STL
presented by
125 4,16,28
預防針
名詞能量高,請小心服用
見到 綠字,代表不用特別記得的名詞,
只要大概知道概念就好
Basic STL
What are STLs?
Standard Template Library
useful built-in tools
Four Parts Of STL
- containers 容器
- adapters 適配器
- iterator 迭代器
- algorithm 演算法
聽起來好難
都是裝東西的“東西”
常見容器/適配器
反正就是常見的裝東西的東東(資料結構)
vector
deque
list (linked list)
set (or multiset)
map (or multmap)
...
stack
queue
...
前情提要
物件 (Object)
喔不,聽起來很可怕?
其實定義很簡單,就是你想的"Object"





問題來了
誰是一個物件
簡單來亂說
物件要可以「丟」
=
如果東西不能丟?
把它包裝起來!
問題來了
誰是一個物件


來比較一下
C - style array
std::vector
int A[3] = {0,1,2}
int B[3];
B = A; // 不合法
vector<int> C = {0,1,2};
vector<int> D;
D = C; // 合法void foo(int arr[]) {
cout << "function\n";
}
// 呼叫時
int arr[];
foo(arr); // 只用指標傳遞void foo(vector<int> arr) {
cout << "function\n";
}
// 呼叫時
vector<int>arr;
foo(arr); // 直接傳遞所以,STL為什麼重要
- 把許多東西物件化!
- 提供好用的成員函數!
這又是啥?
成員
包裝完的物件,會有許多功能

取用方式?用眼睛看
object.member_name
栗子
Student 陳彥臻;
cout << 陳彥臻.height << endl;
那成員函數勒?
for (int i = 0; i < INF; ++i) {
陳彥臻.AfraidOfWater()
}
STL 常見成員函數
.empty()
.size()
.clear()
.pop_back()
.push_back()
.pop_front()
.push_front()
.insert()
.erase()
.front()
.back()
.top()
.begin()
.end()
.find()
.......
回傳iterator
Iterator
迭代器

Iterator是什麼
進化版的指標
用法跟指標差不多
那為什麼需要多一個東西呢?
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 12 | 23 | 10 | 35 |
以vector為例
vector <int> water = {12, 23, 10, 35};
water.begin()
water.end()
water.front() == 12
water.back() == 35
vector<int>::iterator it = water.begin()
auto it2 = water.begin()以set為例
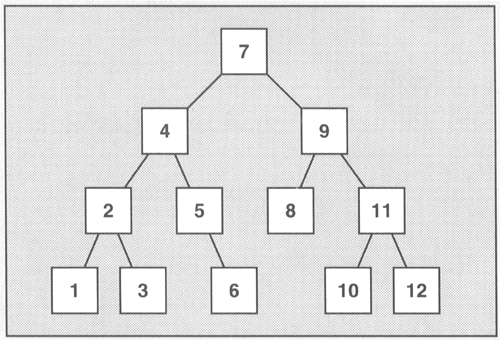
orz.begin()
orz.end()
orz.end()-1
因為記憶體不連續,所以需要用iterator這種特別的東東
it++
還是看不懂?
Vector
容器之王
Vector是甚麼?
其實就是陣列
可以伸縮自如的那種
如果是Array
宣告時就要有大小了
例如:arr[10]
但vector沒在跟你管這些的啦
直接伸縮
by 建電一二學術長檸檬
宣告
vector<型態> 名字;
vector<型態> 名字(大小,值);
vector<型態> 名字 = {2,3,4};
vector<float> foo;
vector<int> bar(30); // 30個0
vector<int> water(10,-1); // 填十個-1
vector<string> dian = {"Brine", "Che", "Willy"};取值,改值
時間複雜度 O(1)
water[0] = 16;
cout << water[0] << endl;push_back
在後面插入一個東東
時間複雜度 O(1)
vector <int> water;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
water.push_back(i*i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << water[i] << " ";
}OUTPUT:
0 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81
pop_back
把最後面一個東東丟掉
時間複雜度 O(1)
vector <int> water = {1,2,3,4,5};
water.pop_back();
cout << "size: " << water.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < water.size(); ++i) {
cout << water[i] << endl;
}OUTPUT:
size: 4
1 2 3 4如果不是在最後面插入勒?
vector沒有pop_front(), push_front()
用insert(), erase()
O(n)!!!
.empty()
陣列為空?
時間複雜度 O(1)
回傳bool
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(5);
if(v.empty()){
cout << "empty!\n";
} else {
cout << "not empty!\n"
}
//輸出 "not empty!".size()
陣列大小
時間複雜度 O(1)
回傳 size_t (aka long)
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(7);
v.pop_back(); // 7被移出去
cou t<< v.size(); // 1
v.pop_back(); // 5被移出去
cout << v.size(); // 0跑過整個vector
how?
1. 一般for迴圈
vector <int> water = {1,2,5,16};
for (int i = 0; i < water.size(); ++i) {
cout << water[i] << " ";
}跑過整個vector
how?
2. 迭代器
vector <int> water = {1,2,5,16};
for (auto it = water.begin(); it != water.end; it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}跑過整個vector
how?
3. for range
vector <int> water = {1,2,5,16};
for (auto item : water) {
cout << item << " ";
}剛剛只大致介紹一下
code有空自己再去看
Deque
雙頭龍
做簡報好累
vector只能push屁股好討厭?
用deque!
push_back() pop_back()
push_front() pop_front()
通通O(1)
deque <string> water = {"Hong-An", "is", "so", "dian"};
water.pop_front(); // {"is", "so", "dian"};
water.pop_back(); // {"is", "so"};
water.push_front("AaW"); // {"AaW", "is", "so"}
water.push_back("week"); // {"AaW", "is", "so", "week"}缺點,常數大
但也蠻好用的
List
串列
做簡報好累
反正就是一個長這樣的東西
插入刪除O(1)
查東西O(n)
可以用來插隊
插入O(1) !!!
Stack
來玩疊疊樂摟
鄭竣陽aka資訊社學術長 好像也講過
是一個adapter
內部容器要有 empty、size、back、push_back、 pop_back 這些函式
stack<int> a; // 預設用vector
stack<int, vector<int>> b;
stack<int, deque<int>> c;
stack<int, list<int>> d;LIFO aka last in first out
| 4 |
| 3 |
| 2 |
| 1 |
pop() push()
top()
範例
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> iamweek;
iamweek.push(1);
iamweek.push(2);
cout << iamweek.top() << endl; // 2
iamweek.pop();
cout << iamweek.top() << endl; // 1
return 0;
}
Queue
來排隊摟
鄭竣陽aka資訊社學術長 好像也講過
queue<int> a; // 預設用deque
queue<int, deque<int>> c;
queue<int, list<int>> d;這個vector不能用
Structure
1 2 3 4
.front()
.back()
FIFO aka first in first out
out
in
範例
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
cout << q.front() << ' ' << q.back() <<endl; // 1 3
q.pop();
cout << q.front() << ' ' << q.back() <<endl; // 2 3
return 0;
}
Priority Queue
照號碼排隊喔
- 加入一個元素
- 查詢最大元素
- 刪除最大元素
我只需要...
有個叫heap的資料結構
反正就是會排序的Queue
算是set的子集(不重要)
- 查詢最大(小)O(1)
- 插入O(log N)
- 刪除O(log N)
用法
#include <iostream>
#include <priority_queue>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(1);//加入元素
cout << pq.top() << '\n';//找最大
pq.pop();//刪除最大
}
更改比較函式
#include <iostream>
#include <priority_queue>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
//要多寫一個底層容器
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > pq;
//最小在上面
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > pq;
//最大在上面
}
用處
- 不須排序只需極值
- set被卡時間
- 有點像急診
- Greedy用的到
- 最小生成樹
Set
一棵樹

