COMP2511
Week 5
TUESDAY 1PM - 4PM (T13B)
This week
- Strategy pattern
- Observer pattern
- State Pattern
You have an assignment viva in your lab.
You must come to the lab this week
Liskov Substitution Principle
Liskov Substitution Principle
What is it?
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) states that objects of a superclass should be replaceable with objects of its subclasses without breaking the application.
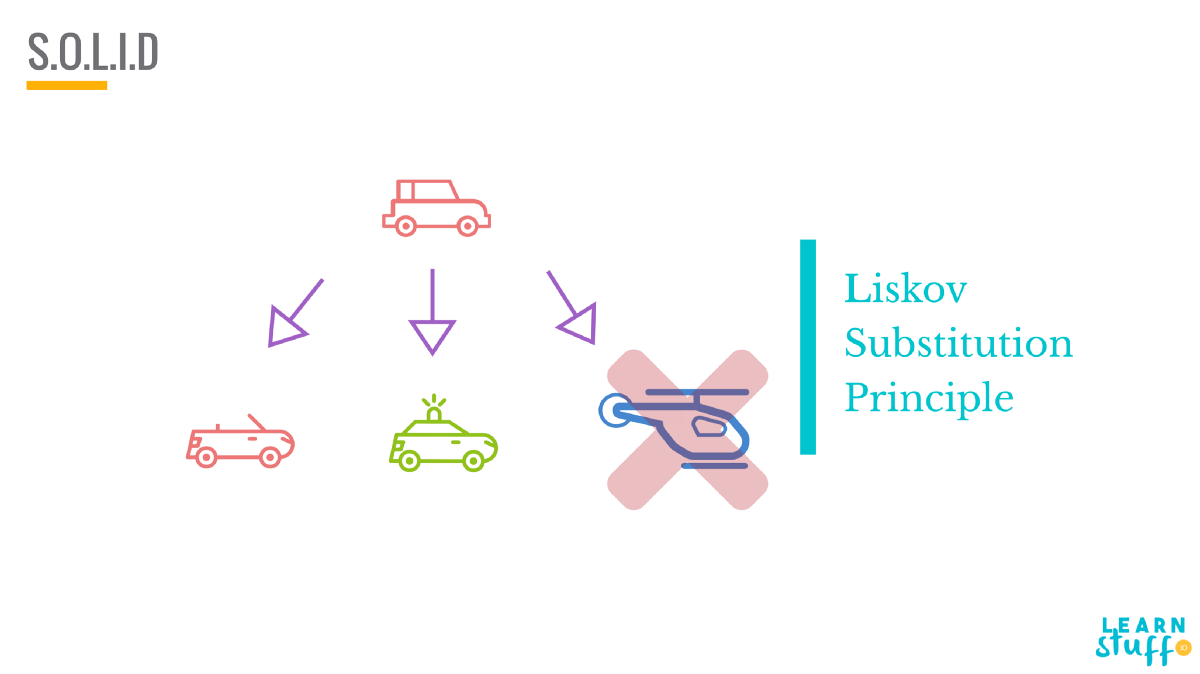
*inheritance arrows are the other way around
Precondition Weaking
- An implementation or redefinition (method overriding) of an inherited method must comply with the inherited contract for the method
- Preconditions may be weakened (relaxed) in a subclass, but it must comply with the inherited contract
- An implementation or redefinition may lesson the obligation of the client, but not increase it
from 0 <= theta <= 90 to 0 <= theta <= 180 is weakening
Why?
LSP. I should be able to use the subclass's implementation in place of my super class.
Strategy Pattern
Strategy Pattern
What type of design pattern is strategy?
