skrollr.JS
From: https://github.com/Prinzhorn/skrollr
Official plugins
THIRD PARTY
- skrollr-menu - Hash navigation
- skrollr-ie - IE < 9 CSS fixes
- skrollr-stylesheets - Keyframes inside CSS files
In the wild
- http://www.fontwalk.de/
- http://kitkat.com/
- http://www.kia.co.uk
- http://www.cabletv.com/the-walking-dead
- http://hypervenom.nike.com/
- http://www.guardian.co.uk
- http://www.evanshalshaw.com/bondcars/
Let's get serious
<script type="text/javascript" src="skrollr.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var s = skrollr.init();
</script>
</body>Example
<divdata-0="background-color:rgb(0,0,255);"data-500="background-color:rgb(255,0,0);">WOOOT</div>
Let's change the background-color of a div starting at #00f when the scrollbar is at the top and ending with #f00 when the user scrolled 500 pixels down
FIRST LEARANED
<divdata-0="background-color:rgb(0,0,255);"data-500="background-color:rgb(255,0,0);">WOOOT</div>
- You can suppress this using the forceHeight option(EX.scroll down 500 pixels)
- You can't use #00f or #0000ff
-
You need to use rgb or hsl and explicitly decide which color space you want
EXAMPLE 2
Now let's do a barrel roll at the same time
<div data-0="background-color:rgb(0,0,255);transform:rotate(0deg);" data-500="background-color:rgb(255,0,0);transform:rotate(360deg);">WOOOT</div>
Skrollr handles all these nasty CSS prefixes for you
EXAMPLE 3
Now let the rotation bounce like it were a hip-hop video
<div
data-0="background-color:rgb(0,0,255);transform[bounce]:rotate(0deg);"
data-top="background-color:rgb(255,0,0);transform[bounce]:rotate(360deg);"
>WOOOT</div>Skrollr allows non-linear animations
The so called easing functions
EXAMPLE 4
LEARNED Summary
- You can suppress this using the forceHeight option(EX.scroll down 500 pixels)
- You can't use #00f or #0000ff
- You need to use rgb or hsl and explicitly decide which color space you want
- Skrollr handles all these nasty CSS prefixes for you
- Skrollr allows non-linear animations The so called easing functions
-
Skrollr keyframes can either be absolute or relative
If you're not a fan of data-attributes or if you're planning a big website where you want a better and more flexible structure, take a look at skrollr-stylesheets.

Mobile support -1
Mobile browsers try to save battery wherever they can. That's why mobile browsers delay the execution of JavaScript while you are scrolling. iOS in particular does this very aggressively and completely stops JavaScript
行動裝置為了省電,會延遲甚至是停止JAVASCRIPT的執行
When using skrollr on mobile you don't actually scroll.
When detecting a mobile browser skrollr disables native scrolling and instead listens for touch events and moves the content using CSS transforms.
skrollr會停止行動裝置的原生scrolling事件,而且監聽觸控事件改成用css3來移動內容
MOBILE SUPPORT - 2
What you need in order to support mobile browsers
