to IRAS 16293--2422 (e.g. Sadavoy+ 2018, van der Wiel+ 2019, Maureira+ 2020)
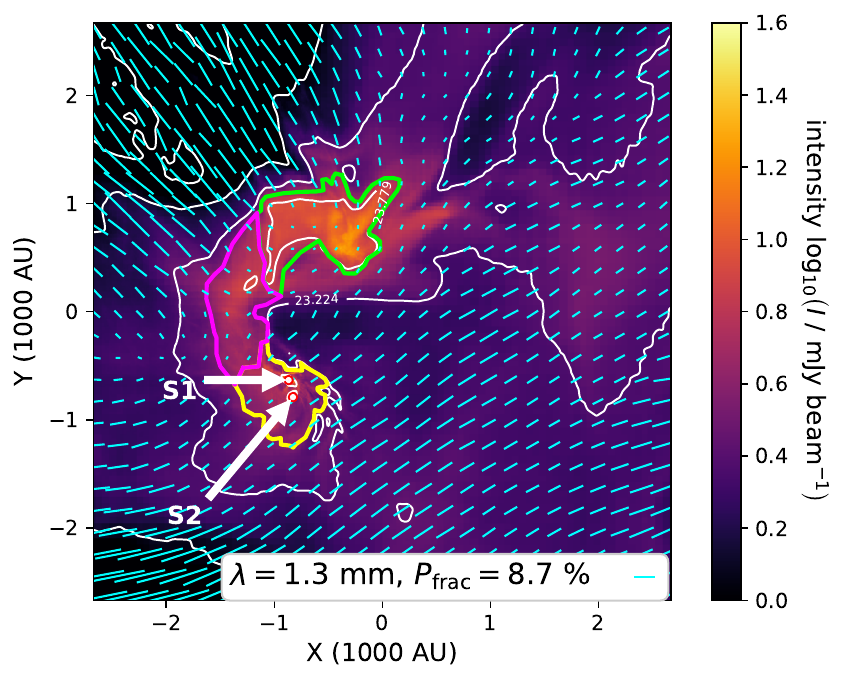
Wavelength dependence: 1.3 mm vs 53 micron

Emitted radiation
1.3 mm: good tracer of magnetic field
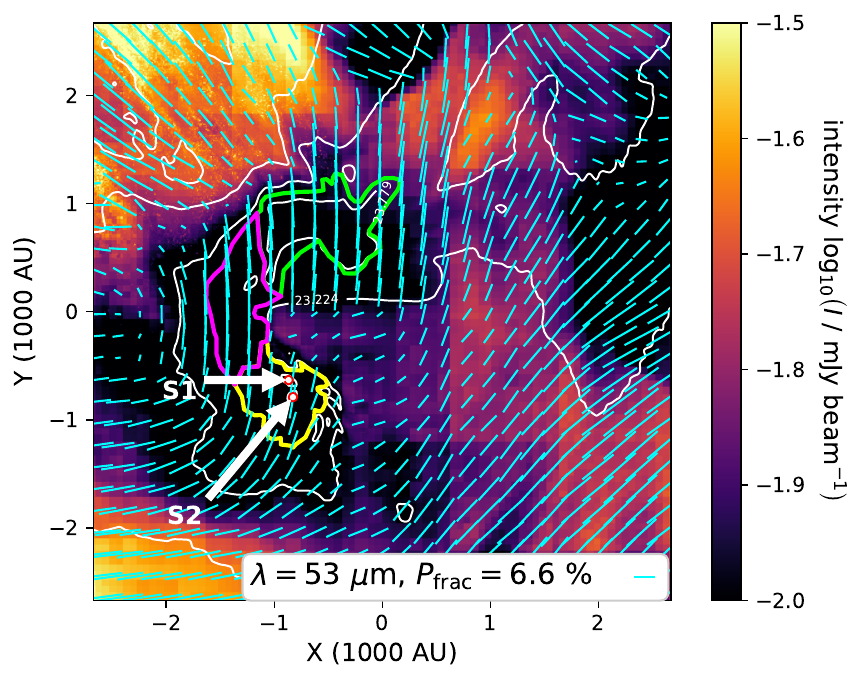
53 micron: poor tracer of magnetic field
