The Knowledge Base Paradigm for
Decision & Process Management
Representation
- DMN
- Decision Tables
- FEEL
- BPMN
- YAWL
- DECLARE
- Petri nets
Task
- Enactment
- Completeness/Exclusivity checking
- ...
- Compliance checking
- Conformance checking
- Monitoring
- Automation
- ...
DM & BPM
Representation
- Deductive logic
- Query languages (SQL, datalog)
- Constraint programming
- Abductive Logic Programming
- Inductive Logic Programming
- PDDL, strips
- Answer set programming
Inference
- Deduction
- Query answering
- Constraint solving
- Abduction
- Induction
- Planning
- Model generation
Declarative
Problem Solving
Deduction Example
No_Class(X) :- Day(X, wednesday), Time(X, afternoon).
Day(14:00-30/03/2016, wednesday).
Time(14:00-30/03/2016, afternoon).
Deduction: No_Class(14:00-30/03/2016).
Query Example
not(Class(X) and Date(X, wednesday) and Time(X, afternoon)).
Result: True if there is no class scheduled on a wednesday afternoon, false otherwise.
Declarative
Problem Solving
Focus on a single specific form of inference
=> One representation, one problem
Example
Class(15:00-30/03/2016).
Deduction: ¬Class(14:00-30/03/2016)
Query: False
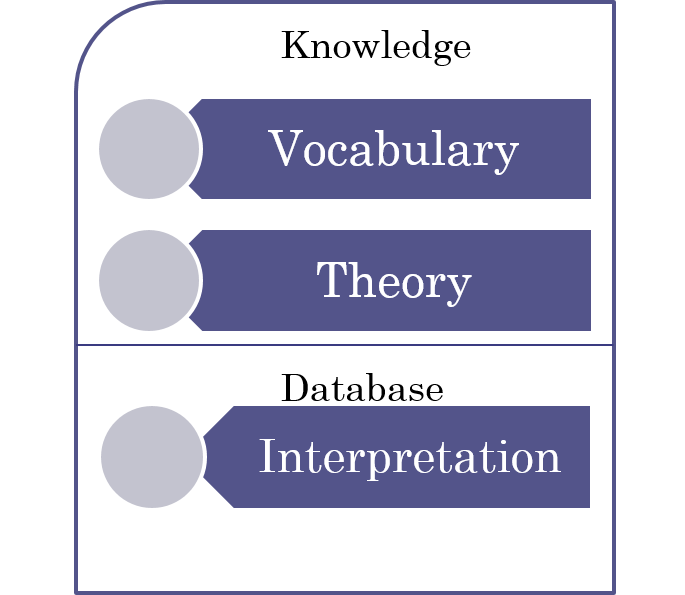
Knowledge Base
Paradigm
Information
≠ Solution
≠ Problem description
= Passive, independent of specific problem
=> One representation, many problems
Knowledge Base
Paradigm
FO(.)
- IDP's Representation Language
- Extension of first-order logic:
- Types
- Arithmetic
- Aggregates
- Inductive definitions
- ...
- Formal Model Semantics
- Extension of first-order logic:
Decision Logic
+
Decision
Specification
+
Inference
Decision Management
Knowledge Base Paradigm
Modelling Business Decisions
An Example
Car Insurance
DMN - DRD
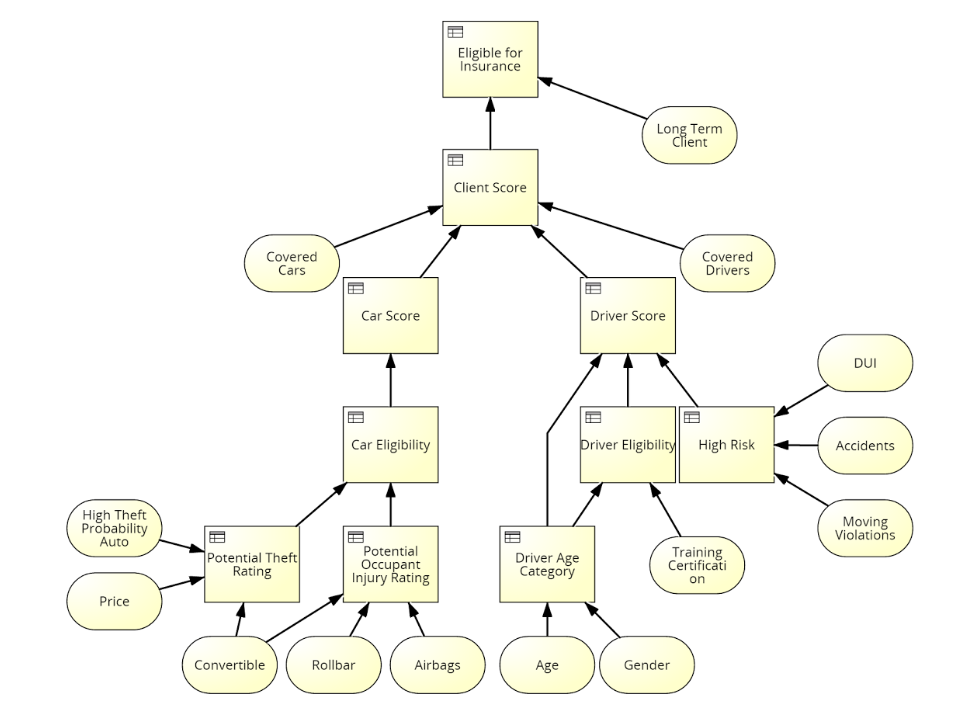
Potential Theft Rating
-
A car's theft rating is high if any of the following applies:
- The car is a convertible
- The car's price is over $45 000
- The car's model is on the High Theft Probability Auto list
-
If all of the following are true the car's theft rating is moderate:
- The car's price is between $20 000 and $45 000
- The car's model is not on the High Theft Probability Auto list
-
If all the following are true the car's theft rating if low:
- The car's price is lower than $20 000
- The car's model is not on the High Theft Probability Auto list
Decision Table
