C++
By 楓資教學長
關於我......
#中山資研教學長
#高一開始學程式
#成績炸裂
#宅宅兼怪人
#ㄌㄌ
#迷因人
#行走的冷笑話製造機
#沉迷星鐵
#www
課程簡介
C++介紹
變數&輸入輸出
運算子
條件判斷
陣列
迴圈
C++介紹
認識一下?
用來定義電腦程式的形式語言
一種被標準化的交流技巧,用來向電腦發出指令
讓程式設計師準確定義電腦所需要資料的電腦語言
並精確定義在不同情況下所應當採取的行動
- 維基百科
什麼是程式語言?



基於C語言所擴充出來的語言
讓C語言更接近人類而非機器

打開 !
Ctrl+N
補充:online gdb
File - New - File
Dev-C++
CodeBlocks
右上角language選C++
TRY TRY SEE
下載gogo!
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
return 0;
}#include<函式庫名稱>
引入函式庫(給電腦字典!)
引入一個命名空間
(避免名稱重複)
int main()
主函式 寫指令
return 0
回傳一個值 當成結束就好了
標頭檔
AC (Accept): 即表示通過
NA (Not Accept): 在多測資點的題目中若未通過所有測資點則出現 NA
WA (Wrong Answer): 表示答案錯誤,並在訊息中指出錯誤行數及正確答案
TLE (Time Limit Exceed): 表示執行超過時間限制
MLE (Memory Limit Exceed): 表示程序執行超過記憶體限制
OLE (Output Limit Exceed): 表示程序輸出檔超過限制
RE (Runtime Error): 表示執行時錯誤,通常為記憶體配置錯誤 如:使用了超過
陣列大小的位置
RF (Restricted Function): 表示使用被禁止使用的函式,並在錯誤訊息中指明使用了
什麼不合法的函式。
CE (Compile Error): 表示編譯錯誤,並在訊息中列出完整錯誤訊息,以利判斷
SE (System Error): 包含 Compile, Runtime 等未定義錯誤均屬於 System Error
C++
變數&輸入輸出
變數
| 變數型別 | 中文 | 舉例 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 整數 | 1、2、3 |
| long long | 長整數 | 100000000000000000 |
| float | 小數(浮點數) | 3.14 |
| double | 長小數(雙精度浮點數) | 3.14159 |
| char | 字元 | 'a'、'b'、'c' |
| string | 字串 | "hello world" |
| bool | 布林 | true、false |
宣告
變數型別 變數名稱 = 值int a=1;舉例:
定義:
char a='i';string a="yumeoi kakeru"注意!
變數名稱不可使用純數字、保留字(int、char)或特殊字(&、%)
cin>>變數;輸入
int a;
cin>>a;string a;
cin>>a;分號: 表命令末尾(句號)
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;舉例:
定義:
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
return 0;
}cout<<"hello world"<<endl;輸出
(輸入是cin)
字串
(一串字)
換行
(end line)
輸出
注意!
cin箭頭向右(>>) cout箭頭向左(<<)
TRY TRY SEE
寫題目gogo!
ANSWER