Include an element on your page with the id skrollr-body.
That's the element we move in order to fake scrolling.
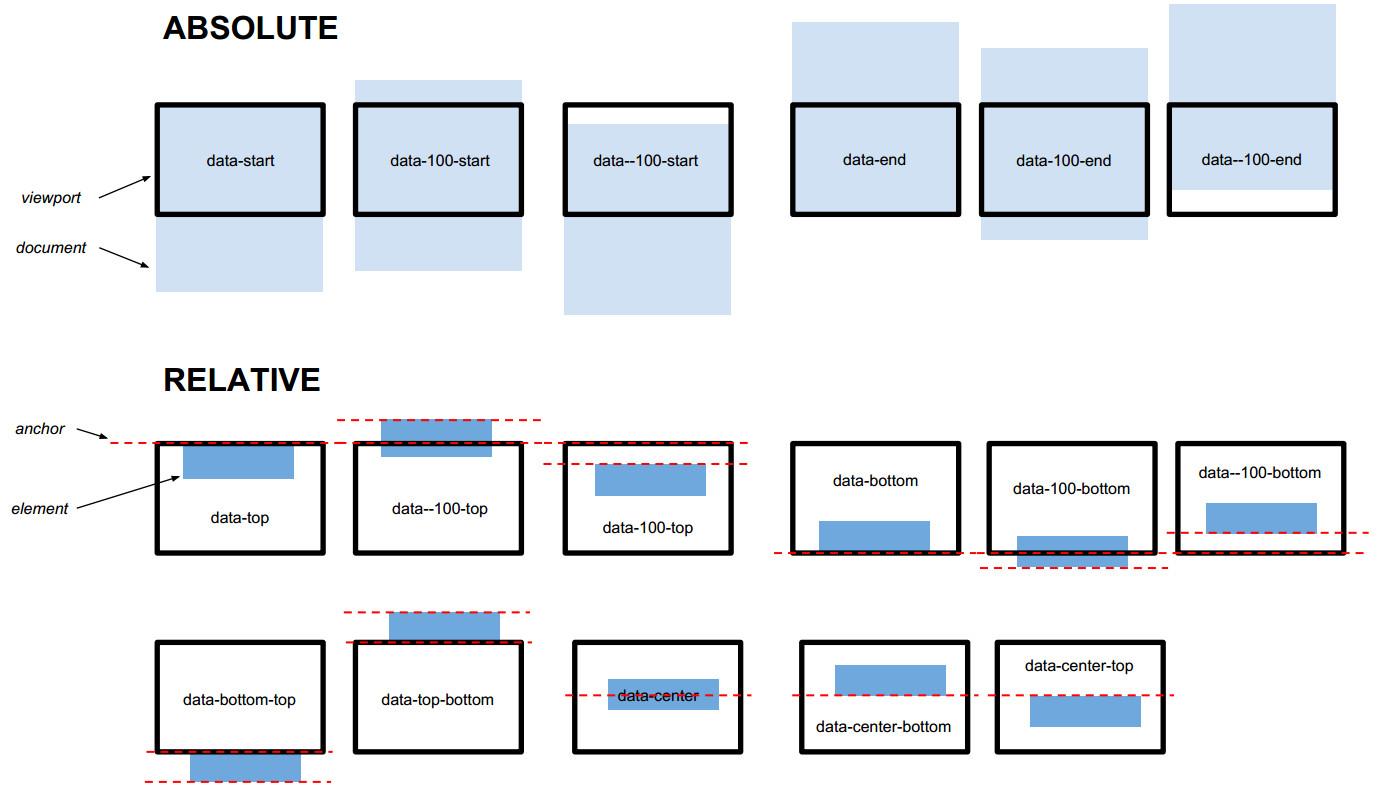
absolute mode
(or document mode)
The syntax is data-[offset]-[anchor]
offset 定位
(-n~n 可以是% 10% 寫作 10p)
anchor 錨點 標的物參考對像
(start/end)
data-0 = data-start = data-0-start
data-100 = data-100-start
data--100 = data--100-start
data-end = data-0-end
data-100-end
data--100-end
ABSOLUTE MODE
(OR DOCUMENT MODE)
relative mode
(or viewport mode)
data-[offset]-[viewport-anchor]-[element-anchor]
offset 位置(-n~n 可以是% 10% 寫作 10p)
viewport-anchor 可視區域的錨點top or bottom
element-anchor dom 物件的錨點top center bottom
RELATIVE MODE
(or viewport mode)
data-top = data-0-top = data-top-top = data-0-top-top
data-100-top = data-100-top-top
data--100-top = data--100-top-top
data-top-bottom= data-0-top-bottom
data-center-center = data-0-center-center
data-bottom-center = data-0-bottom-center
summary
data-anchor-target
data-anchor-target
PERCENTAGE OFFSETS
WORKING WITH CONSTANTS
skrollr.init({
constants: {
foobar: 1337
}
});
<div data-_foobar="left:0%;" data-_foobar--100="left:50%;" data-_foobar-100="left:100%;"></div>
<!--Equal to-->
<div data-1337="left:0%;" data-1237="left:50%;" data-1437="left:100%;"></div>
CSS classes
css class
Filling missing values
<divdata-100="left:0%;"data-200="top:0%;"data-300="left:50%;"data-400="top:50%;"></div>
One could expect left to have a value of 25% at keyframe 200
skrollr only interpolates values between key frames which are direct neighbors
<div
data-100="left:0%;"
data-200="top:0%;"
data-300="left:50%;"
data-400="top:50%;">
</div>
<div
data-100="left:0%;"
data-200="top:0%;"
data-300="left:50%;"
data-400="top:50%;">
</div>
<!--這才是真正的結果--><div
data-100="left:0%;top:0%;"
data-200="left:0%;top:0%;"
data-300="left:50%;top:0%;"
data-400="left:50%;top:50%;">
</div>
<!--這才是真正的結果--><div data-100="left:0%;top:0%;" data-200="left:0%;top:0%;" data-300="left:50%;top:0%;" data-400="left:50%;top:50%;"> </div>
Preventing interpolation
<!-- This will get your image url f***** up because there's no "kitten1.4561799.jpg" and the like --><div data-0="background-image:url(kitten1.jpg);" data-100="background-image:url(kitten2.jpg)"></div> <!-- Better --><div data-0="background-image:!url(kitten1.jpg);" data-100="background-image:!url(kitten2.jpg)"></div>
Limitations SUMMARY
-
All numeric values have to have the same unit
It's not possible to animate from 5% to 100px.
- Animations between values which are composed of multiple numeric values like margin:0 0 0 0; are only possible for the same number of values.
margin:0px 0px 0px 0px; to margin:0px 100px 50px 3px; is fine,
but not margin:10px; to margin:5px 10px;. -
Animations between CSS transforms only work when they use the same functions in same order.
From rotate(0deg) scale(1) to rotate(1000deg) scale(5) is fine.