Behavioural Pattern
Behavioural patterns are patterns concerned with algorithms and the assignment of responsibility between object
- Uses composition instead of inheritance
- Allows for dependency injection (Selects and adapts an algorithm at run time)
- Encapsulates interchangeable behaviours and uses delegation to decide which one to use
- Useful when you want to share behaviour across an inheritance tree
Strategy Pattern
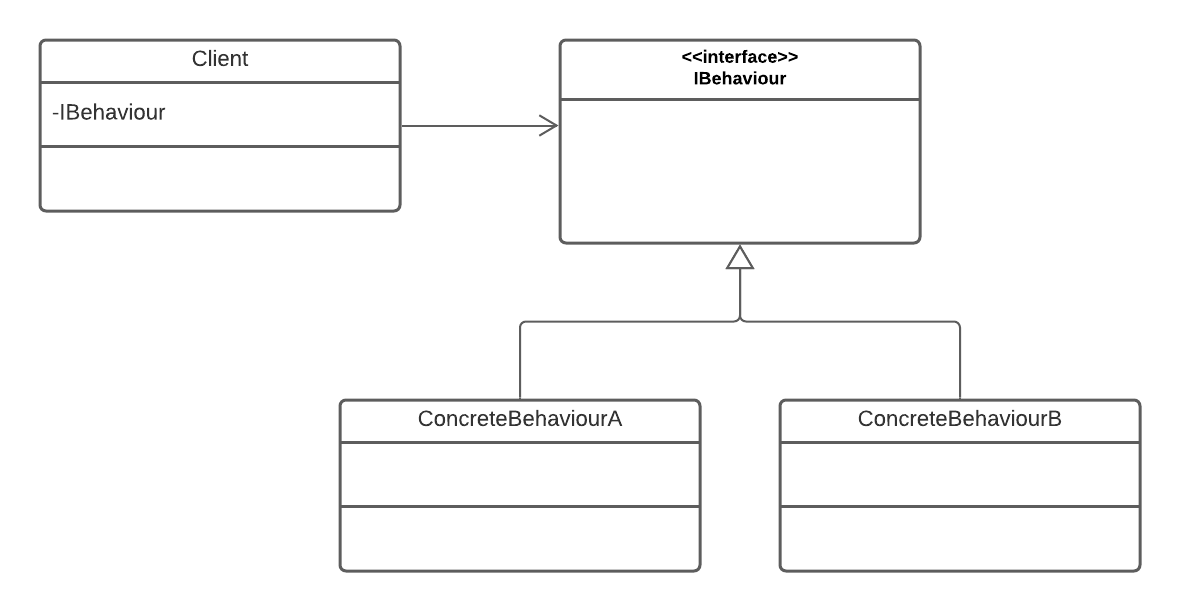
Strategy Pattern
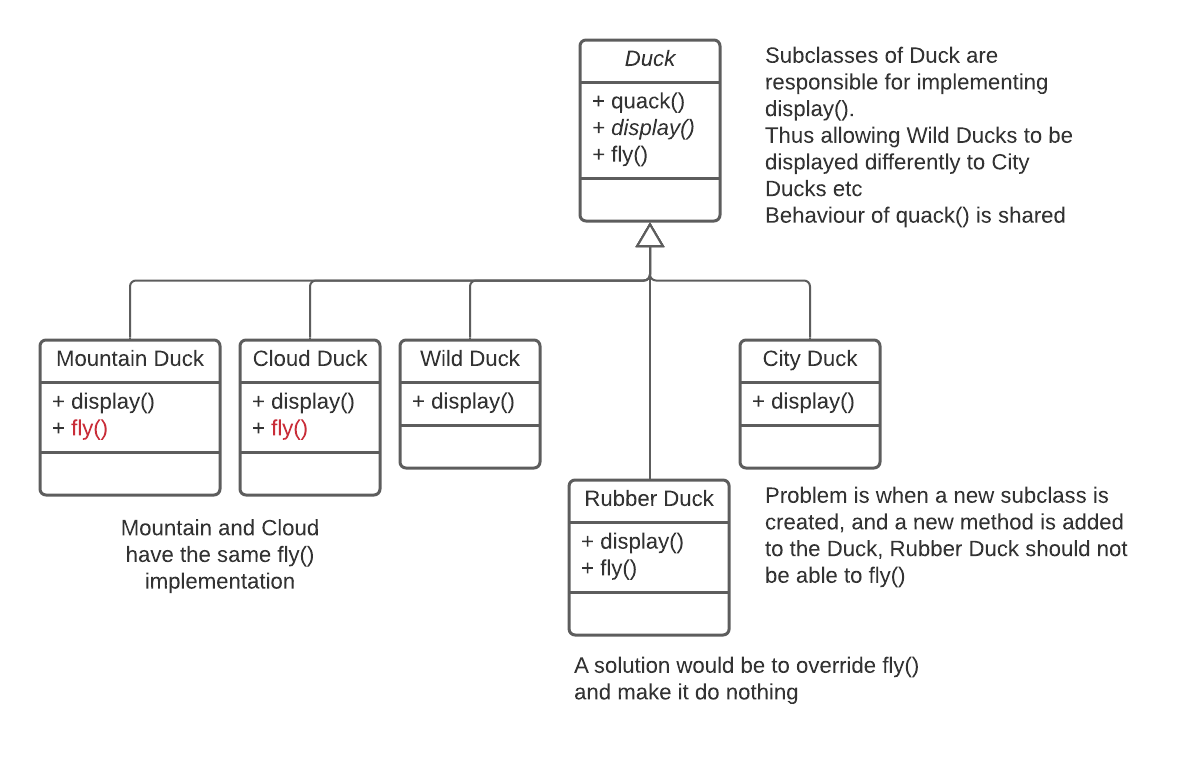
'Share behaviour across inheritance tree'
Code Demo
Strategy Pattern
Restaurant payment system with the following requirements:
- The restaurant has a menu, stored in a JSON file. Each meal on the menu has a name and price
- The system displays all of the standard meal names and their prices to the user so they can make their order
- The user can enter their order as a series of meals, and the system returns their cost
- The prices on meals often vary in different circumstances. The restaurant has four different price settings:
-
Standard - normal rates
- Holiday - 15% surcharge on all items for all customers
- Happy Hour - where registered members get a 40% discount, while standard customers get 30%
- Discount - where registered members get a 15% discount and standard customers pay normal prices
The prices displayed on the menu are the ones for standard customers in all settings
public class Restaurant {
...
public double cost(List<Meal> order, String payee) {
switch (chargingStrategy) {
case "standard":
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost()).sum();
case "holiday":
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost() * 1.15).sum();
case "happyHour":
if (members.contains(payee)) {
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost() * 0.6).sum();
} else {
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost() * 0.7).sum();
}
case "discount":
if (members.contains(payee)) {
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost() * 0.85).sum();
} else {
return order.stream().mapToDouble(meal -> meal.getCost()).sum();
}