C++
運算子
運算子
指派運算子
算術運算子
邏輯運算子
比較運算子
指派運算子
int a=0;
b=a;
b=b+1;先判斷完右邊 再將結果指定給左邊
判斷a=0 又b=a 所以b=0
判斷b+1=1 再把1指定給b 所以b變成1
算術運算子
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| + | 加 |
| ++ | 遞增1 |
| - | 減 |
| -- | 遞減1 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
| % | 取餘數 |
和數學四則運算規則相同 先乘除後加減 括號內先算
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| + | 加 |
| ++ | 遞增1 |
| - | 減 |
| -- | 遞減1 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
| % | 取餘數 |
int i=2;
cout<<i+i<<endl;
cout<<i++<<endl;
cout<<++i<<endl;
cout<<i-i<<endl;
cout<<i--<<endl;
cout<<--i<<endl;
cout<<i*i<<endl;
cout<<i/i<<endl;
cout<<i%i<<endl;4
2
4
2
3
4
0
4
2
4
3
2
4
1
0
2
2
2
輸出
i值
i++ => 先輸出i 再讓i遞增1
--i => 先讓i遞減1 再輸出i
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<'0'+'1'<<endl;
return 0;
}
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) error
97
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<'0'+'1'<<endl;
return 0;
}97
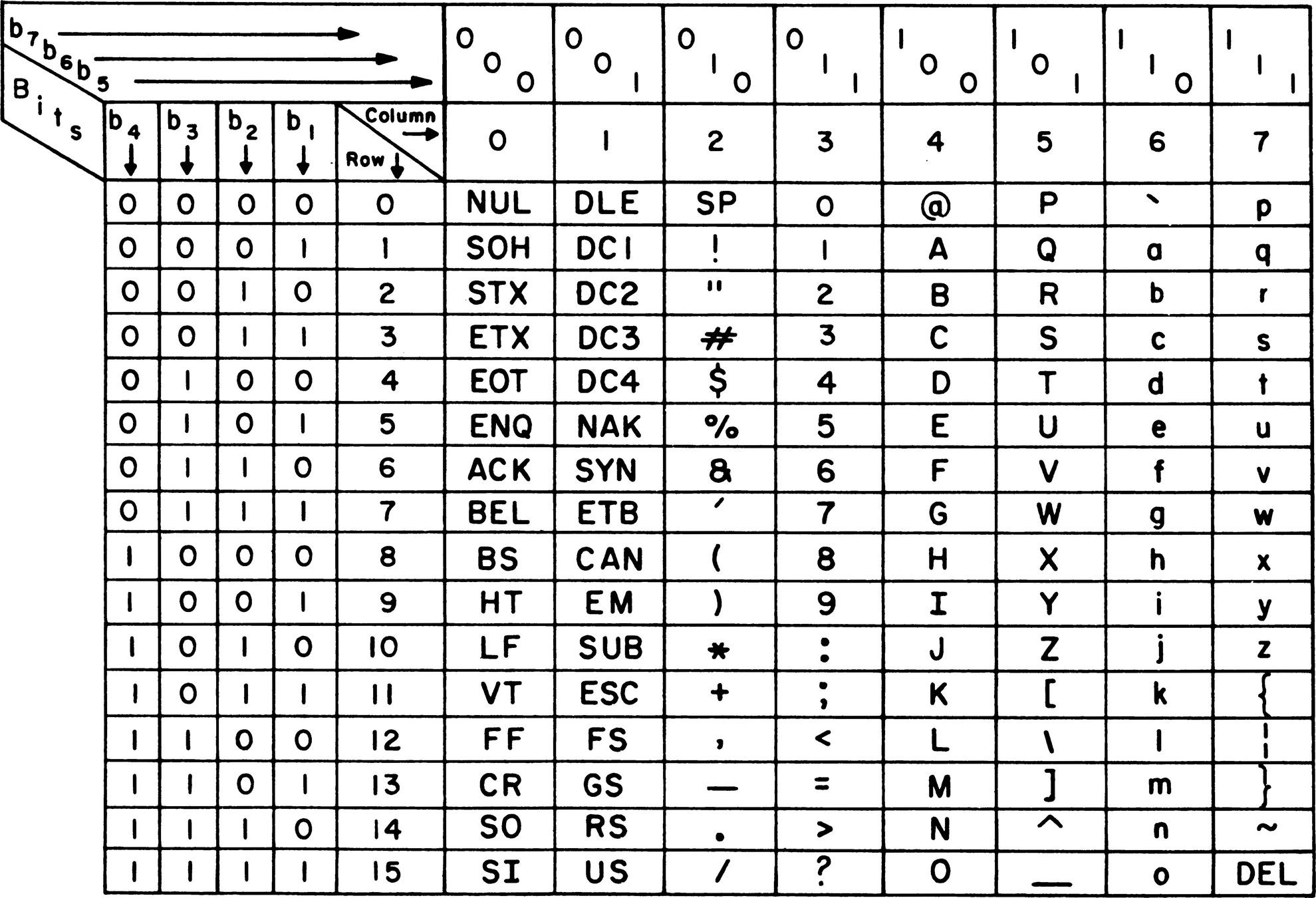
為什麼會這樣?
ASCII碼
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
每個字元都有對應的ascii碼
0的ascii碼是48
1的ascii碼是49
因此相加為97
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
0110001 二進位轉十進位 = 2^5+2^4+2^0 = 32+16+1 = 49
比較運算子
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| > | 大於 |
| >= | 大於等於 |
| < | 小於 |
| <= | 小於等於 |
| == | 等於(判斷式) |
| != | 不等於 |
邏輯運算子
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| && | 且 |
| || | 或 |
| ! | 否定 |
TRY TRY SEE
寫題目gogo!
ANSWER