LIMITATIONS SUMMARY 2
- Color animations don't support named values like "red" or hex values like "#ff0000".
- Color animations only work for same color functions.
hsl() to hsl() or hsla() is fine, but not rgb() to hsl().
JavaScript
skrollr.init([options])
INIT-1
skrollr.init([{ smoothScrolling:true,//順暢的滑動 smoothScrollingDuration:200, //The number of milliseconds the animations run after the scroll position changed the last time. constants:{}, //Example: data-_myconst-200 and skrollr.init({constants: {myconst: 300}}) result in data-500. scale:1, // If your animation runs too fast or too slow, just adjust the scale value. //When forceHeight is set to false, scale is ignored.//scale does only affect key frames in absolute mode, e.g. data-500 but not data-top. forceHeight:true //為true時自動幫你把文本的高度對應成可以滿足所有錨點 }])
init-2
skrollr.init([{ mobileCheck=function() {return (/Android|iPhone|iPad|iPod|BlackBerry|Windows Phone/i).test(navigator.userAgent || navigator.vendor || window.opera);}}])
This option allows you to pass a function to skrollr overwriting the check for mobile devices. The function should return true when mobile scrolling should be used and false if not.
INIT-3
skrollr.init([{ mobileDeceleration=0.004}])
The amount of deceleration for momentum scrolling on mobile devices. This options tells skrollr how fast or slow you want the scrolling to stop after the user lifted his finger.
INIT-4
skrollr.init([{ edgeStrategy='set'//元素的初始值策略}])
-
set (default) : When before/after the first/last keyframe, apply the styles of the first/last keyframe to the element.(在跑第一格前把第一個影格的值加到元素上)
-
ease : Same as set, but the values will be transformed using the given easing function.(在跑第一格前把第一個影格的值加到元素上,但使用自已傳進去的function)
- reset : When before/after the first/last keyframe, apply the styles which the element had before skrollr did anything. This means resetting the class attribute as well as removing all styles which have been applied to the style property. This means the element won't have any skrollable-* CSS classes.
INIT-5
skrollr.init([{ beforerender:function(){},render: function(data) { //Log the current scroll position. console.log(data.curTop); }}])
{ curTop: 10, //the current scroll top offset lastTop: 0, //the top value of last time maxTop: 100, //the max value you can scroll to. curTop/maxTop will give you the current progress. direction: 'down' //either up or down }
INIT-6
skrollr.init([{ easing: { sin: function(p) { return (Math.sin(p * Math.PI * 2 - Math.PI/2) + 1) / 2;}, cos: function(p) { return (Math.cos(p * Math.PI * 2 - Math.PI/2) + 1) / 2; }//可以傳入自己定義的easing方法//使用方式 <div id="thing" data-0="left[cos]:10%;top[sin]:10%;" data-10000="left:90%;top:90%;"></div>}])
skrollr.get()
Returns the skrollr instance if init () has been called before or undefined.
Public API
refresh([elements])
Reparses all given elements. You can pass a single element or an array-like element (Array, NodeList, jQuery object)
Useful when
- elements in relative mode change and need to be updated 物件必需更新他的定位模式
- data-attributes are manipulated dynamically data的屬性是動態操作
- new elements are added to the DOM and should be controlled by skrollr 新的dom物件加入
-
When no elements are given, all elements in the document will be parsed again. In fact, when calling skrollr.init() skrollr uses refresh() without parameters internally. 當已經沒有元素 或是 init執行的時後
!!! 耗效能 不要在每次渲染時都使用
relativeToAbsolute (element, viewportAnchor, elementAnchor)
returns an integer which represents the absolute scroll position which correlates to the relative anchor
var offset = s.relativeToAbsolute(document.getElementById('foo'), 'top', 'bottom');
//offset contains the scroll position at which #foo's bottom is at the top of the viewport.
//If you now use setScrollTop(offset) or animateTo(offset) #foo's bottom will be perfectly aligned with the top of the viewport. Yay.getScrollTop()
回傳現在scroll的值
getMaxScrollTop()
回傳可以scroll的最大值,如果force為true時通常是最大的keyframe
setScrollTop(top[0, force = false])
- Sets the top offset using window.scrollTo(0, top) on dektop or updating the internal state in case of mobile scrolling. 把window定位到你設定的值手機跟行動裝置都ok
-
When force is set to true, skrollr will jump to the new position without any kind of transition. By default the global smoothScrolling setting applies. 如果force 設為true 則會順暢的滑動到設定的位置
animateTo(top[0, options])
Animates the scroll position from current position to top.
Possible options are
durtion
easing
done
stopAnimateTo()
Stops the animation and calls the done callback passing true as interrupted arguments.
isAnimatingTo()
Returns if an animation caused by animateTo is running.
on(name, fn)
啟動click 等等的監聽事件
off(name)
關掉click 等等的監聽事件
destroy()
Destroys skrollr. All class and style attributes will be set to the values they had before.
SKROLLR
By lauraluo






