PARATHYROID HORMONE INDUCES ADIPOCYTE LIPOLYSIS VIA PKA-MEDIATED PHOSPHORYLATION OF HORMONE-SENSITIVE LIPASE
- PTH and metabolic effects: lipolytic action
- Aim of the study: describe the molecular control of lipolysis mediated by PTH
CLASSICAL ACTION OF PTH
PTH is released from parathyroid glands in response to lowered blood Calcium and acts mainly on bone, kidney,intestine.

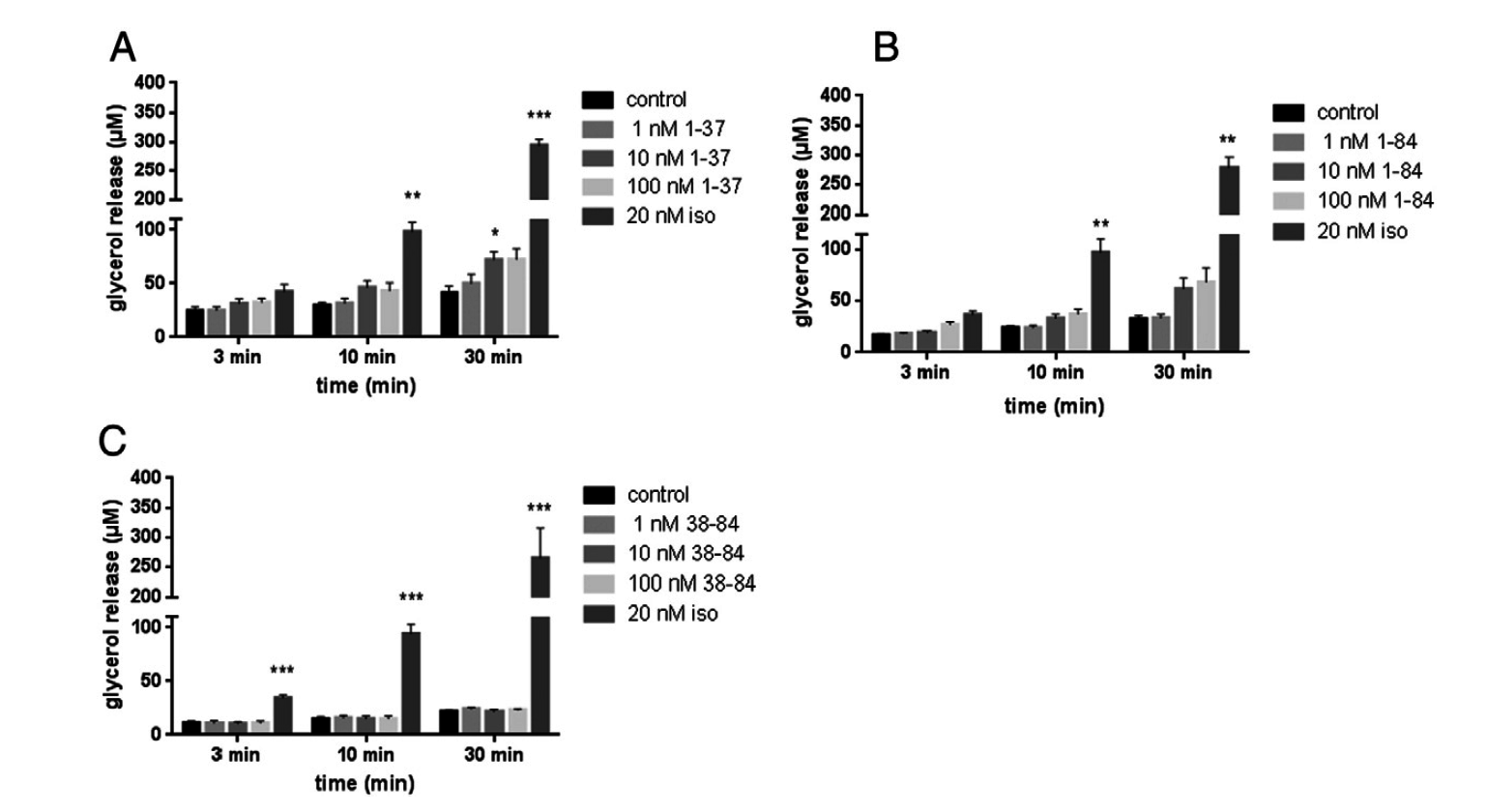
Lipolysis in response to stimulation with different PTH fragments. Primarymouse adipocytes were isolated and stimulatedwith (A) intact PTH (1-84), (B) the N-terminal fragment of PTH (1-37) or (C) the C-terminal fragment of PTH (38-84) in increasing concentrations from1 to 100 nM for 3, 10 or 30min. Untreated cells (control) and cells stimulated with 20 nM isoprenaline (iso) were used for comparison. Lipolysis was measured as glycerol concentration in the medium. The graphs represent mean values ± SD from three experiments per fragment. *p b 0.05, **p b 0.01, ***p b 0.001.
