Compartment Syndrome
Laurie Kuestner MD
Iowa Heart and Vascular Institute
Acute

July 29, 2021
- Muscle groups of human limbs are divided into sections (compartments) formed by strong unyielding fascial membranes
- Compartment syndrome occurs when increased pressure within a compartment compromises the circulation and function of the tissue within that space
- Acute compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency
Introduction
Anatomy
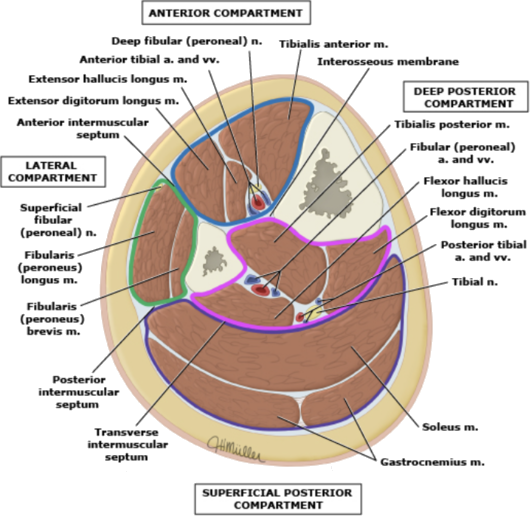
Muscle Compartments of the Leg

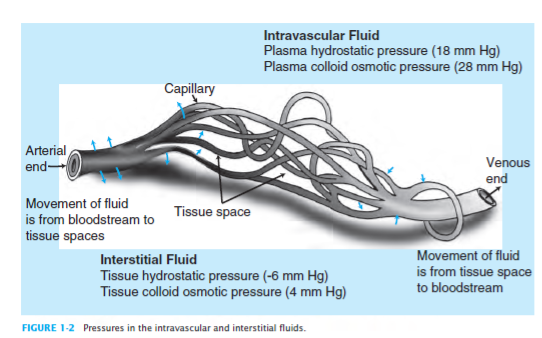
Pathophysiology
- Normal capillary pressure is between 20 and 33 mm Hg
- Pressures above this shut off flow and cause ischemia
- Normal interstitial fluid pressure ~ 10 mm Hg
- long bone fracture
- acute extremity ischemia with reperfusion
- crush injury
- burn injury
- spontaneous hemorrhage/hematoma
- prolonged immobilization
Causes / Symptoms
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Causes / Symptoms
Acute Compartment Syndrome
- pain out of proportion to apparent injury
- persistent deep ache or burning pain
- paresthesias
(early and common finding)
(onset within 30" to 2 hours of ACS)
- tense compartment with a firm "wood-like" feeling
- pain with passive stretch of muscles
- diminished sensation
- muscle weakness (onset within ~2-4 hours of ACS)
- paralysis (late finding)
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Examination
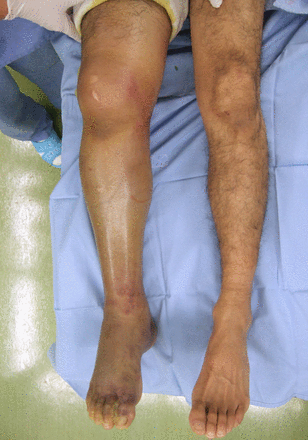
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Patient's normal leg
Examination