什麼是樹呢?
完全連通無環圖
Depth
Root
leaf
Edge
Binary Search Tree
二元搜尋樹
Set是平衡二元搜尋樹
旋轉 or 換根,以保持tree的平衡,以免深度爆炸,影響複雜度
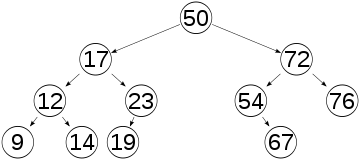
Unbalanced
Balanced
Set 內部是紅黑樹
我也不會
插入、查詢、刪除是O(log N)
基本用法
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
set <int> s; //宣告 或是set <int, less<int>> s
s.insert(5);//insert elements
s.insert(2);
s.insert(3);
s.erase(s.begin());//use iter (= s.erase(5))
cout<< *s.begin();//3
cout<< *s.rbegin();//2
multiset<int> ms; //可重複元素
}
一般set不能有重複元素,multiset可

orz.begin()
orz.end()
orz.rbegin()
還有一個unorder_set
Hash實作
插入刪除是常數較大的O(1)
有哪些應用呢?
- 維護一個排序好的集合
- 處理離散資料
- Greedy Algorithm
- 酷酷的Longest increasing subsequence (LIS)
Map
喔這也是紅黑樹
插入、查詢、刪除都是O(log N)
N是map大小
What can map do?
將一個KEY對應到一個VALUE
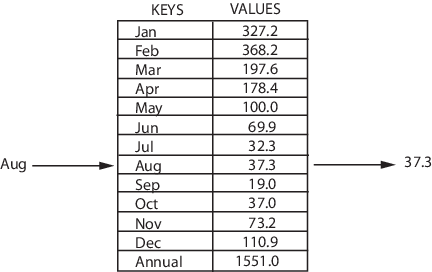
語法
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map <string, int> mp; // map<KEY, VALUE>
mp["Iamweek"] = 1;//新增
mp["Iamstrong"] = 0;
mp["Iamweek"] = 666;//更改
cout << mp["Iamweek"]; // 666
mp.erase("Iamweek");//刪除
}也可以unorder_map
key不排序,O(1)
能幹嘛?
- 處理字串
- KEY的範圍很大但用的很少->節省空間
有點像python的字典
Algorithm
簡單說就是STL的函式模板
min_element / max_element
最大最小
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//vector and deque
*min_element(v.begin(),v.end());
*max_element(v.begin(),v.end());
}
reverse
倒過來
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) arr.push_back(i);
reverse(arr.begin(),arr.end());
for (auto i : arr) cout<<i<<' ';//4 3 2 1 0
return 0;
}
upper_bound()/lower_bound()
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//set
s.upper_bound(x);//O(log N)
upper_bound(s.begin(),s.end(),x);//O(n)
//vector or deque
//記得先sort
upper_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x);//O(log n)
}
就二分搜的概念,大於或大於等於
sort
O(N log N)~~
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector <int> arr;
for(int i = 5; i >= 0; --i) arr.push_back(i);
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),greater<int>);//543210
sort(arr.begin(),arr.end(),less<int>);//012345
}
Set的酷酷LIS
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n; cin>>n;
multiset <int> lis;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int a; cin>>a;
lis.insert(a);
auto iter = lis.upper_bound(a);
if (iter != lis.end()) lis.erase(iter);
}
cout<< lis.size() << endl;
return 0;
}4叫我不要講,但我偏要
Thanks~
STL Presentation
By Lai Hong An
STL Presentation
- 548