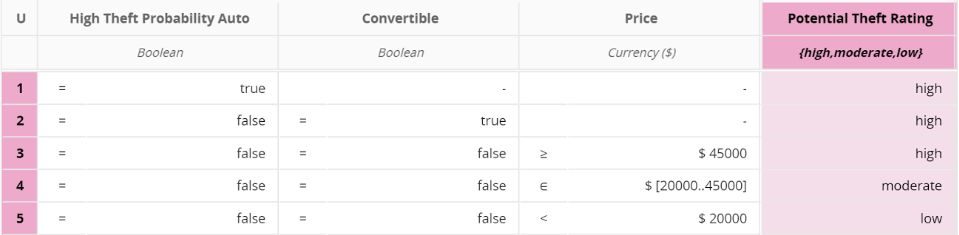
Potential Theft Rating
Definition
Potential Theft Rating

Some inferences
- Completeness checking
- Exclusivity checking
- Compliance checking
- Invokation
{
counter examples
Complete Input
Incomplete Input
Alternatives
Completeness
At least one outcome for every input value assignment
Violated if:
There exists a value assignment for which there is no outcome.
Exclusiveness
At most one outcome for every input value assignment
Violated if:
There exists a value assignment for which there is no outcome.
Stronger
Requires quantification over rules
=> rule reification
Compliance
Check whether the decision logic satisfies a certain property
"Minors can not be insured as drivers"
Violated if:
It is possible for someone younger than 18, to be insured.
Invokation
- Invoke decision with
- all input values available
- some input values available
- Determine input alternatives for desired outcome
Process Logic
+
Compliance checking
Conformance checking
Monitoring
Specification
+
Inference
Process Management
Knowledge Base Paradigm
Modelling Business Processes
Why are process miners so much more determined than data miners?
Their Wil is stronger.
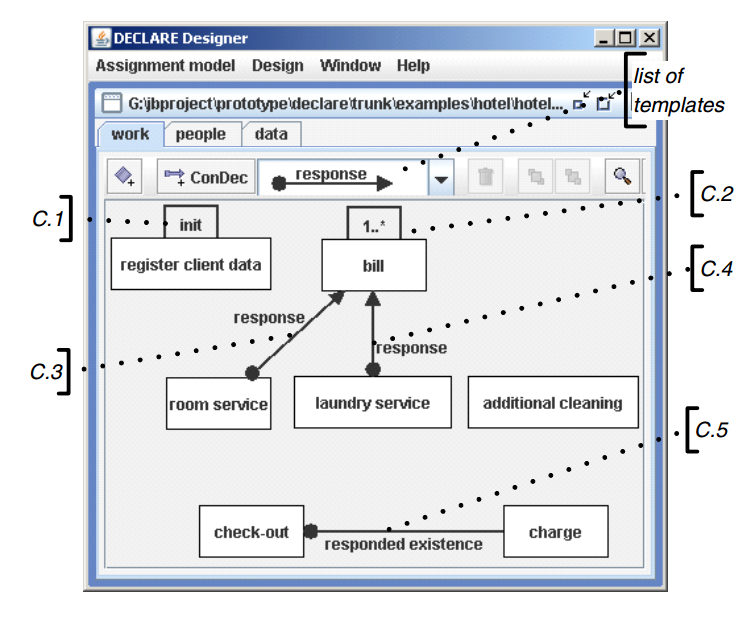
An Example
Hotel charges
Current & Future
Research Questions
- What is a decision?
- How to best represent the decision logic?
- Which types of decisions are there?
- Which inferences are relevant?
- Which knowledge is present in a process?
- How can this knowledge be represented?
- Which inferences are relevant?
- How can decisions and processes be integrated?
Thank you
What is a decision?
The description of the decision logic required to determine an outcome from a given set of inputs
The act of determining an outcome from a given set of inputs using the decision logic
What is a decision?
DetermineResult(T, V_i, V_o, S_i) is an inference with:
-
Input:
- theory T
- set of input symbols V_i
- set of output symbols V_o
- partial structure S_i interpreting the symbols in V_i.
-
Output:
-
If (T, V_i, V_o, S_i) is determinable:
- a structure S_o over V_o, such that S_i ∪ S_o can be expanded to a model of T
-
Otherwise:
- "Not determinable"
-
If (T, V_i, V_o, S_i) is determinable:
What is a decision?
If T, V_i, V_o are fixed, DetermineResult(S_i) is a decision.
Thank you
KB for DPM
By laurentjanssens
KB for DPM
- 1,448