Examination
Acute Compartment Syndrome
ACS tense swelling
with
Title Text
- history and clinical findings
- measurement of compartment pressures
- elevation in serum creatinine kinase
- myoglobinuria
Diagnosis
Acute Compartment Syndrome
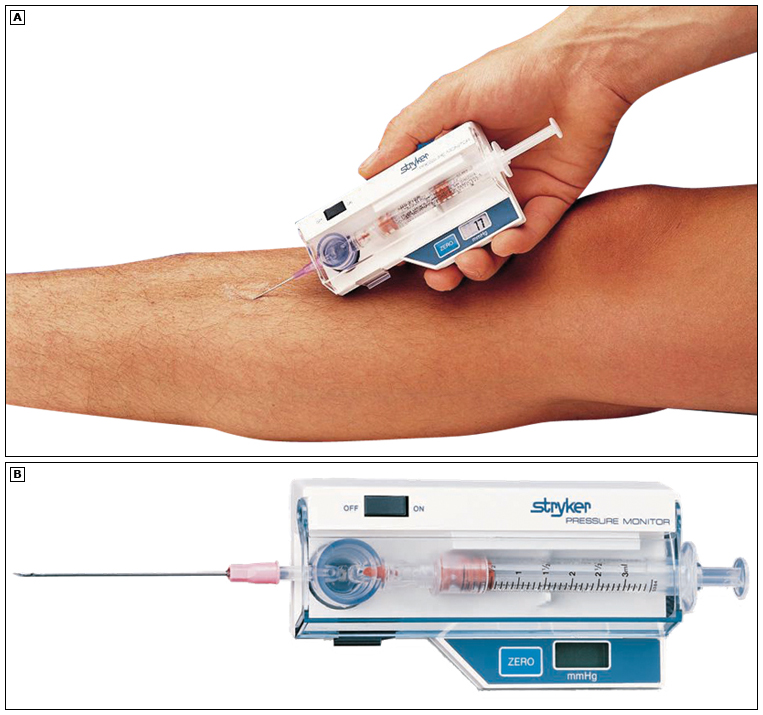
Stryker
Pressure
Monitor
Diagnosis
Acute Compartment Syndrome

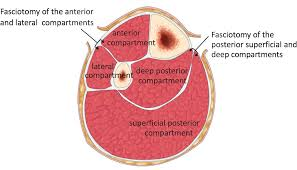
Management
Emergency Fasciotomy
Fasciotomy of the anterior
and lateral compartments
Fasciotomy of the
posterior superficial and
deep comparments
Management
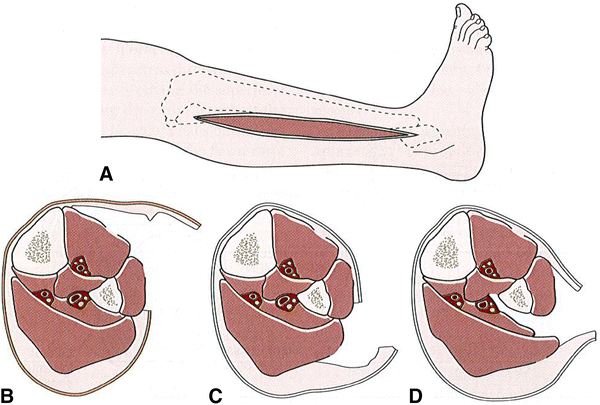
Emergency Fasciotomy