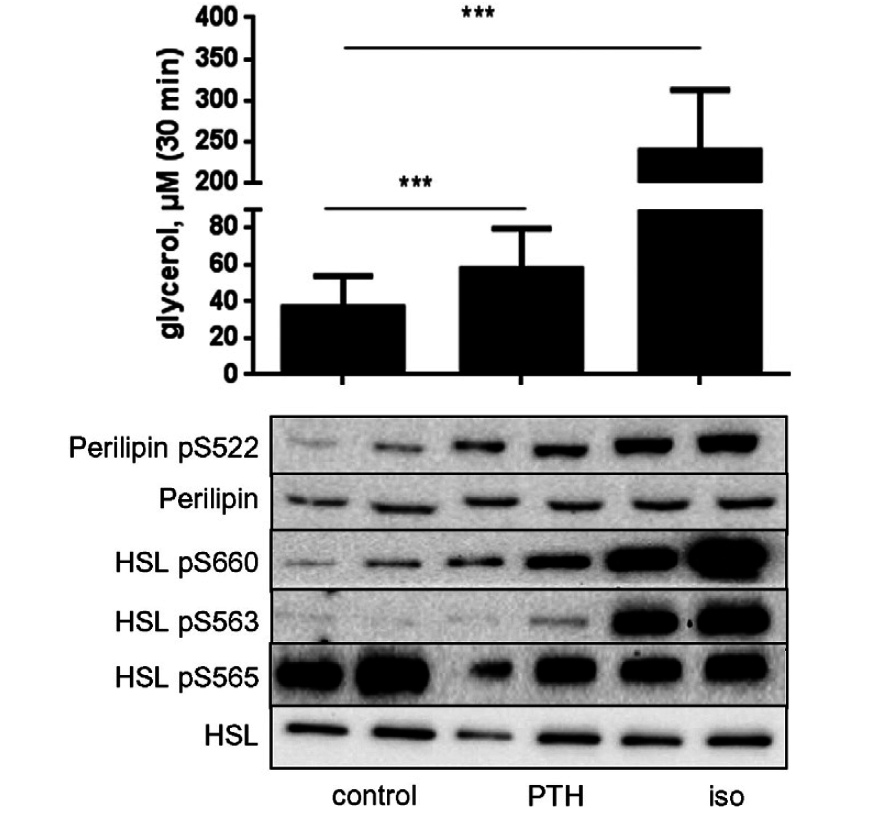
PTH stimulation of adipocytes results in phosphorylation of known PKA substrates
Inhibition of PKA signaling pathway blocks the lipolyitic effect of PTH
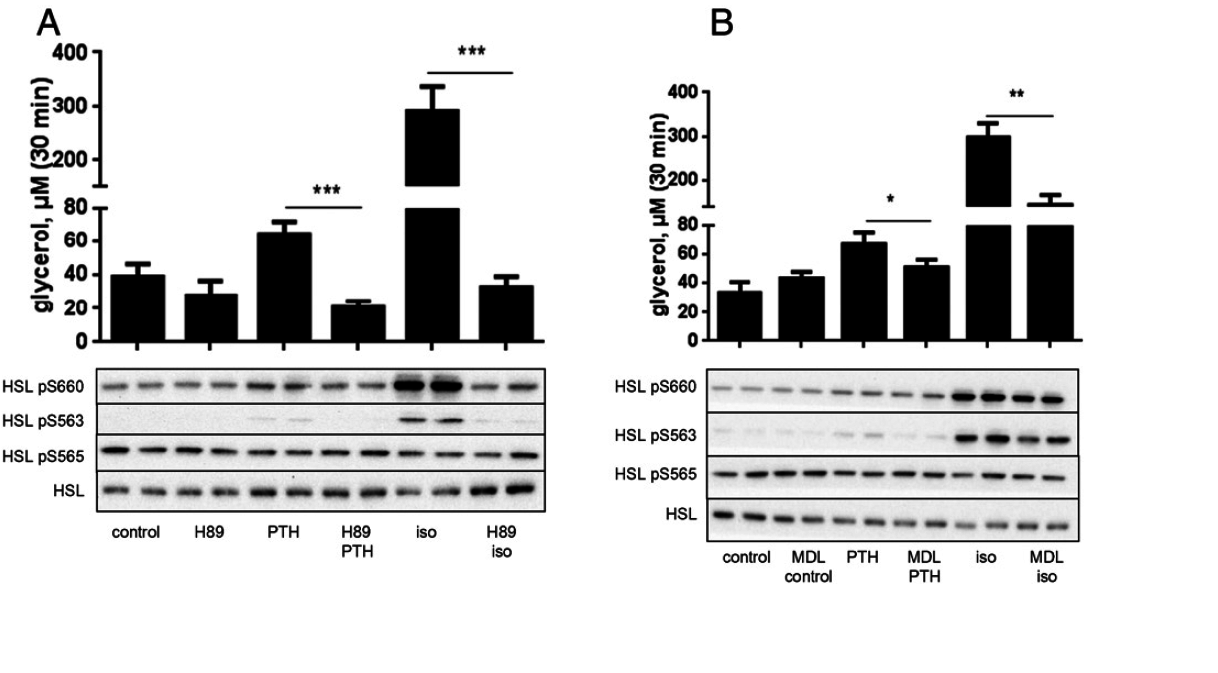
Effect of inhibitors of PKA and adenylate cyclase on PTH-induced lipolysis and HSL phosphorylation. Primary mouse adipocytes were isolated and pre-treated for 30 min with or
without 50 μM of the PKA inhibitor H89 (A) or for 60 min with 25 μM of the adenylate cyclase inhibitor MDL-12330A (B). Cells were then stimulated with 10 nM PTH (1-37) or 20 nM
isoprenaline for 30 min or left untreated. Lipolysis was measured as glycerol concentration in the medium. Aliquots of whole cell lysates were subjected toWestern blot analysis with
antibodies recognizing HSL phosphorylated at S563, S660 and S565 and total HSL. The graph illustrates mean values ± SD from three experiments, shown together with
representative blots. *p b 0.05, **p b 0.01, ***p b 0.001.
