Single Page Application Authentication
Advanced

Ado Kukic
Evangelism Lead

Auth0
@kukicado



http://bit.ly/spa-security
Traditional Auth



{ username / password }
{ sid 123 }


http://bit.ly/spa-security
Traditional Auth




{ sid 123 }
{ html }

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Traditional Auth
Single Page App
Authentication


http://bit.ly/spa-security


Scenario 1
{ json }


http://bit.ly/spa-security
https://myapp.com/api/
https://myapp.com/
Same Domain


Scenario 2
{ json }


http://bit.ly/spa-security
https://api.myapp.com/
https://app.myapp.com/
Sub-Domain


Scenario 3
{ json }


http://bit.ly/spa-security
https://api.epicapp.com/
https://myapp.com/
Different Domain
OAuth 2.0
An open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for Internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords.
An open standard for access delegation.

http://bit.ly/spa-security
OpenID Connect
An authentication layer built on top of OAuth 2.0, allowing clients to verify the identity of an end-user based on the authentication performed by an authorization server.

An authentication layer built on top of OAuth 2.0
http://bit.ly/spa-security
OAuth 2.0 Roles

Resource Owner
The entity that can grant access to a protected resource. Typically this is the end-user.

Resource Server
The server hosting the protected resources. This is the API you want to access.

Client
The app requesting access to a protected resource on behalf of the Resource Owner.

Authorization Server
The server that authenticates the Resource Owner, and issues tokens.
Codes and Tokens
Authorization Code
An opaque string, meant to be exchanged with an Access Token at the token endpoint.
Access Token
An opaque string or JWT that denotes who has authorized which permissions (scopes) to which application.
Refresh Token
A special kind of token containing the information required to obtain a new Access Token or ID Token.
Id Token
A JWT that contains user profile information (name, email, etc.), represented in the form of claims.

http://bit.ly/spa-security
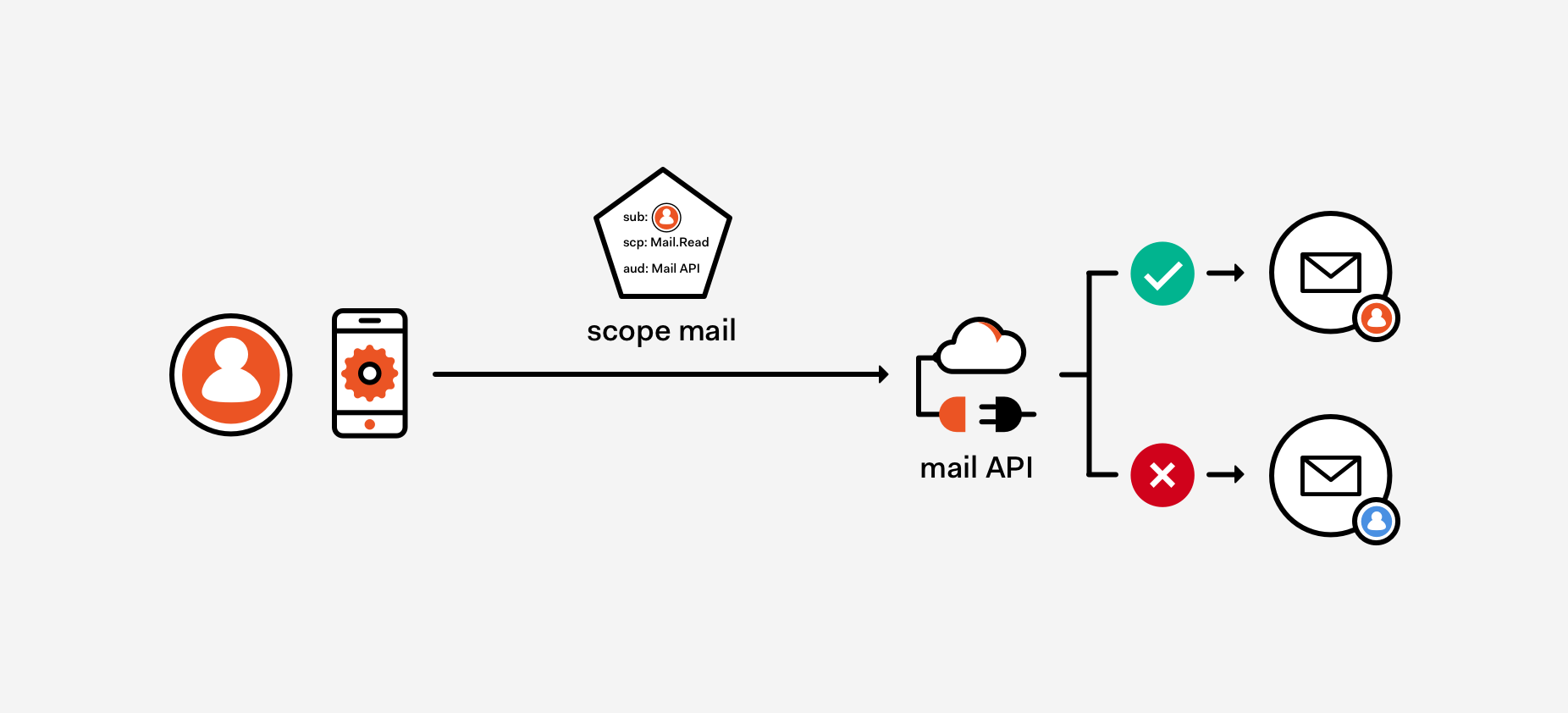
OAuth 2.0 Scopes

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Scopes only come into play in delegation scenarios, and limit what an app can do on behalf of a user.
OAuth 2.0 Flows
Authorization Code
Authorization Code with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)
Implicit
Client Credentials

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Single Page Application
Implicit Grant Flow


http://bit.ly/spa-security


Baseline
{ json }


http://bit.ly/spa-security



Authentication





http://bit.ly/spa-security


Authenticated





{ json }
{ json }

http://bit.ly/spa-security


Silent Authentication





{ json }
{ json }





http://bit.ly/spa-security


Silent Authentication





{ json }
{ json }




iframe

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Single Page Application
Authorization Code with PKCE Grant Flow


http://bit.ly/spa-security


Baseline
{ json }


http://bit.ly/spa-security



Authentication


{ code_challenge }
code={123}

http://bit.ly/spa-security



Authentication


{ code={123} code_verifier }



http://bit.ly/spa-security


Authenticated





{ json }
{ json }

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Summary

Modern authentication is complex
Two ways to approach SPA authentication
Auth Code with PKCE is the BCP
http://bit.ly/spa-security
Your architecture will guide your needs
Resources

On The Nature of OAuth 2 Scopes
http://bit.ly/oauth-scopes
Angular Authentication Tutorial
http://bit.ly/ng-auth-quick
React Authentication Tutorial
http://bit.ly/react-auth-quick
http://bit.ly/spa-security
Thank You!
@kukicado

http://bit.ly/spa-security
Advanced Single Page Application Security
By Ado Kukic
Advanced Single Page Application Security
- 1,099