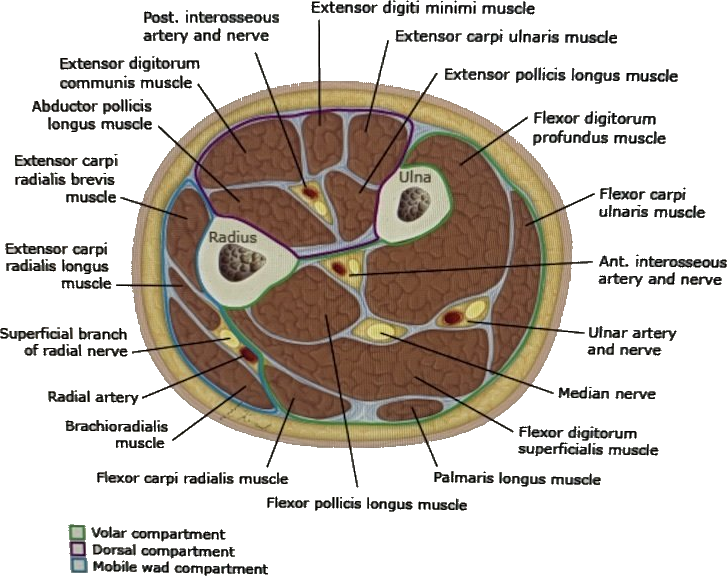
Anatomy
Compartments of the Forearm

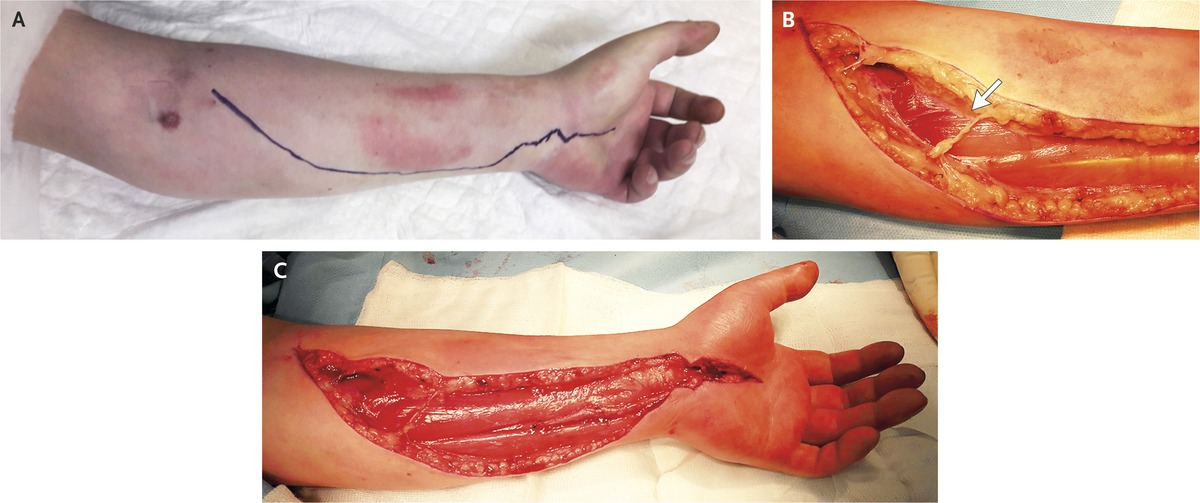
Management
26 year old male presented with compartment syndrome after prolonged immobilization
Delayed decompression restored perfusion to ischemic muscles
Clinical and functional outcomes of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome at a major trauma hospital
Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2016;6(3):133
Lollo L, Grabinsky A
- retrospective chart analysis
- 124 patients enrolled
- 104 patients assessed @ 12 months
- 81% male
- MVA caused injury in 51%
- tibia fractures in 41%
- acute kidney injury 2.4%
- mean peak serum CK 58,600 u/ml
OutComes
Clinical & Functional
Clinical and functional outcomes of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome at a major trauma hospital
Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2016;6(3):133
Lollo L, Grabinsky A
OutComes
Clinical & Functional
- 12.9% required leg amputation
- foot numbness occurred in 20.5%
- foot drop in 18.2%
- @long-term f/u moderate lower extremity pain in 10.2%
- 69.2% returned to work
Clinical and functional outcomes of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome at a major trauma hospital
Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2016;6(3):133
Lollo L, Grabinsky A
OutComes
Clinical & Functional
Conclusion:
Escalation in leg pain and changes in sensation are the cardinal signs for ACS rather than reliance on assessing for firm compartments and pressures
- 53 yo morbidly obese white male with HTN, hypothyroidism transferred to Mercy West Lakes from Ankeny urgent care with right calf pain and swelling
- wore 'too tight fitting socks & boots ' yesterday and performed manual snow removal for 6 hours then stood around fire for 2 hours drinking beers
- awoke 0900 with right calf pain and swelling
- denies injury to right calf
HPI
Case Presentation
Prolonged Immobilization

PE
Case Presentation

- c/o significant pain, tingling/numbness sensation in the right calf
- difficult to ambulate due to lack of sensation and motor function of right foot and ankle
- swollen right calf
- extreme tenderness to right calf
- palpable pulses
- distal RLE limited movement & sensation
- unable to dorsiflex/plantarflex right foot
Prolonged Immobilization
Labs
Case Presentation