Küffmeier, Reißl et al. 2020
RAT models predict less alignment than observations (see V. Le Gouellec's talk)
Resistivity depends on ionization rate
Küffmeier, Zhao & Caselli 2020
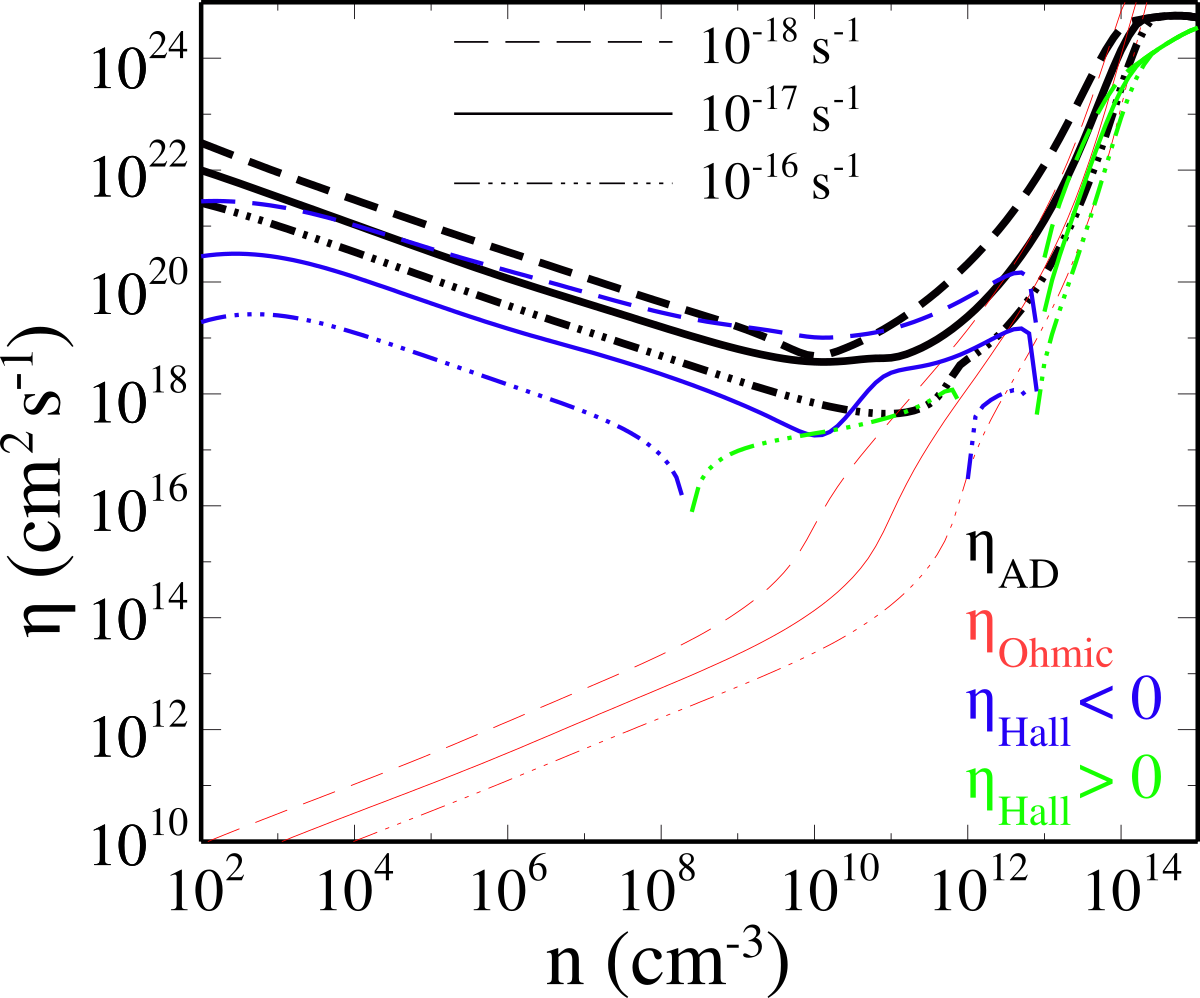
Question: What is the effect on disk formation when differing the ionization rate?