C++
條件判斷
if - else if - else
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
if(判斷式)//如果條件成立
{
程式主體;//若只有一行 可不寫大括號
}
else if(判斷式)
{
程式主體;
}
else
程式主體;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score;
if(score>=60)
cout<<"及格"<<endl;
if(score>=40)
cout<<"重考"<<endl;
else
cout<<"死當"<<endl;
return 0;
}若score=100
會輸出什麼?
(A) 及格
(B) 重考
(C) 死當
及格
重考
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score;
if(score>=60)
cout<<"及格"<<endl;
if(score>=40)
cout<<"重考"<<endl;
else
cout<<"死當"<<endl;
return 0;
}score=100
score>=60
輸出及格
score>=40
輸出重考
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score;
if(score>=60)
cout<<"及格"<<endl;
else if(score>=40)
cout<<"重考"<<endl;
else
cout<<"死當"<<endl;
return 0;
}跳過else if
跟else
小結
if - if => 即使第一個if成立 仍舊會執行第二個if
if - else if =>若第一個if成立 則不會執行第二個if
else的意思是"其他的"
所以在"如果(if)"不成立的情況下才會去找"其他的如果(else if)"
TRY TRY SEE
寫題目gogo!
A004:西元年被4整除且不被100整除,或被400整除者即為閏年
About 提示
D050:用條件判斷寫會比較簡單 但只用數學(會用到%)也可以
ANSWER




C++
迴圈
迴圈
迴圈
while 迴圈
for 迴圈
break/continue
for迴圈
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;for(int a=0;a<5;a++)
{
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
}
for迴圈
認識一下for迴圈
包含初始值、判斷式、遞增遞減及程式主體
須注意範圍
適合處理有次序的事
for迴圈
for(變數初始值;判斷式;調整)//如果判斷成立
{
執行程式;
}for(int day=1;day<8;day++)
{
cout<<"今天是星期"<<day<<endl;
}宣告整數變數day=1
若day<8 繼續迴圈
每執行完一次迴圈 day遞增1
for(int day=1;day<8;day++)
{
cout<<"今天是星期"<<day<<endl;
}int day=1
day<8
輸出
day++
巢狀迴圈 - 現在是幾點?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int hr=1;hr<13;hr++)
{
for(int min=1;min<13;min++)
{
cout<<"時針指向"<<hr<<" 分針指向"<<min<<endl;
}
}
}
while迴圈
先檢查條件再執行程式
無限循環的條件判斷
包含判斷式及程式主體
while迴圈
while(判斷式)//如果判斷成立
{
執行程式;
}int vacation=3;
while(vacation>2)
{
cout<<"yeah";
}無限輪迴?

無窮迴圈終結者!
調整變數
使用break/continue
int vacation=3;
while(vacation>2)
{
cout<<"yeah";
break;
}int vacation=3;
while(vacation>2)
{
cout<<"yeah";
cin>>vacation;
}
for/while迴圈可以互換!
int vacation;
for(vacation=5;vacation>0;vacation--)
{
cout<<"你的假期還剩下"<<vacation<<"天"<<endl;
}int vacation;
vacation=5;
while(vacation>0)
{
cout<<"你的假期還剩下"<<vacation<<"天"<<endl;
vacation--;
}億點點小補充Do-while迴圈
先執行程式再檢查條件
int vacation;
cin>>vacation;
while(vacation>2)
{
cout<<"yeah";
cin>>vacation;
}int vacation;
do
{
cout<<"yeah";
cin>>vacation;
}
while(vacation>2);記得加分號!
默認條件符合 直接執行程式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string n;
while(cin>>n)
{
cout<<"hello, "<<n<<endl;
}
return 0;
}while(cin>>變數)
break的小檔案
可用在while迴圈跟for迴圈
表強制結束該迴圈
搭配條件判斷使用