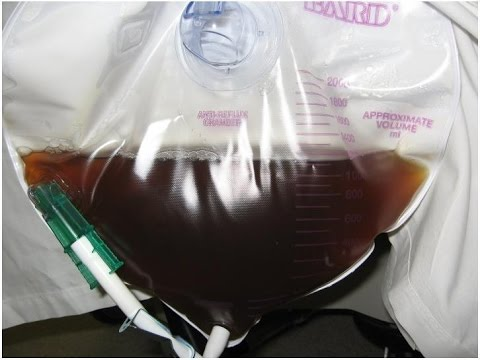
- CK >41,000
- Covid negative
- potassium 5.7
- creatinine 1.6
- Hgb/Hct 19.4/56.3
Prolonged Immobilization
Case Presentation
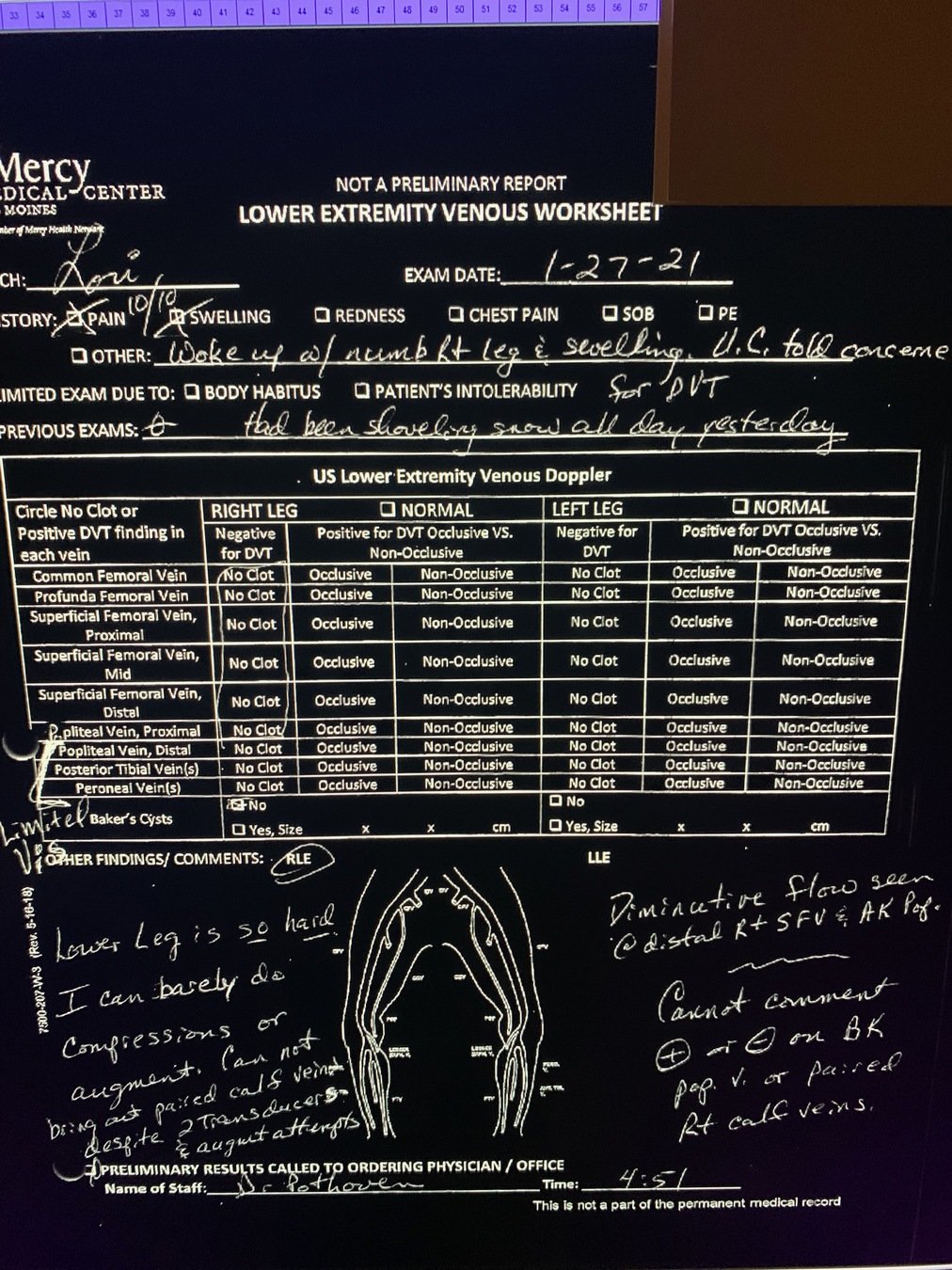
Prolonged Immobilization


- no DVT right groin to popliteal fossa
- calf veins could not be visualized
- RLE could not be compressed
Imaging: Venous Duplex
Title Text

- 09:00 awoke with symptoms
- ??:?? Ankeny urgent care
- 14:26 Mercy West Lakes triage
- 15:23 CK >41,000
- 16:55 venous duplex
- 18:15 vascular called
Case Presentation