Disk size distribution
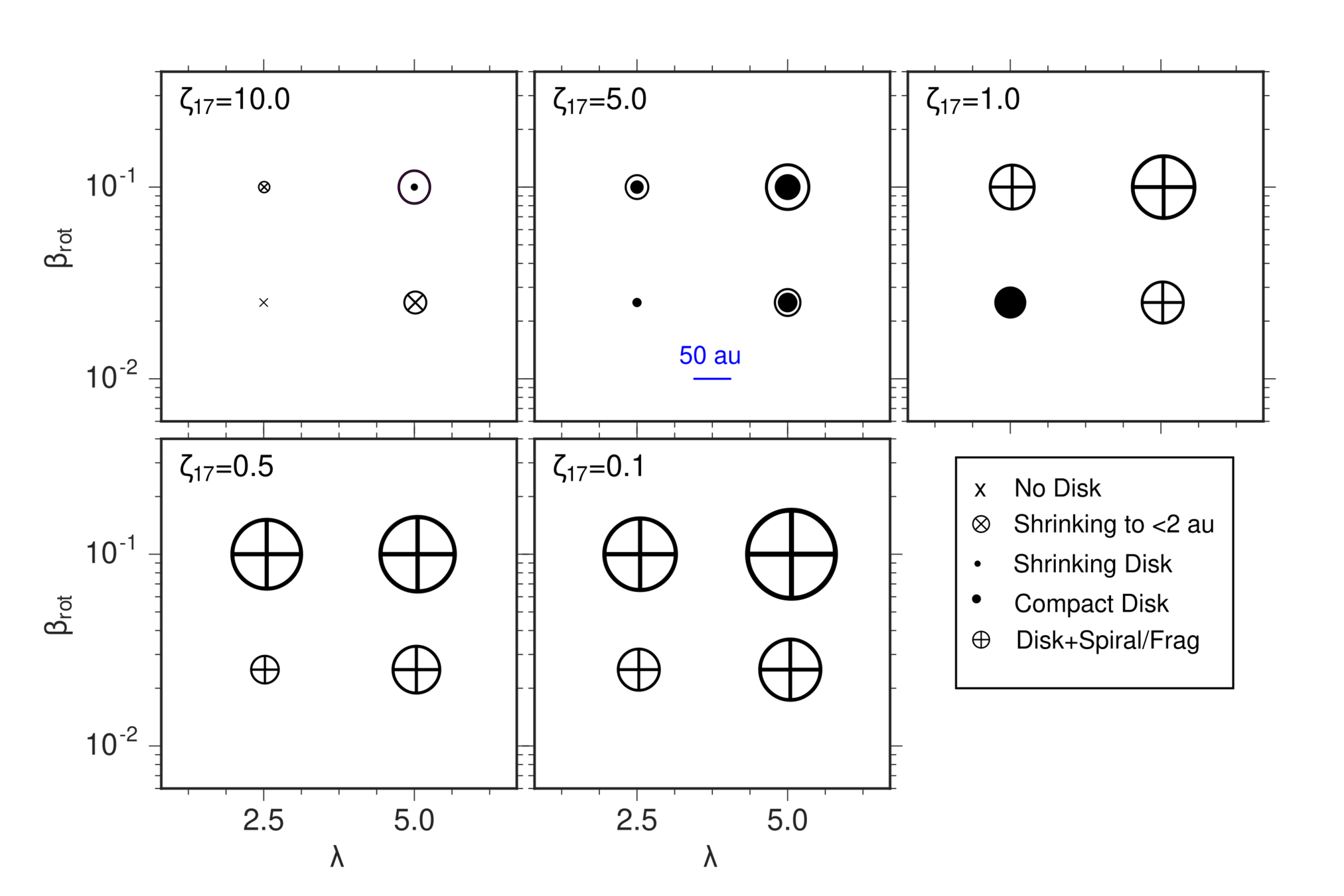
Küffmeier, Zhao & Caselli 2020
Disk size distribution
Alternative/additional effect to external photoevaporation:
Disks are born small in regions with high ionization/magnetic field
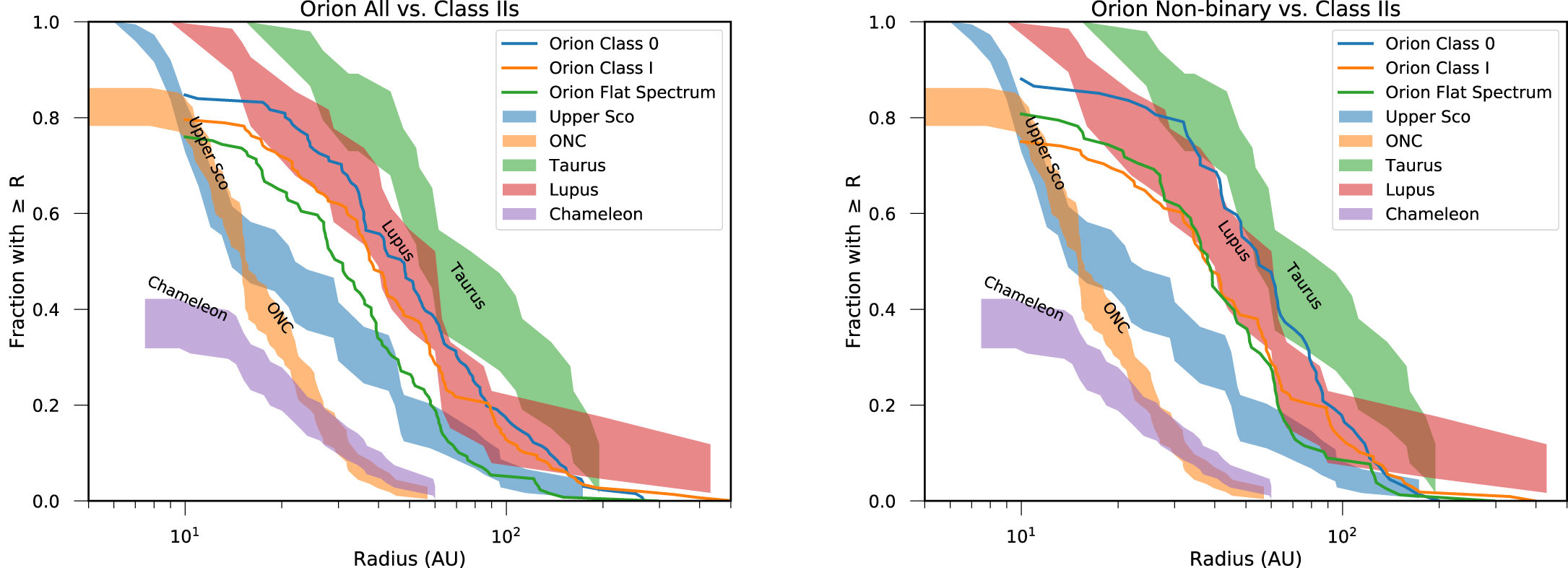
Tobin+ 2020
Take-away points
Linear polarization of dust reemission at wavelength >200 micron is good tracer of magnetic field structure on scales >100 au


