The terminal
The basics
Change the current directory
cd ~/code/ruby/ror/my_project
The long way
The short way
cd ~/c/r/ro/my_pro + tab
Thanks Zsh!
Create a folder
mkdir -p project1/code project2/presentationmkdir : create a folder
-p : create also the subfolders
Final result :
current folder -> project1 -> code
current folder -> project2 -> presentation
Create and edit a file
touch my_file.[file extension e.g. txt, rb, html,...]Create a file: touch
Edit a file: nano
nano my_file.[file extension e.g. txt, rb, html,...]save with CTRL + O and exit with CTRL + X
See the content of a file
cat my_file.txt
In the terminal
In Sublime Text
stt my_file.txtThe owners
The super user : root
apt-get updateTry :
Result :
permission deniedNow, do it with a 'sudo' :
sudo apt-get update=> if you don't have the permission
to do something, you can do it
with the root permissions
Create a file or folder
with the root permissions
sudo nano a_file.txtexit and open this file with a simple nano
=> if the root user creates a file/folder,
by default, the simple user doesn't have
any permissions on it
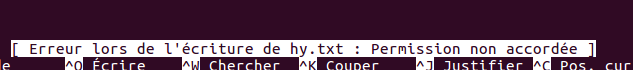
you don't have the permission...
List all files & folders
with their permissions
ls -l
This file is owned by the root user (and the root group)
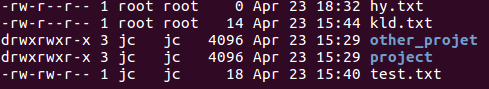
Change the owner
sudo chown jc:jc hy.txtTo change the owner of a file/folder,
you NEED to be the owner of that file/folder
now, the owner of the file hy.txt is jc and the group jc
you can find your user name with the command
whoamiyou can change the owner of a directory with the argument : -R
sudo chown -R jc:jc a_folderManage the users
adduser JohnDoeAdd a user
Change the password of a user
passwd JohDoeDelete a user
deluser JohDoePermissions
Read-Write-Execute

d = directory
(- = file )
Read
Write
Execute
The owner
Read
Write
Execute
The group
Execute
Other
Change the permissions
| Permission | number | sum |
|---|---|---|
| --- | 0 | 0+0+0 |
| r-- | 4 | 4+0+0 |
| -w- | 2 | 0+2+0 |
| --x | 1 | 0+0+1 |
| rw- | 6 | 4+2+0 |
| -wx | 3 | 0+2+1 |
| r-x | 5 | 4+0+1 |
| rwx | 7 | 4+2+1 |
example: 7 3 0
owner-group-other
Change the permissions
(sudo) chmod 777 my_file.txtFor a file
For a directory (and its files)
(sudo) chmod 777 *
For everything in a file
(sudo) chmod -R 777 my_direcotoryFor everything in a file and in his directory
(sudo) chmod -R 777 *
Some last useful commands
Remove files and folders
# DELETE A FILE
rm a_file
# DELETE A DIRECTORY
rm -r a_directory
# DELETE EVERYTHING
rm *
# FORCE DELETING
rm -f a_file
Never run this command
sudo rm -rf /*=> it would delete everything
(your OS, your files,...)
Ping a website
ping google.be=> it gives the IP address of a website and
says if you are connected to the network
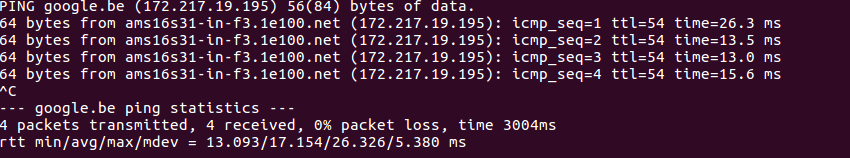
Stop the command with CTRL+C
Your network status
ifconfig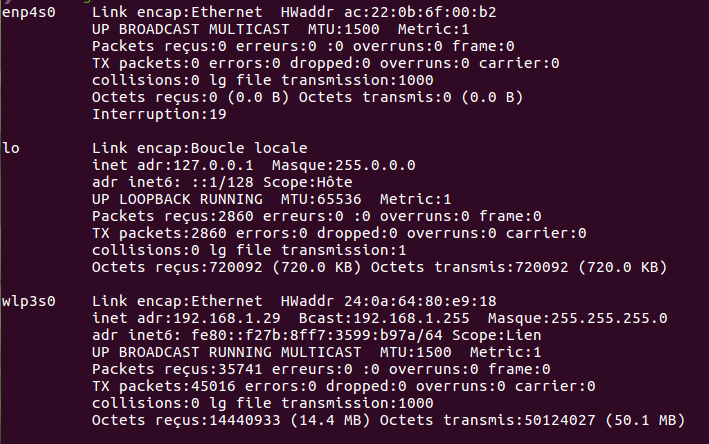
Ethernet connexion
= eth0
Wifi connexion
= wlan0
My local IP (ipv4) address
My local IP (ipv6) address
My MAC address (not real)
My local connexion (useless)
Change your MAC address
Each computer has a unique MAC address.
For privacy reasons, you can change your MAC address,
to connect to free wifi hotspots for instance.
examples of MAC addresses :
09-74-A3-D4-D1-43
ED-40-74-9F-EA-8A
BA-89-E7-1E-92-F4
.......
Change your MAC address on Ubuntu
sudo nmcli connection modify --temporary the_wifi_name 802-11-wireless.cloned-mac-address mac_addr
# THEN YOU SHOULD DO :
nmcli connection up wifi_name
sudo ifconfig en0 xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
Enjoy your terminal (and your privacy) ! :)
Change your MAC address on Mac
Terminal Basics
By Le Wagon Brussels
Terminal Basics
by Jean-Christophe Baudoin
- 1,083