Timeline
Prolonged Immobilization

- 55 yo white male presented to MGMC with chest pain and diaphoresis, EKG with NSTEMI, in ER converted to Vtach, cardioverted , intubated, IV heparin, transferred to Mercy One
- on arrival to Mercy arrested, CPR, epi x2, ROSC after 5"
- emergently to cath lab in cardiogenic shock, 85% L main, 14Fr Impella placed L CFA, VA ECMO placed, 17 Fr R CFA, 8Fr antegrade sheath R SFA
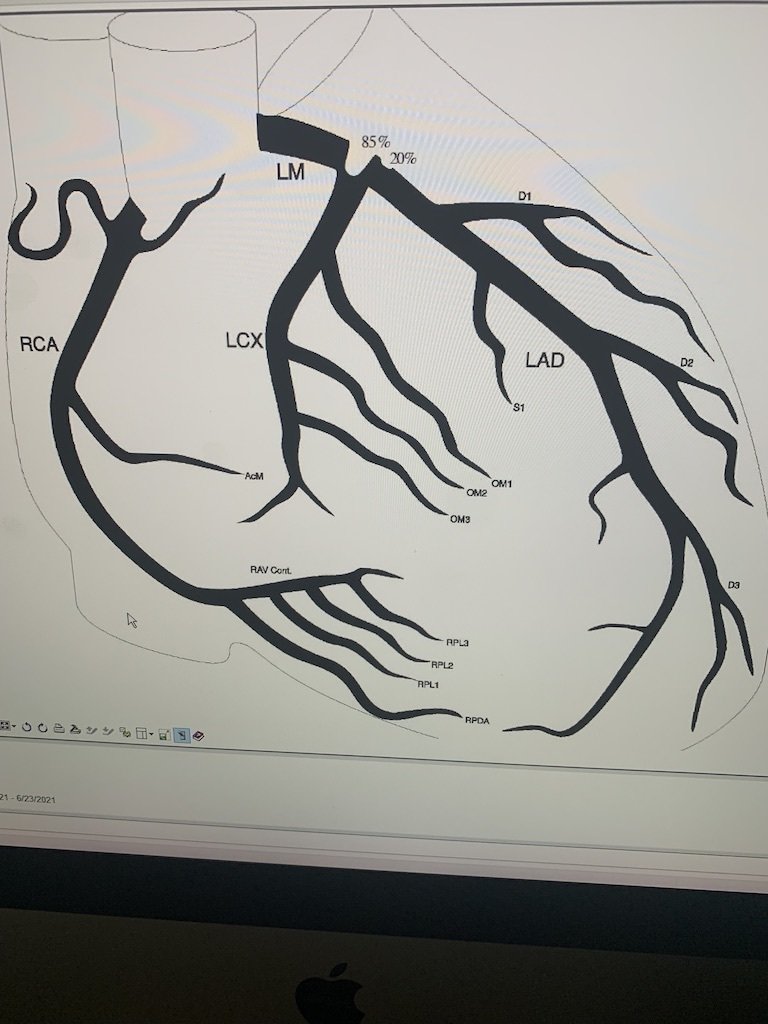
Case Presentation
Reperfusion of Ischemic Extremity

Case Presentation
Reperfusion of Ischemic Extremity

- 6/20/21 vascular consult for diminished pulse right leg , no dopplerable pulses left leg
- 6/21/21 returns to cath lab for treatment of left main / LAD
removal of 14 Fr Impella L CFA
- return to SICU - new left thigh and calf swelling
- emergency calf and thigh fasciotomy performed in SICU procedure room

Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Aug; 67:143-147
Legal
Considerations & Costs
Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Aug; 67:143-147
Legal
Considerations & Costs

Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Aug; 67:143-147
Malpractice Litigation for ACS
failure to diagnose most frequently cited claim ( 71.8%)
32.25% of cases were found for the plaintiff or settled
average award $1,553,993.66
51.6% hospital included as defendant
traumatic compartment syndrome causing nerve damage was the most common complication attributed to failure to diagnose
Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Aug; 67:143-147
Malpractice Litigation for ACS
32.25% of cases were found for the plaintiff or settled
award = $1,553,993.66
- clinical diagnosis
- requires a high level of suspicion for a timely diagnosis
- perform emergency fasciotomy
Time is of the essence!
Summary
Acute Compartment Syndrome
If you're going through hell, keep going.
Winston Churchill
Acute Compartment Syndrom
By l kuestner
Acute Compartment Syndrom
Crisis and consequences of mis-diagnosis of ACS
- 271