continue的小檔案
可用在while迴圈跟for迴圈
表強制結束此次迴圈循環
搭配條件判斷使用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int num=1;num<10;num++)
{
if(num==5)
{
break;
}
cout<<num<<endl;
}
}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int num=1;num<10;num++)
{
if(num==5)
{
continue;
}
cout<<num<<endl;
}
}論兩者的差距
輸出1 2 3 4
因為當num=5的時候break
會略過下面的cout跳出迴圈
輸出1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9
因為當num=5的時候continue
會略過下面的cout回到條件判斷
回到這行
繼續迴圈
TRY TRY SEE
寫題目gogo!
A005:等差數列a,b,c => c-b=b-a或a+c=2b
等比數列a,b,c => c/b=b/a 記得判斷式用==!
About 提示
C013:首先輸入有幾組測資
最外層for迴圈寫測資數 第二層寫數字 第三層寫振福
振幅隨數字遞增 所以第二層的變數可以在第三層用
遞減的部分反過來就可以ㄌ
(這題比較複雜 不會也沒關係啦
d010:找因數=從1開始用迴圈跑 如果相除取餘數=0就是因數
ANSWER



C++
陣列
陣列
int izcc0,izcc1,izcc2,izcc3,izcc4,izcc5;
int izcc[6];陣列的原理
我是一個抽屜
可以放一個整數資料 ᐕ)ノ
arr

我是一個叫做arr的陣(櫃)列(子)
可以放三個抽屜 ᐕ)ノ
資料型別 陣列名稱[陣列長度]={陣列內容};char arr[3]={'a','b','c'};開一個叫做arr的陣列 三格可以放三個字元
陣列的宣告

0
1
2


a
b
c
(不一定要寫)
關於陣列......
第一格從0開始
用法和變數差不多
格數從一開始就指定好 不能隨意變大
陣列的賦值
一個一個指定:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3];
arr[0]=100;
arr[1]=200;
arr[2]=300;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3];
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
cin>>arr[i];
}透過迴圈輸入:
進階陣列之二維陣列


2*3=6個格子
二維陣列的宣告
資料型別 陣列名稱[櫃子數量][抽屜數量];int arr[2][3]={{100,200,300},{101,202,303}};櫃子0
櫃子1


arr[0][0]=100
arr[0][1]=200
arr[0][2]=300
arr[1][0]=101
arr[1][1]=202
arr[1][2]=303
櫃子0
櫃子1
二維陣列的賦值
一個一個指定:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2][3];
arr[0][0]=100;
arr[0][1]=200;
arr[0][2]=300;
arr[1][0]=101;
arr[1][1]=202;
arr[1][2]=303;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2][3];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int t=0;t<3;t++)
{
cin>>[i][t];
}
}
return 0;
}透過迴圈輸入:
TRY TRY SEE
寫題目gogo!
A015:翻轉陣列=輸入arr[a][b] 輸出arr[b][a](用迴圈!)
About 提示
A693:EOF=end of line 代表要用while(cin>>變數)
這題用for會tle QAQ
所以我們要用類似等差級數的方式弄!
C067:先求出平均高度後 跑陣列看要加還是減
1
2
3
[1]
[3]
[2]
1
3
5
[1]
[3]
[2]
ANSWER


C++
關於成發
那些我寫過的小東西
1a2b - 輸入輸出、條件判斷、迴圈、陣列
賀卡 - 輸入輸出、迴圈(微複雜)
猜數字 - 輸入輸出、迴圈、條件判斷
自我介紹 - 輸入輸出(極簡單)
猜拳 - 輸入輸出、條件判斷
想寫賀卡(輸出聖誕樹的圖案之類的)可以用這三題練手!
可能(像我一樣)被迴圈的範圍搞瘋!各位多點耐心 加油!
ANSWER



summercamp_C++
By ㄌㄌ
summercamp_C++
- 213