default:
return 0;
}
}
...
}- How does the code violate the open/closed principle?
- How does this make the code brittle?
Not closed for modification, open for extension. If more cases need to be added, the switch statement has to be changed.
New requirements may cause the code to break or may be difficult to implement
public class Restaurant {
...
public void displayMenu() {
double modifier = 0;
switch (chargingStrategy) {
case "standard":
modifier = 1;
break;
case "holiday":
modifier = 1.15;
break;
case "happyHour":
modifier = 0.7;
break;
case "discount":
modifier = 1;
break;
}
for (Meal meal : menu) {
System.out.println(meal.getName() + " - " + meal.getCost() * modifier);
}
}
...
}Similar idea here, if new cases need to be added, the class's method itself needs to be changed. Cannot be extended
Code Demo - Strategy
To fix these issues, we can introduce a strategy pattern and move all the individual case logic into their own classes
public interface ChargingStrategy {
/**
* The cost of a meal.
*/
public double cost(List<Meal> order, boolean payeeIsMember);
/**
* Modifying factor of charges for standard customers.
*/
public double standardChargeModifier();
}
The prices on meals often vary in different circumstances. The restaurant has four different price settings:
- Standard - normal rates
- Holiday - 15% surcharge on all items for all customers
- Happy Hour - where registered members get a 40% discount, while standard customers get 30%
- Discount - where registered members get a 15% discount and standard customers pay normal prices
Observer Pattern
Observer Pattern
What type of design pattern is strategy?
Behavioural Pattern
An object (subject) maintains a list of dependents called observers. The subject notifies the observers automatically of any state changes.
- Used to implement event handling systems ("event driven" programming).
- Able to dynamically add and remove observers
- One-to-many dependency such that when the subject changes state, all of its dependents (observers) are notified and updated automatically
- Loosing coupling of objects that interact with each other.