Other kinases are involved in the lipolytic process, but the inhibition of them has not significant effect on the lipolytic action of PTH
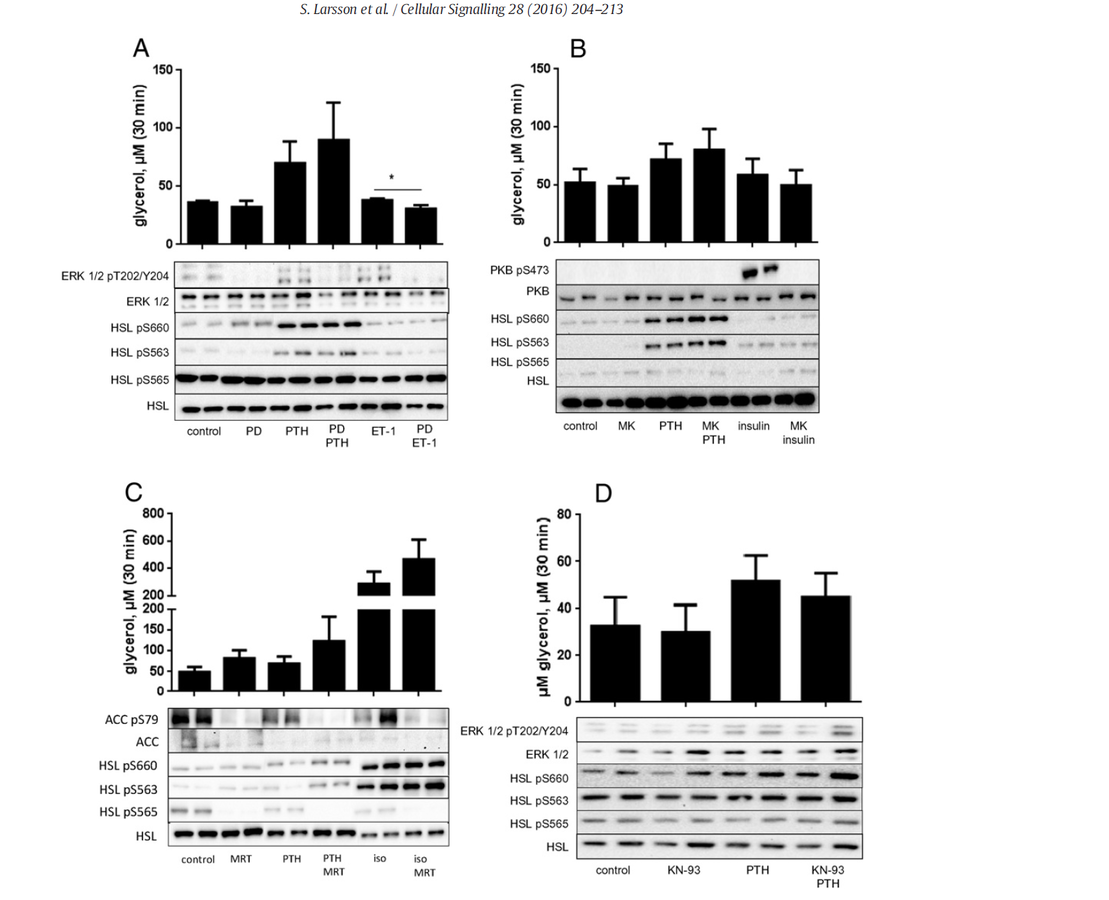
Potentiation of lipolyisis mediated by PTH through the inhibition of PDE4, an enzyme that modulate the duration and intensity of intracellular response to cAMP by hydrolyzing it.
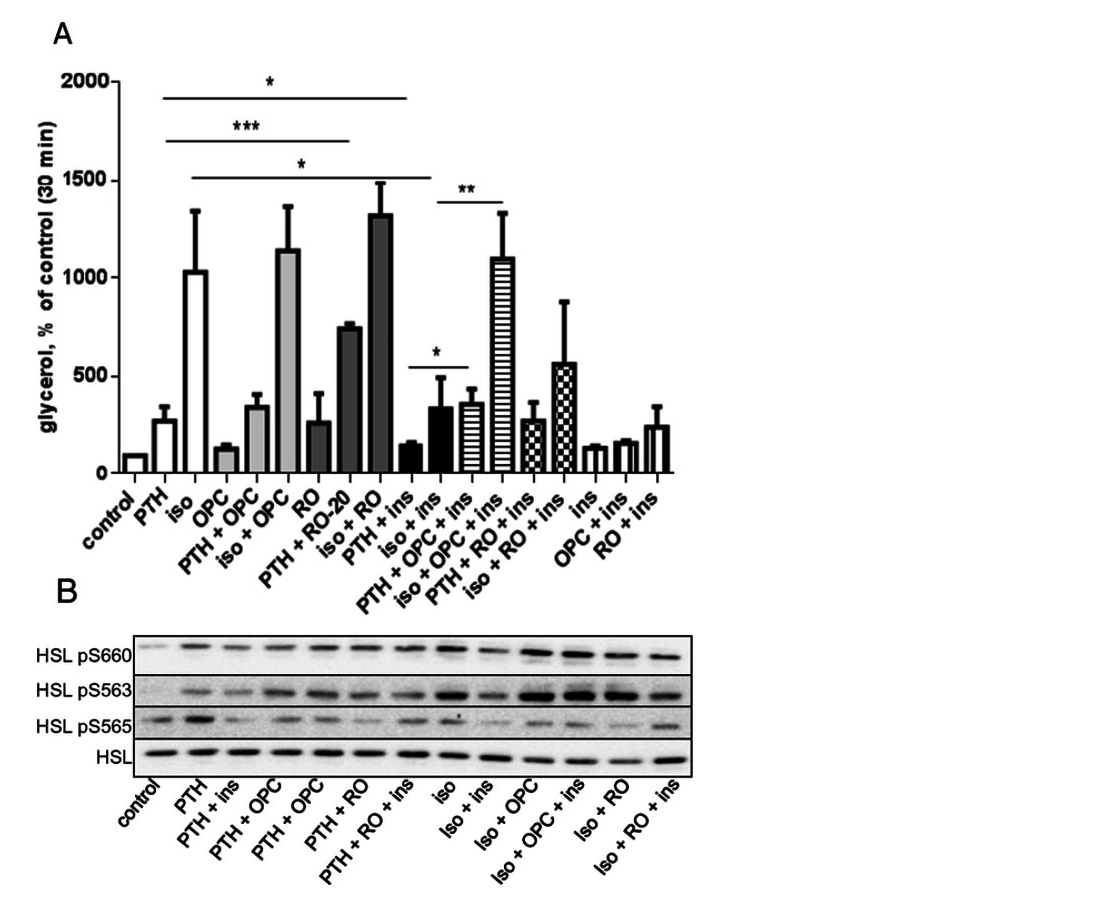
Insulin is able to block the lipolytic effect exerted by isoprenailne and PTH by the activation of PDE3B