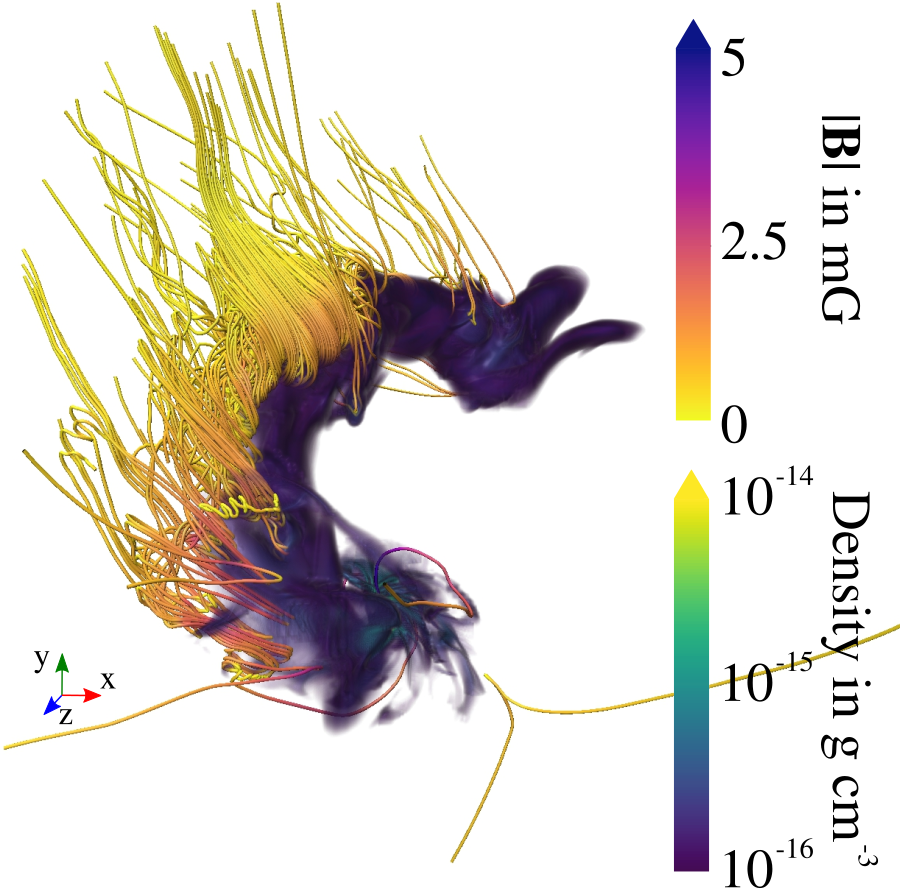
Bridge structures form as a result of converging flows and their magnetic field strength is ~1 to ~10 mG (consistent with estimates for IRAS 16293--2422)

(Cosmic-ray) ionization might be the actual explanation for the difference in mean disk size between star-forming regions of similar age
5 min magnetic fields
By kuffmeier
5 min magnetic fields
- 209