Observer Pattern
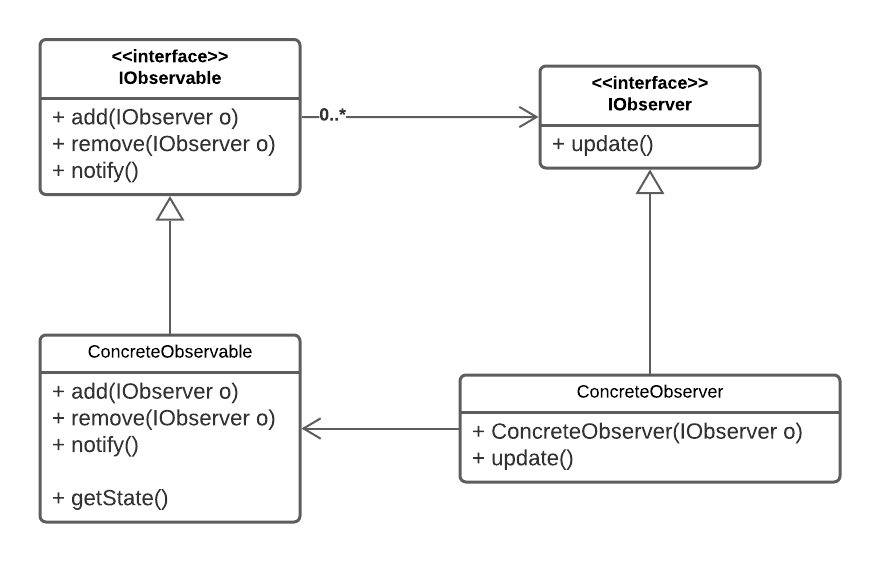
Observer
Subject
Code Demo
Observer Pattern
Code Demo
In src/youtube, create a model for the following requirements of a Youtube-like video creating and watching service using the Observer Pattern:
- A Producer has a name, a series of subscribers and videos
- When a producer posts a new video, all of the subscribers are notified that a new video was posted
- A User has a name, and can subscribe to any Producer
- A video has a name, length and producer
State Pattern
State Pattern
What type of design pattern is strategy?
Behavioural Pattern
Allows an object to alter its behaviour at run-time when its internals state changes.
- Similar to a state machine
- Clean way for an object to partially change its type at run-time
- Cannot add new functionality at run-time, can only switch
- Reduces conditional complexity (less if/switch statements)
- Encapsulates state-based behaviour and uses delegation to switch between behaviours
State Pattern
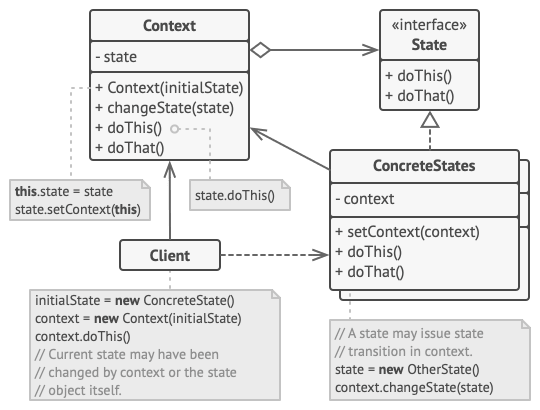
Code Demo
State Pattern
Code Demo
Continues from previous exercise/demo.
Extend your solution to accomodate the following requirements:
- Users can view a video, and a viewing has a series of states:
- Playing state - the video is playing
- Ready state - the video is paused, ready to play
- Locked state - the video is temporarily 'locked' from being watched
| Current \ Input | Locking | Playing | Next |
|---|---|---|---|
| Locked | If playing, switch to ready state, else locked | Switch to ready state | Return error: Locked |
| Playing | Stops playing, switch to locked | Pauses video, switch to ready | Starts playing next video |
| Ready | Go to locked | Start playback, change to play state | Returns error: Locked |
Code Demo
package youtube.state;
import youtube.Viewing;
public abstract class ViewingState {
private Viewing viewing;
public ViewingState(Viewing viewing) {
this.viewing = viewing;
}
public abstract String onLock();
public abstract String onPlay();
public abstract String onNext();
public Viewing getViewing() {
return this.viewing;
}
}public class Viewing {
private Video video;
private Video nextVideo;
private Producer user;
private ViewingState state = new ReadyState(this);
private boolean playing = false;
public Viewing(Video video, Video nextVideo, Producer user) {
this.video = video;
this.nextVideo = nextVideo;
this.user = user;
}
public void setPlaying(boolean play) {...}
public boolean isPlaying() {...}
public void changeState(ViewingState newState) {...}
public String startPlayback() {...}
public String getNextVideo() {...}
public String lock() {...}
public String play() {...}
public String next() {...}
}State Interface/Abstract Class
Attendance
Feedback

COMP2511 Week 5 22T3
By kuroson
COMP2511 Week 5 22T3
- 322