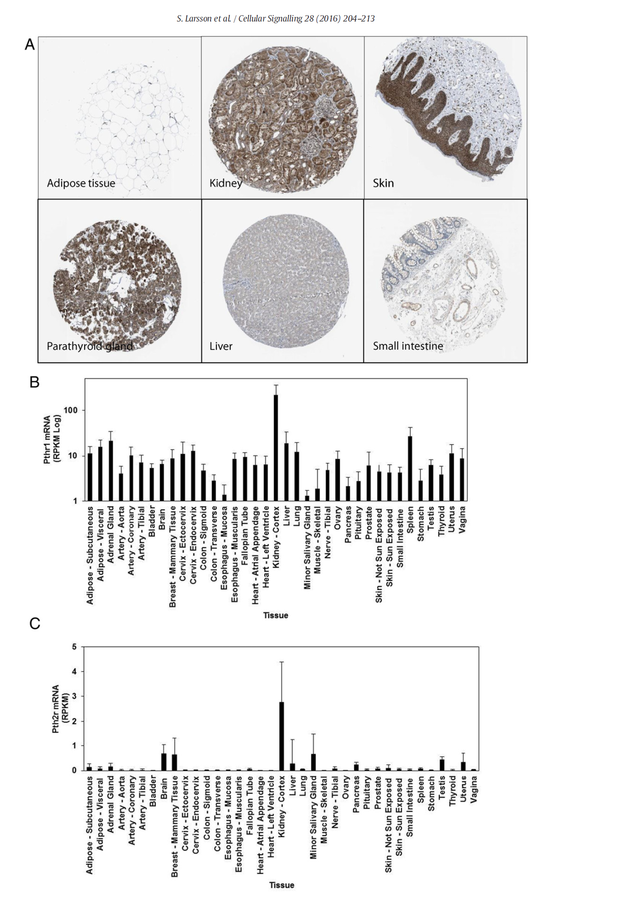
Expression of PTH receptors in adipose tissue
PTH1R is medium in human adipose tissue
PTH2R is below detectable levels
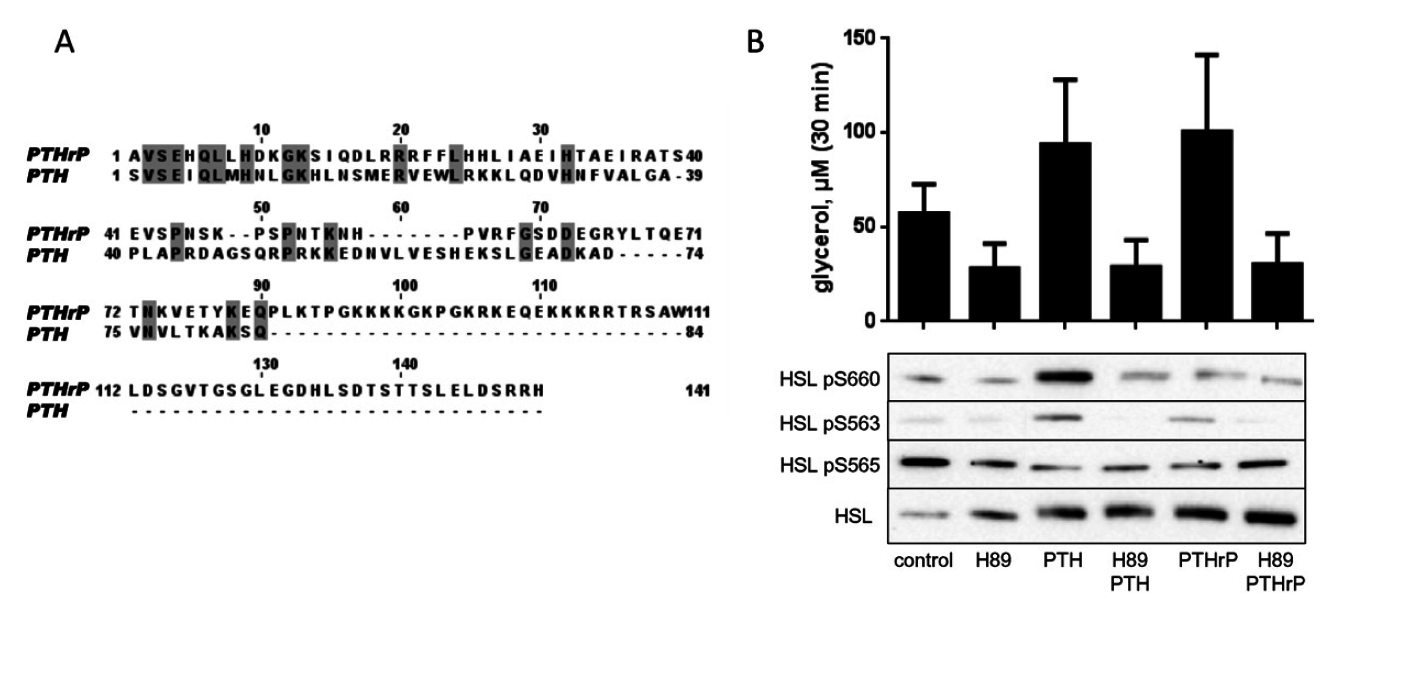
PTHrP acts lipolytically as well as PTH(1-37)
PTHrP: global sequence identity to PTHof 14% and local sequence identity of 34% within the 32 aa of N-terminal fragment.
Elevated levels of PTH during hyper parathyroidsm may contribute to metabolic diseases, lead to increased of fatty acid from adipose tissue and thereby ectopic lipid deposition: insulin resistance.
conclusions
Obese people show decreased levels of PDE4 activity so the lipolytic action of PTH increases.
PTH induces lipolysis via cAMP-PKA pathway, weak action respect to the non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist isoprenaline, but PTH lipolytic action is potentiated using an inhibitor of PDE4.
ARTICLE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM
By laura91
ARTICLE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM
The involvement of PTH in lipolysis
- 2,000